Hedging is a strategy used to reduce or mitigate risk. It involves taking an offsetting position in a financial instrument to reduce the potential losses or gains from an underlying asset or investment. For example, if an investor owns a stock that they believe may decline in value, they may hedge their position by purchasing a put option. This gives the investor the right to sell the stock at a predetermined price, thereby limiting their potential losses. Hedging can also be used in other areas, such as in agriculture, where farmers may use futures contracts to lock in prices for their crops and protect against price fluctuations. In general, hedging is a way to manage risk and reduce uncertainty in various industries and markets. Derivatives are financial instruments whose value depends on the performance of an underlying asset, index, or interest rate. They are widely used in hedging strategies to manage different types of risks. Options are contracts that provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price before a specified expiration date. Options can be used to hedge against potential price movements in stocks, bonds, and other assets. Futures are standardized contracts to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price on a future date. They are commonly used to hedge against price changes in commodities, currencies, and interest rates. Swaps are agreements between two parties to exchange cash flows or other financial instruments. The most common types of swaps are interest rate swaps and currency swaps, which are used to hedge against fluctuations in interest rates and exchange rates, respectively. Forward contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a future date. They are similar to futures but are not standardized and traded on exchanges. Forward contracts are often used to hedge against currency risks. Insurance products can be used to hedge against certain risks in wealth management, providing financial protection and stability. Annuities are financial products that provide a stream of income, usually for life or a specified period. They can be used to hedge against longevity risk, ensuring that an individual's wealth lasts throughout their retirement. Life insurance policies provide financial protection for beneficiaries in case of the policyholder's death. They can be used to hedge against the risk of premature death, ensuring that dependents are financially secure. Diversification is an essential aspect of hedging, as it helps to spread risk across various asset classes and investments. Asset allocation is the process of dividing an investment portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. A well-diversified asset allocation can help to reduce overall portfolio risk and increase returns. Alternative assets, such as real estate, private equity, and hedge funds, can provide diversification benefits and help to hedge against market risks. Portfolio hedging aims to mitigate the overall risk of an investment portfolio using various strategies and financial instruments. The first step in portfolio hedging is assessing the risks associated with the investments, such as market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk. Diversifying the investment portfolio across different asset classes and investment styles can help to reduce overall risk and increase returns. Derivatives, such as options, futures, and swaps, can be used to manage specific risks within the portfolio effectively. Interest rate hedging focuses on managing the risk of changes in interest rates, which can impact bond prices and borrowing costs. Interest rate swaps can be used to hedge against fluctuations in interest rates by exchanging fixed-rate payments for floating-rate payments or vice versa. Bond laddering involves purchasing bonds with staggered maturity dates, which helps to manage reinvestment risk and allows investors to take advantage of changes in interest rates over time. Currency hedging aims to manage the risk of fluctuations in foreign exchange rates, which can impact international investments. Forward contracts can be used to hedge against currency risk by locking in an exchange rate for a future transaction. Currency options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific currency at a predetermined price before a specified expiration date. They can be used to hedge against potential currency fluctuations. Commodity hedging is used to manage the risk of price fluctuations in commodities such as oil, gold, and agricultural products. Commodity futures allow investors to lock in a price for a specific commodity at a future date, providing protection against price volatility. ETFs that invest in commodities can be used as a hedging tool to provide exposure to a specific commodity or a diversified basket of commodities. Implementing a hedging strategy requires a thorough understanding of the client's needs, risk tolerance, and investment objectives. Understanding the client's financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon is essential in developing a customized hedging strategy. Based on the client's needs and risk tolerance, a customized hedging strategy should be developed, taking into account the various financial instruments and hedging strategies available. Regular monitoring and adjustment of the hedging strategy are necessary to ensure that it remains effective and aligned with the client's goals and risk tolerance. Hedging can provide several benefits for investors, including: Hedging can help to reduce overall portfolio risk and protect against potential losses. Effective hedging can help to stabilize the value of a portfolio, reducing the impact of market volatility. Hedging strategies can be used to take advantage of market opportunities and potentially increase returns. Hedging strategies also come with risks, including: Hedging can be expensive, and the costs associated with using financial instruments to hedge must be carefully considered. Hedging strategies may not always be effective in mitigating risks, and there is a risk that hedges can fail. The use of derivatives and other financial instruments for hedging may have regulatory and tax implications that must be carefully considered. Hedging is a strategy used to reduce or mitigate risk in various industries and markets. Derivatives, insurance products, and diversification strategies are the most commonly used financial instruments for hedging. There are various hedging strategies, such as portfolio hedging, interest rate hedging, currency hedging, and commodity hedging, which can be used to manage specific risks effectively. Implementing a hedging strategy requires a thorough understanding of the client's needs, risk tolerance, and investment objectives. Regular monitoring and adjustment of the hedging strategy are necessary to ensure its effectiveness. While hedging can provide several benefits, including risk mitigation, portfolio stabilization, and potential for improved returns, it also comes with risks such as hedging costs, ineffective hedges, and regulatory and tax implications. Overall, the decision to hedge should be based on a careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks involved, taking into account the client's individual circumstances and objectives.What Is Hedging?
Types of Financial Instruments for Hedging
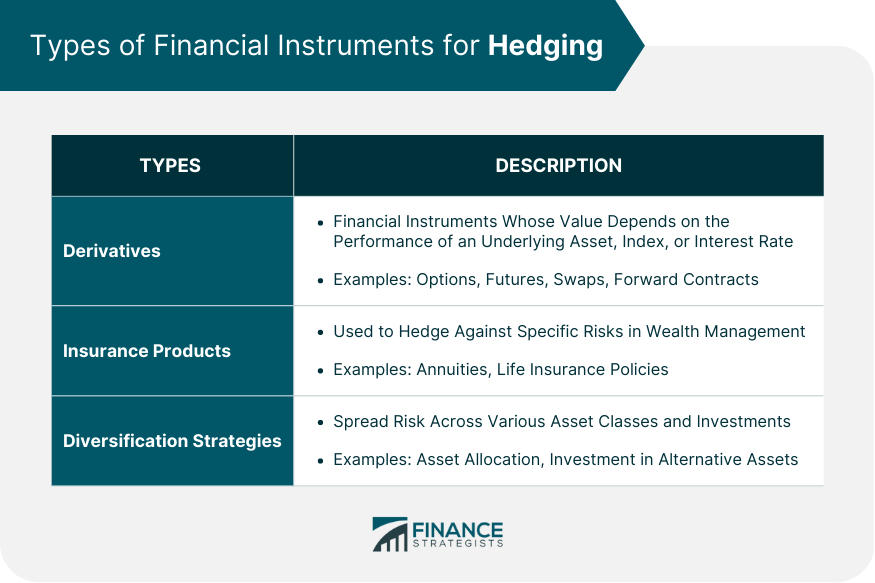
Derivatives
Options
Futures
Swaps
Forward Contracts
Insurance Products
Annuities
Life Insurance Policies
Diversification Strategies
Asset Allocation
Investment in Alternative Assets
Hedging Strategies

Portfolio Hedging
Risk Assessment
Diversification
Use of Derivatives for Risk Mitigation
Interest Rate Hedging
Interest Rate Swaps
Bond Laddering
Currency Hedging
Forward Contracts
Currency Options
Commodity Hedging
Commodity Futures
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Implementing Hedging
Assessing Client Needs and Risk Tolerance
Developing a Customized Hedging Strategy
Monitoring and Adjusting the Strategy Over Time
Benefits and Risks of Hedging
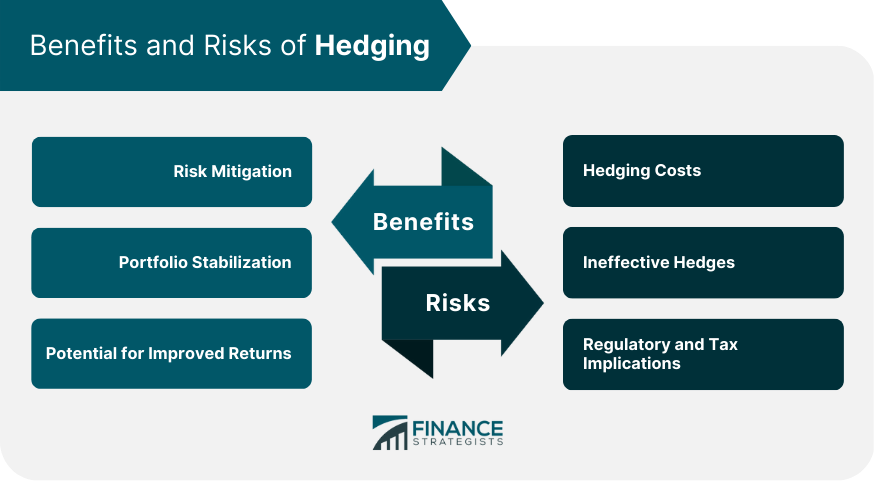
Benefits
Risk Mitigation
Portfolio Stabilization
Potential for Improved Returns
Risks
Hedging Costs
Ineffective Hedges
Regulatory and Tax Implications
Conclusion
Hedging FAQs
Hedging is the practice of using financial instruments, such as derivatives and insurance products, to mitigate financial risks and protect investments.
The benefits of hedging in wealth management include risk mitigation, portfolio stabilization, and the potential for improved returns.
Financial instruments used for hedging in wealth management include derivatives (options, futures, swaps, and forward contracts), insurance products (annuities and life insurance policies), and diversification strategies (asset allocation and investment in alternative assets).
Investors can implement hedging strategies in wealth management by assessing client needs and risk tolerance, developing a customized hedging strategy, and regularly monitoring and adjusting the strategy over time.
The risks associated with hedging in wealth management include hedging costs, ineffective hedges, and regulatory and tax implications.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











