Global investment strategies refer to investment approaches that involve the allocation of investment funds across various geographic regions of the world, in order to achieve a particular financial objective or goal. Such strategies may involve investing in equities, bonds, real estate, and other asset classes in different parts of the world. Global investment strategies may be pursued by individual investors, institutional investors such as pension funds, endowments, or sovereign wealth funds, or by investment managers on behalf of their clients. Global index funds are a type of passive investment strategy that seeks to replicate the performance of a specific index, such as the MSCI World Index. By investing in a global index fund, investors gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of equities from different countries and sectors. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are investment funds that trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. Global ETFs can track indices representing various countries, regions, or sectors, allowing investors to achieve international diversification with ease. Global mutual funds are managed by professional portfolio managers who actively select stocks and other assets from around the world. These funds aim to outperform their benchmark indices and provide higher returns than passive strategies. Separately managed accounts (SMAs) are personalized investment portfolios managed by investment professionals. Investors can customize their global exposure based on individual preferences, risk tolerance, and investment goals. Hedge funds are private investment funds that employ a range of strategies, including global macro, long/short equity, and merger arbitrage, to generate high returns. They often use leverage and derivatives to enhance returns and manage risk. The United States boasts the world's largest economy and offers a diverse range of investment opportunities in various industries such as technology, healthcare, and finance. European markets, comprising both the European Union and non-EU countries, present investment opportunities in industries like automotive, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy. Japan is the third-largest economy globally, offering investors access to innovative technology, consumer electronics, and automotive companies. China, the world's second-largest economy, presents investment opportunities in sectors like e-commerce, technology, and infrastructure. India is one of the fastest-growing major economies, providing investment prospects in industries such as technology, financial services, and pharmaceuticals. Brazil is the largest economy in Latin America, offering investment opportunities in sectors like agriculture, energy, and consumer goods. Vietnam's rapidly growing economy presents investment potential in sectors like manufacturing, technology, and infrastructure. Nigeria, the largest economy in Africa, offers investment opportunities in industries like energy, agriculture, and telecommunications. Argentina, despite its economic challenges, provides investment prospects in industries like agriculture, renewable energy, and technology. Investing in global technology companies can provide exposure to innovative products, services, and trends shaping the world. Global healthcare investments offer exposure to pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and medical device companies, benefiting from an aging global population and increasing healthcare spending. Infrastructure investments provide access to companies involved in transportation, utilities, and communication networks, essential for global economic growth. Energy investments involve companies engaged in the production, transportation, and distribution of various energy sources, including fossil fuels, renewables, and nuclear power. Consumer goods investments encompass companies producing and distributing goods and services that cater to the global consumer market, such as food and beverage, personal care products, and household items. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are companies that own, operate or finance income-producing real estate properties. Global REITs provide investors with exposure to the international real estate market and its potential for capital appreciation and income generation. Commodities are tangible assets like oil, gold, and agricultural products. Global commodity investments can serve as a hedge against inflation and provide diversification benefits. Investing in foreign currency can offer diversification and profit opportunities from exchange rate fluctuations. However, currency investments come with a higher risk due to market volatility. Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms connect borrowers and lenders directly, facilitating loans across international borders. This alternative investment strategy can provide attractive returns but carries the risk of borrower default. Venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) investments involve investing in private companies with growth potential. Global VC and PE investments can provide exposure to disruptive technologies and innovative business models worldwide. Market risk refers to the potential for losses due to fluctuations in market prices. Diversifying investments across multiple countries and sectors can help mitigate market risk. Currency risk arises from fluctuations in exchange rates, which can affect the value of foreign investments. Hedging strategies and currency ETFs can help manage currency risk. Political risk involves potential losses due to changes in political conditions, such as government policies or social unrest. Diversifying investments across multiple countries can help reduce political risk. Liquidity risk refers to the difficulty in buying or selling an investment without significantly affecting its price. Investing in liquid assets, such as ETFs and publicly traded stocks, can help manage liquidity risk. Credit risk is the risk of loss due to a borrower's failure to repay a loan or meet contractual obligations. Thorough research and diversification can help manage credit risk, particularly in fixed income and P2P lending investments. Double taxation treaties help prevent investors from being taxed twice on the same income, both in their home country and the country where the income is earned. Investors should familiarize themselves with relevant tax treaties. Foreign tax credits may be available to offset taxes paid in other countries, reducing the investor's overall tax liability. Investing globally may require additional reporting for tax purposes, such as disclosing foreign bank accounts or assets. Investors should consult a tax professional for guidance on their specific situation. ESG investing focuses on companies that demonstrate strong performance in environmental, social, and governance factors, contributing to a more sustainable and ethical world. Impact investing involves investments in companies or projects that generate positive social or environmental impact alongside financial returns. Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) involves the integration of ethical, social, and environmental considerations into investment decisions, often by avoiding investments in controversial industries or companies. Investors should evaluate their risk tolerance and investment objectives before allocating assets to various global investment strategies. Diversification across countries, regions, and sectors can help reduce risk and enhance potential returns in a global investment portfolio. Regular monitoring and rebalancing of a global investment portfolio can help maintain alignment with investment objectives and risk tolerance. A well rounded global investment strategy can provide numerous benefits, including diversification, access to growth opportunities, and exposure to various sectors and markets. By adapting to changing market conditions and global trends, investors can optimize their portfolios for long-term success. By considering various investment types, risks, tax implications, and ethical considerations, investors can construct a global investment portfolio that aligns with their individual goals and risk tolerance. Regular monitoring and rebalancing are essential to ensure that the portfolio remains on track to achieve its objectives.What Are Global Investment Strategies?
Types of Global Investment Strategies

Passive Investment Strategies
Global Index Funds
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Active Investment Strategies
Global Mutual Funds
Separately Managed Accounts
Hedge Funds
Regional Investment Approaches
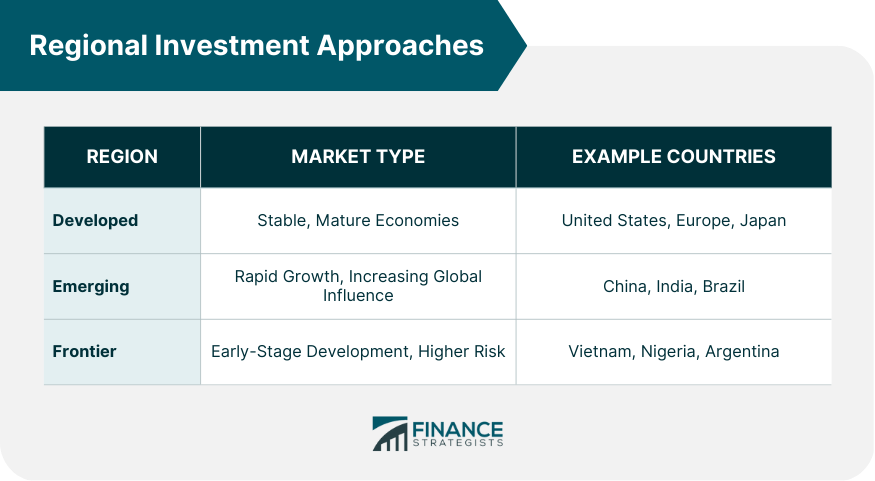
Developed Markets
United States
Europe
Japan
Emerging Markets
China
India
Brazil
Frontier Markets
Vietnam
Nigeria
Argentina
Sector-Based Investment Strategies
Global Technology Investments
Global Healthcare Investments
Global Infrastructure Investments
Global Energy Investments
Global Consumer Goods Investments
Alternative Global Investment Strategies
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Commodities
Foreign Currency
Peer-to-Peer Lending
Venture Capital and Private Equity
Evaluating Risks and Returns
Market Risk
Currency Risk
Political Risk
Liquidity Risk
Credit Risk
Tax Considerations
Double Taxation Treaties
Foreign Tax Credits
Reporting Requirements
Ethical and Sustainable Investing
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Investing
Impact Investing
Socially Responsible Investing (SRI)
Building a Global Investment Portfolio
Assessing Risk Tolerance and Investment Objectives
Diversification Across Regions and Sectors
Monitoring and Rebalancing
Conclusion
Global Investment Strategies FAQs
Global investment strategies can provide several benefits, including diversification, exposure to growth opportunities in various regions and sectors, reduced risk from concentrating investments in a single country or market, and potential currency appreciation.
Passive global investment strategies typically involve investing in index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track international indices, while active strategies involve professional portfolio managers actively selecting stocks and assets from around the world with the aim of outperforming benchmark indices.
Alternative global investment strategies include investing in real estate investment trusts (REITs), commodities, foreign currency, peer-to-peer lending, and venture capital or private equity investments in private companies worldwide.
To manage risks associated with global investment strategies, investors can diversify their investments across regions, sectors, and asset classes, use hedging strategies or currency ETFs to manage currency risk, research political and economic stability in target countries, and invest in liquid assets to manage liquidity risk.
Yes, ethical and sustainable global investment strategies include environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing, impact investing, and socially responsible investing (SRI), which focus on companies that demonstrate strong performance in ethical, social, and environmental factors or generate positive social or environmental impacts alongside financial returns.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











