A Multilateral Trading Facility is a self-regulated financial trading venue or system that brings together multiple third-party buying and selling interests in financial instruments in a way that results in a contract. These trading facilities allow eligible contract participants to gather and transfer a multitude of securities, especially instruments that may not have an official market. These may include shares, bonds, and other financial instruments. MTFs were established to enhance market competition and provide an alternative to traditional stock exchanges. These platforms offer a marketplace where multiple financial instruments can be traded, providing a more flexible trading environment than typical exchanges. They play a significant role in improving market transparency and price discovery while reducing trading costs. MTFs emerged in response to the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID) implemented by the European Union in 2007. MiFID aimed to create a more competitive and integrated financial market, leading to the birth of MTFs as alternative trading venues to traditional exchanges. Over the years, regulatory changes have propelled the evolution and expansion of MTFs. For instance, the introduction of MiFID II in 2018, requiring investment firms to take all reasonable steps to obtain the best possible outcome for their clients, has strengthened the role of MTFs in providing fair and transparent trading conditions. The trading process on MTFs involves various market participants, including traders, brokers, and market makers. These parties interact in a virtual environment to buy or sell financial instruments based on predefined rules. MTFs utilize sophisticated technology systems to facilitate this trading process, ensuring efficient execution of trades. Market makers and brokers play a crucial role in the functioning of MTFs. Market makers provide liquidity to the market by being ready to buy or sell securities at any time, while brokers facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers. MTFs utilize advanced electronic systems for price formation and trade matching. Price discovery occurs through the interaction of multiple buying and selling orders. Once a match is found, the trade is executed, and the transaction details are recorded. While both MTFs and traditional stock exchanges serve as platforms for trading financial instruments, they differ significantly in their structures. MTFs are generally more flexible and less regulated than traditional exchanges, offering a wider range of financial instruments for trading. In terms of trading processes, MTFs offer a more streamlined and rapid execution of trades, facilitated by advanced technology systems. Traditional exchanges, however, typically involve a more complex and time-consuming trading process. MTFs enhance market liquidity by providing additional trading venues for a broad range of financial instruments. Moreover, by consolidating multiple buying and selling interests, they contribute to greater market transparency. MiFID and its subsequent iteration, MiFID II, have significantly influenced the operations and regulatory framework of MTFs. These directives have introduced stricter transparency requirements and heightened investor protection measures, shaping the operations of MTFs. In the United States, the equivalent of MTFs are Alternative Trading Systems (ATS), regulated under the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). These systems are subject to stringent regulation to ensure fair and transparent trading practices. Several other international regulatory bodies have an impact on MTFs, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) in the EU. These bodies enforce regulations to ensure the fairness and transparency of MTF operations. MTFs provide access to a wide range of financial instruments that may not be listed on traditional exchanges. This includes equities, bonds, derivatives, and other complex financial products. By offering a more diverse portfolio, MTFs allow market participants to better optimize their trading strategies and potentially enhance returns. MTFs contribute significantly to market transparency. They operate electronic trading systems which display current bid and ask prices for securities and the depth of trading interests at those prices. This allows market participants to have real-time access to market information, thereby improving price discovery and promoting fair trading. By consolidating multiple buying and selling interests, MTFs increase the liquidity of the market. This is particularly beneficial for securities that may have limited liquidity on traditional exchanges. High liquidity allows traders to buy and sell securities more easily and helps ensure that market prices do not fluctuate excessively due to large trades. MTFs are known for their ability to execute trades quickly and efficiently. These facilities leverage advanced technology and algorithms to match trading orders, enabling faster trade execution compared to traditional exchanges. Speedier trade execution can help market participants take advantage of short-lived trading opportunities and reduce the risk of price slippage. MTFs can potentially offer lower trading costs compared to traditional exchanges. This is primarily due to their competitive fee structures and the elimination of intermediaries. Lower trading costs enhance the profitability of trading activities and can make a significant difference, especially for high-frequency traders. Unlike traditional exchanges, which have set trading hours, some MTFs offer more flexible trading hours. This enables traders to react promptly to market news and events happening outside of standard trading hours. By providing an alternative trading venue, MTFs promote competition among trading platforms. Increased competition leads to better services, including tighter bid-ask spreads, lower trading fees, and improved trading technology. This ultimately benefits all market participants. One of the primary criticisms of MTFs is that they contribute to market fragmentation. With numerous MTFs operating alongside traditional exchanges, liquidity is split across multiple venues. This can make it more challenging for traders to assess the market accurately and could potentially lead to less efficient price discovery. MTFs are heavily reliant on technology for their operations. This dependency introduces risks related to system failures or cyber-attacks. Any technological disruptions can lead to trading delays or losses, impacting the overall market stability. While MTFs are regulated entities, the level of oversight is often less stringent compared to traditional exchanges. This could potentially lead to unfair trading practices. Additionally, regulatory standards can vary between jurisdictions, making it more challenging for traders to understand the rules and requirements of each MTF they trade on. Access to MTFs may be limited for some market participants, particularly smaller retail investors. Additionally, given the global and digital nature of MTFs, connectivity issues could potentially interrupt trading activities. Unlike traditional exchanges, MTFs are entirely electronic with no physical trading floor or location. This lack of physical presence can lead to a perceived lack of transparency or accountability in the eyes of some market participants. The advanced technology and complex financial instruments traded on MTFs can be daunting for less experienced traders. Without a proper understanding of the platform and the instruments being traded, market participants may be exposed to additional risks. On some MTFs, there might be increased counterparty risk. If a counterparty fails to fulfill their obligations in a transaction, it can result in losses for the other party. While this risk is mitigated on regulated MTFs through the use of central clearing parties, it's still a potential concern. Multilateral Trading Facilities serve as alternative trading venues that bring together multiple buyers and sellers of financial instruments, providing a flexible and efficient trading environment. MTFs have evolved in response to regulatory changes, such as MiFID and MiFID II, which have influenced their operations and increased market transparency. These platforms offer advantages such as a broad range of tradable instruments, enhanced market transparency, increased liquidity, efficient trade execution, lower trading costs, and flexible trading hours. However, MTFs also face potential drawbacks and risks, including market fragmentation, technological risks, regulatory differences, access and connectivity issues, lack of physical presence, complexity, and counterparty risk. Market participants should carefully consider these factors and weigh the benefits against the risks when deciding to engage in trading activities on MTFs. It is crucial to seek the advice of a financial advisor. Professional guidance can provide insights into the operation of these platforms and help navigate the complexities of trading on MTFs.What Is a Multilateral Trading Facility (MTF)?
Evolution of MTF
Historical Context
Regulatory Shifts Driving MTF Development
How MTFs Operate
Trading Process on MTFs
Role of Market Makers and Brokers
Price Formation and Trade Matching
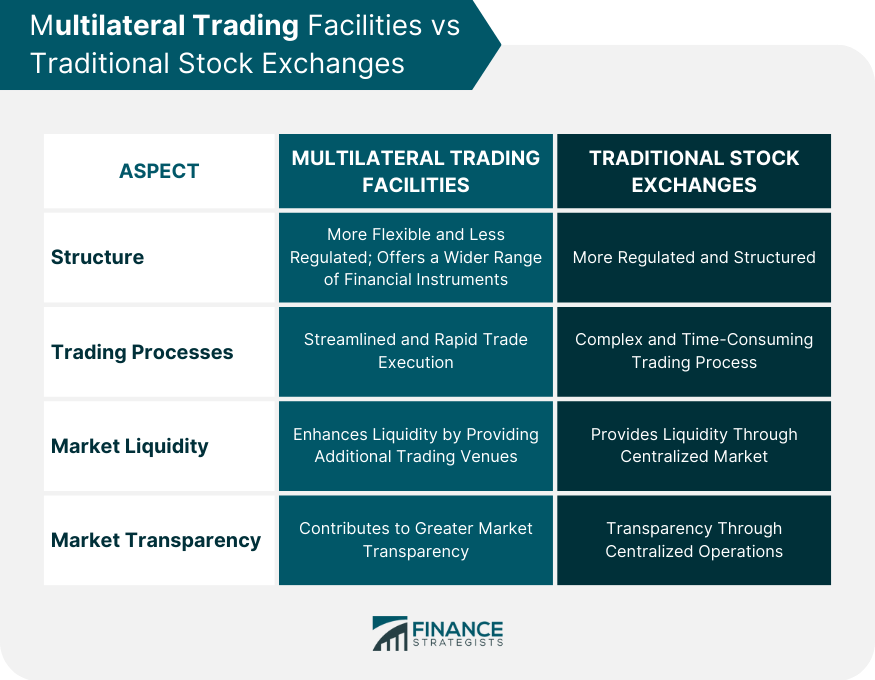
MTFs vs Traditional Stock Exchanges
Differences in Structure
Trading Processes: Comparison and Contrast
Impact on Market Liquidity and Transparency
MTF Regulation and Legal Framework
MiFID and MiFID II: Influences on MTFs
Regulation in the US: ATS Regulations
Other International Regulatory Bodies and Their Impact
Advantages of Trading via MTFs
Broad Range of Tradable Instruments
Enhanced Market Transparency
Increased Liquidity
Efficient Trade Execution
Lower Trading Costs
Flexible Trading Hours
Promotes Competition
Potential Drawbacks and Risks of MTFs
Market Fragmentation
Technological Risks
Regulatory Differences
Access and Connectivity Issues
Lack of Physical Presence
Complexity
Counterparty Risk

Final Thoughts
Multilateral Trading Facility (MTF) FAQs
While both MTFs and traditional stock exchanges provide platforms for trading financial instruments, MTFs offer greater flexibility and a wider range of tradable instruments. MTFs operate with less regulation, allowing for more diverse financial products to be traded. Additionally, MTFs generally offer streamlined and rapid trade execution processes, facilitated by advanced technology systems.
Yes, Multilateral Trading Facilities are regulated entities. In the European Union, MTFs are subject to regulations set forth by the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID) and its subsequent iteration, MiFID II. In the United States, the equivalent of MTFs are Alternative Trading Systems (ATS), which are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). These regulations aim to ensure fair and transparent trading practices on MTFs.
Yes, individual retail investors can trade on Multilateral Trading Facilities. MTFs provide access to a broad range of financial instruments, making them accessible to retail investors who are looking to diversify their investment portfolios. However, it's important for individual investors to understand the risks and complexities associated with the instruments being traded on MTFs and to carefully consider their investment strategies.
Multilateral Trading Facilities enhance market liquidity by consolidating multiple buying and selling interests. By providing additional trading venues for a wide range of financial instruments, MTFs increase the availability of buyers and sellers, making it easier to execute trades. This increased liquidity benefits market participants by improving price stability, reducing the impact of large trades, and facilitating smoother market operations.
While trading on Multilateral Trading Facilities offers advantages, there are potential risks to consider. These include market fragmentation, where liquidity is split across multiple venues, making it harder to assess the market accurately. Technological risks exist, such as system failures or cyber-attacks that could disrupt trading activities. Regulatory differences between jurisdictions can also introduce challenges for traders. Additionally, there may be limited access for smaller retail investors, and the complexity of the instruments traded on MTFs can pose risks for less experienced traders.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











