Outward arbitrage is a type of financial strategy that involves exploiting price discrepancies between different markets, countries, or currencies. It is a form of arbitrage, which seeks to take advantage of price differences for the same asset or security in different markets, allowing investors to buy low in one market and sell high in another, thereby earning risk-free profits. Outward arbitrage plays a crucial role in the finance industry, as it helps to ensure that asset prices remain consistent across different markets and regions. By capitalizing on price discrepancies, outward arbitrageurs contribute to market efficiency, as their actions help to equalize prices and reduce market anomalies. Additionally, outward arbitrage offers investors the potential for risk-free profits and diversification opportunities. Arbitrage is a financial strategy that involves simultaneously buying and selling an asset or security in different markets to capitalize on price discrepancies. This allows investors to earn risk-free profits by taking advantage of price differences for the same asset in different markets. Outward arbitrage is a specific type of arbitrage that focuses on exploiting price discrepancies between different countries, currencies, or markets. It involves buying an asset in one market and selling it in another, where the asset's price is higher. This can be done through various methods, including currency arbitrage, where investors take advantage of exchange rate differences between currencies, or geographic arbitrage, where investors capitalize on price differences between different regions or countries. The key principles of outward arbitrage include identifying price discrepancies between different markets or countries, executing trades to capitalize on these discrepancies, and managing risk through proper hedging strategies. Outward arbitrageurs must be vigilant in monitoring market data and economic indicators to spot profitable arbitrage opportunities and act quickly to take advantage of them. One of the primary factors influencing outward arbitrage opportunities is the presence of disparities in asset prices and exchange rates between different markets or countries. These disparities can arise from various reasons, including market inefficiencies, information asymmetry, and differences in economic conditions or regulations. Market inefficiencies and information asymmetry can create opportunities for outward arbitrage. Inefficient markets may not reflect all available information, leading to price discrepancies between different markets. Similarly, information asymmetry, where some market participants have access to information that others do not, can result in price differences that can be exploited by outward arbitrageurs. Regulatory and legal factors can also influence outward arbitrage opportunities. Differences in tax laws, regulations, and market structures between countries can create price discrepancies that can be exploited by arbitrageurs. However, these factors can also present risks, as regulatory changes or legal disputes can impact the viability of arbitrage strategies. Transaction costs, such as fees and commissions, and currency risk can also influence outward arbitrage opportunities. High transaction costs can erode the potential profits from arbitrage trades, while currency risk can introduce uncertainty into the expected returns of arbitrage strategies involving foreign exchange transactions. Successful outward arbitrage requires identifying and analyzing potential arbitrage opportunities. This involves monitoring market data, economic indicators, and exchange rates to spot price discrepancies between different markets or countries. Arbitrageurs must also consider transaction costs, currency risk, and other factors that may impact the profitability of their arbitrage trades. Once an arbitrage opportunity has been identified, the next step is to execute the necessary trades to capitalize on the price discrepancy. This typically involves buying the asset in the lower-priced market and simultaneously selling it in the higher-priced market. Speed and efficiency are crucial in this process, as arbitrage opportunities can be short-lived, and price discrepancies may quickly disappear as other market participants take advantage of them. Risk management is an essential component of successful outward arbitrage. While arbitrage trades are generally considered risk-free, various factors can introduce risk, such as currency fluctuations, transaction costs, and counterparty risk. Arbitrageurs should employ hedging strategies, such as using derivatives or other financial instruments, to minimize these risks and protect their potential profits. One of the main benefits of outward arbitrage is the potential for profitability and return on investment. By capitalizing on price discrepancies between different markets, countries, or currencies, investors can earn risk-free profits, which can be an attractive prospect in an uncertain economic environment. Outward arbitrage offers investors the opportunity to capitalize on price discrepancies, leveraging market inefficiencies for financial gains. This can be a valuable strategy for investors looking to diversify their portfolios and take advantage of unique investment opportunities. Outward arbitrage can also contribute to portfolio diversification and risk reduction. By investing in different markets, countries, or currencies, investors can spread their risk across various assets and regions, reducing the potential impact of adverse market events on their overall portfolio performance. Market volatility and unpredictability can pose risks to outward arbitrage strategies. Rapid market movements or unexpected events can cause price discrepancies to disappear quickly, potentially leading to losses for arbitrageurs who are unable to execute their trades in time. Counterparty risk, or the risk that one party in a financial transaction will fail to meet its obligations, and settlement risk, or the risk that a transaction will not be settled as expected, can also pose challenges for outward arbitrageurs. These risks can impact the execution and settlement of arbitrage trades, potentially leading to financial losses. Regulatory and legal risks can also impact outward arbitrage strategies. Changes in regulations, tax laws, or market structures can affect the viability of arbitrage opportunities, while legal disputes or enforcement actions can result in financial penalties or other negative consequences for investors engaged in outward arbitrage. Currency risk, or the potential for fluctuations in exchange rates to impact the value of investments, can pose challenges for outward arbitrage strategies involving foreign exchange transactions. Arbitrageurs must manage this risk through proper hedging strategies to protect their potential profits. Outward arbitrage is a financial strategy that capitalizes on price discrepancies between different markets, countries, or currencies, offering investors the potential for risk-free profits and portfolio diversification. While outward arbitrage presents opportunities for profitability and risk reduction, it is not without risks, including market volatility, counterparty risk, regulatory and legal risks, and currency risk. Successful outward arbitrage requires identifying and analyzing arbitrage opportunities, executing trades efficiently, and managing risk through proper hedging strategies. By taking advantage of differences in asset prices, exchange rates, or market conditions, investors can potentially generate risk-free profits and diversify their portfolios. Ultimately, outward arbitrage can be a valuable addition to an investor's toolkit, providing unique opportunities for profit and diversification.What Is Outward Arbitrage?
How Outward Arbitrage Works
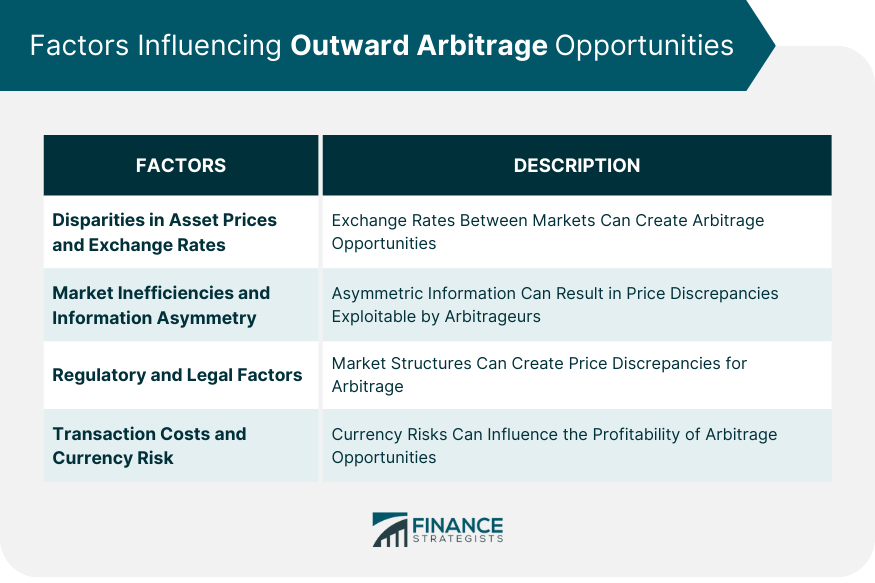
Factors Influencing Outward Arbitrage Opportunities
Disparities in Asset Prices and Exchange Rates
Market Inefficiencies and Information Asymmetry
Regulatory and Legal Factors
Transaction Costs and Currency Risk
Strategies and Techniques in Outward Arbitrage
Identifying and Analyzing Arbitrage Opportunities
Executing Outward Arbitrage Trades
Risk Management and Hedging Strategies
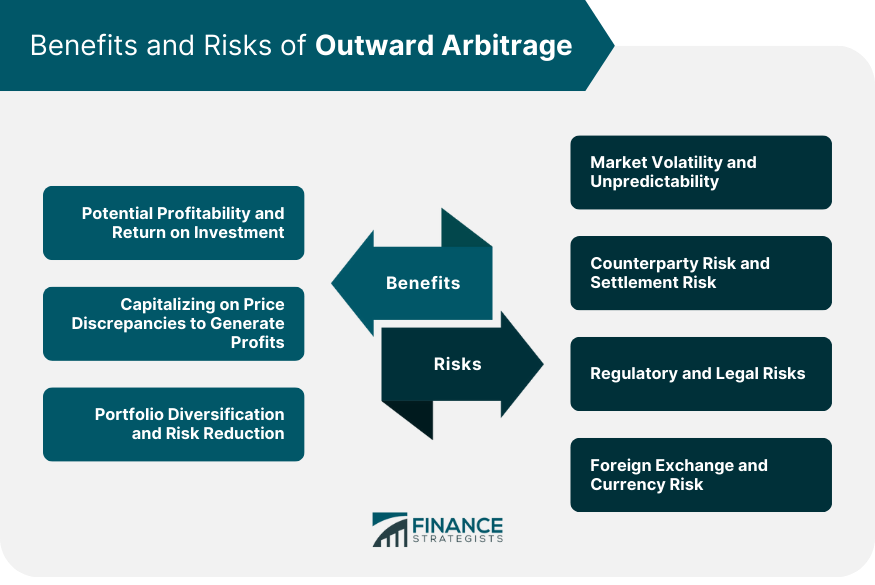
Benefits of Outward Arbitrage
Potential Profitability and Return on Investment
Capitalizing on Price Discrepancies to Generate Profits
Portfolio Diversification and Risk Reduction
Risks of Outward Arbitrage
Market Volatility and Unpredictability
Counterparty Risk and Settlement Risk
Regulatory and Legal Risks
Foreign Exchange and Currency Risk
Final Thoughts
Outward Arbitrage FAQs
Outward arbitrage refers to the practice of capitalizing on price differences between assets or markets located in different countries or regions.
Outward arbitrage involves buying assets in one market where they are undervalued and simultaneously selling them in another market where they are overvalued, profiting from the price disparities.
Common strategies in outward arbitrage include cross-border currency arbitrage, international stock and bond arbitrage, and commodity and futures arbitrage.
Outward arbitrage offers potential profitability and attractive returns on investment. It also provides opportunities for portfolio diversification and risk reduction through exposure to different markets and assets.
Risks in outward arbitrage include market volatility, counterparty and settlement risks, regulatory and legal risks, as well as foreign exchange and currency risk. Proper risk management is crucial.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











