Investment performance refers to the return generated by an investment over a specified period. It is a critical measure of how well an investment is doing and helps investors gauge the success of their investment decisions. Measuring investment performance is essential for investors to evaluate the effectiveness of their investment strategies, compare their investments against benchmarks or peers, and make informed decisions on portfolio adjustments. Understanding investment performance also helps identify areas of improvement and optimize investment returns. Several factors influence investment performance, including market conditions, economic trends, investment strategies, portfolio management, and investor behavior. These factors contribute to an investment's overall success or failure and should be considered when evaluating investment performance. Return on Investment (ROI) is a simple performance metric that calculates the percentage return generated by an investment relative to its initial cost. It is a widely used measure to evaluate the efficiency and profitability of an investment. Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) is a performance metric that calculates an investment's average annual growth rate over a specified period. CAGR smooths out short-term fluctuations and provides a more accurate representation of an investment's long-term performance. The Sharpe Ratio is a risk-adjusted performance metric that measures the excess return generated by an investment per unit of risk taken. A higher Sharpe Ratio indicates a better risk-adjusted return, helping investors compare investments with different risk levels. The Information Ratio measures the excess return of an investment relative to a benchmark, adjusted for the risk taken. A higher Information Ratio indicates a better risk-adjusted performance compared to the benchmark, making it useful for evaluating active investment strategies. Jensen's Alpha is a performance metric that measures the excess return of an investment compared to its expected return based on its risk level and market performance. A positive Jensen's Alpha indicates that an investment has outperformed its expected return, suggesting effective portfolio management. The Sortino Ratio is a risk-adjusted performance measure that evaluates the excess return of an investment relative to its downside risk. It is similar to the Sharpe Ratio but focuses only on downside risk, making it more relevant for investors concerned with potential losses. The Treynor Ratio is a risk-adjusted performance metric that measures the excess return generated by an investment per unit of systematic risk taken. It is useful for comparing the performance of investments with different levels of exposure to market risk. Risk in investing refers to the uncertainty and potential variability of investment returns. Investing is an inherent aspect, and understanding risk is crucial for evaluating investment performance and making informed investment decisions. Market risk is the potential for losses due to fluctuations in market prices or broader market trends. It affects all investments to varying degrees and is often considered the most significant type of risk. Credit risk is the potential for losses due to a borrower's inability to repay a loan or meet their financial obligations. It is most relevant for investments in fixed-income securities, such as bonds and loans. Liquidity risk is the potential difficulty in buying or selling an investment at a reasonable price and within a reasonable time frame. Illiquid investments can be challenging to trade and may result in lower returns or losses. Operational risk is the potential for losses due to failures in a company's internal processes, systems, or personnel. It can affect any investment but is particularly relevant for investments in individual companies. Risk-adjusted performance measures are essential tools for comparing investments with different risk levels on an equal footing. They help investors determine whether the additional returns an investment generates justify the additional risk taken. Diversification is the practice of spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce overall portfolio risk. Effective risk management through diversification can enhance investment performance by reducing the impact of adverse events on any single investment. Benchmarks are reference points against which investment performance is measured and evaluated. They provide a standard for comparison and help investors assess whether their investments meet their objectives and outperform their peers. Market indices are broad market measures representing the performance of specific market segments or asset classes. They are widely used as benchmarks for passive and active investment strategies. Peer group comparison involves comparing the performance of an investment against a group of similar investments or funds. This type of benchmarking helps investors evaluate the relative performance of their investments within a specific category or style. Customized benchmarks are tailored to an investor's unique goals, risk tolerance, and investment preferences. They provide a more personalized basis for performance evaluation and decision-making. Active investment strategies aim to outperform a benchmark through active portfolio management, while passive strategies seek to replicate the benchmark's performance. Comparing active and passive investment performance helps investors understand the benefits and drawbacks of each approach and make informed decisions. Benchmarking has limitations, including the potential for biases, the difficulty of finding appropriate benchmarks, and the risk of overemphasizing past performance. Investors should be aware of these limitations and use benchmarking as just one tool in their performance evaluation toolbox. Economic conditions, such as growth rates, inflation, interest rates, and fiscal policies, can significantly influence investment performance. Investors should monitor these conditions and adjust their strategies accordingly to optimize returns. Market trends and cycles, such as bull and bear markets, can also affect investment performance. Understanding these trends and adapting investment strategies to different market environments can enhance performance over time. Investment strategy and style, such as value or growth investing, can impact performance due to differing risk and return profiles. Aligning an investment strategy with an investor's objectives and risk tolerance is critical for achieving desired performance. Effective portfolio management involves selecting, monitoring, and adjusting investments to optimize performance and manage risk. Regular portfolio reviews and adjustments can help maintain a balanced and diversified investment mix, contributing to better performance. Investor behavior, such as emotional decision-making or lack of discipline, can negatively impact investment performance. Developing a disciplined investment approach and avoiding common behavioral biases can help improve performance. Regularly reviewing and adjusting investment strategies can help ensure they remain aligned with an investor's objectives and risk tolerance, leading to improved performance over time. Managing risk through diversification and asset allocation is critical to improving investment performance. A well-diversified and balanced portfolio can enhance returns while reducing overall risk. Monitoring investment performance and benchmarking against relevant indices or peers can help identify areas of improvement and inform future investment decisions. Learning from past performance and mistakes can lead to better decision-making and improved investment performance. Analyzing what worked and what didn't can help refine investment strategies and avoid repeating errors. Seeking professional advice from financial advisors or wealth managers can help improve investment performance by providing expert guidance, personalized recommendations, and ongoing support. Evaluating investment performance is essential for making informed decisions, optimizing returns, and managing risk. Understanding performance metrics and their limitations helps investors assess their investment strategies and make necessary adjustments. Performance metrics and risk management play a crucial role in investment decision-making by providing a framework for comparing investments, assessing risk, and measuring success. Investors should use a combination of metrics and risk management tools to optimize their investment decisions. Continuous monitoring and improvement are vital for enhancing investment performance over time. By regularly reviewing strategies, managing risk, and learning from past experiences, investors can adapt to changing market conditions and achieve their financial goals. Seeking professional guidance from financial advisors or wealth managers can be invaluable in optimizing investment performance. These professionals offer expert advice, personalized strategies, and ongoing support to help investors navigate the complex world of investing and achieve their financial objectives.What Is Investment Performance?
Key Performance Metrics and Ratios for Investment Performance
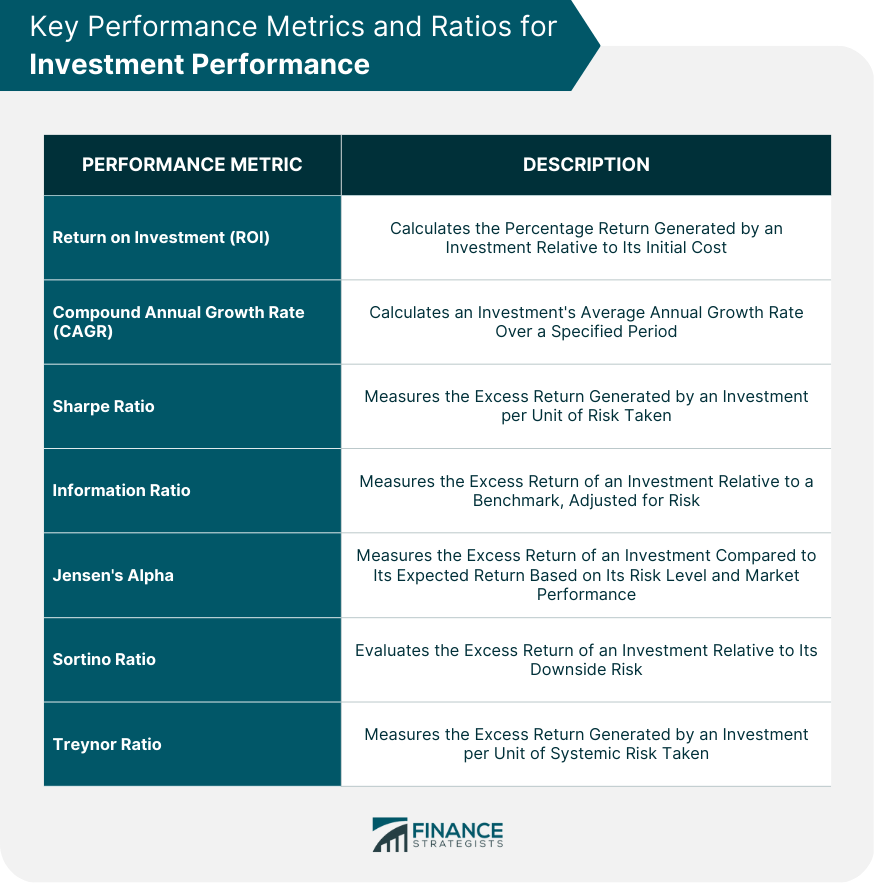
Return on Investment (ROI)
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)
Sharpe Ratio
Information Ratio
Jensen's Alpha
Sortino Ratio
Treynor Ratio
Risk and Investment Performance
Types of Investment Risks
Market Risk
Credit Risk
Liquidity Risk
Operational Risk
Risk-Adjusted Performance Measures
Diversification and Risk Management
Benchmarking and Investment Performance Evaluation
Definition of Benchmarks
Types of Benchmarks
Market Indices
Peer Group Comparison
Customized Benchmarks
Active vs Passive Investment Performance
Limitations of Benchmarking
Factors Affecting Investment Performance

Economic Conditions
Market Trends and Cycles
Investment Strategy and Style
Portfolio Management
Investor Behavior
Improving Investment Performance
Reviewing and Adjusting Investment Strategy
Managing Risk Through Diversification and Asset Allocation
Monitoring Performance and Benchmarking
Learning from Past Performance and Mistakes
Seeking Professional Advice
Final Thoughts
Investment Performance FAQs
Investment performance refers to the return generated by an investment over a specific period, which is a measure of how well an investment is doing.
The key performance metrics and ratios for investment performance include Return on Investment (ROI), Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR), Sharpe Ratio, Information Ratio, Jensen's Alpha, Sortino Ratio, and Treynor Ratio.
Risk refers to the uncertainty and potential variability of investment returns, and understanding risk is crucial for evaluating investment performance and making informed investment decisions.
Benchmarking is the process of measuring and evaluating investment performance against a reference point or benchmark. It is important for investment performance evaluation because it provides a standard for comparison and helps investors assess whether their investments meet their objectives and outperform their peers.
Investors can improve their investment performance by regularly reviewing and adjusting investment strategies, managing risk through diversification and asset allocation, monitoring performance and benchmarking, learning from past performance and mistakes, and seeking professional advice from financial advisors or wealth managers.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











