Over-the-Top (OTT) refers to the delivery of video, audio, and other media content directly to users over the internet, bypassing traditional broadcast or cable networks. OTT platforms have revolutionized the way we consume media, providing convenient access to a vast array of content on demand. Services like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video have become household names, offering subscription-based models that give users the freedom to stream content whenever and wherever they choose. OTT has disrupted the traditional media landscape, challenging established broadcasting and cable providers. However, it also presents challenges such as content fragmentation, piracy concerns, and intense competition among streaming platforms. Understanding the concept of OTT is essential in comprehending the changing dynamics of the media industry in the digital age. Video streaming services represent one of the most common forms of OTT. Platforms such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ provide a vast library of films, TV shows, documentaries, and original content accessible on demand. OTT also extends to music streaming services, allowing users to listen to millions of songs on demand. Services like Spotify, Apple Music, and Amazon Music have transformed the music industry by providing a lucrative alternative to physical sales and digital downloads. OTT messaging apps like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and WeChat have revolutionized communication by offering free messaging services over the internet. These apps provide features such as voice and video calls, group chats, and multimedia sharing, effectively replacing traditional SMS and MMS services. Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services, such as Skype and Zoom, are another form of OTT. They enable voice calls, video conferencing, and file sharing over the internet, providing a cost-effective alternative to traditional telephony systems. The gaming industry has also been impacted by OTT, with cloud gaming services like Google Stadia and Microsoft's xCloud offering on-demand gaming experiences. These platforms allow users to play games on various devices without needing a console or high-spec PC. The subscription-based model is one of the most popular OTT business models. Users pay a recurring fee to access the service, usually monthly or annually. This model provides a steady revenue stream and is employed by platforms such as Netflix and Spotify. In the advertisement-based model, content is offered for free to users, but revenue is generated through advertising. This model is used by platforms such as YouTube and Peacock TV. Advertisements can be displayed before, during, or after the content and can be targeted based on user data. The transaction-based model, also known as pay-per-view, involves users paying for individual pieces of content. This model is often used for special events, like live sports or concerts. Examples include platforms like Amazon Video, where users can rent or buy individual movies or TV episodes. Some OTT platforms employ hybrid models, combining aspects of the models mentioned above. For instance, Hulu offers both a subscription-based service and an ad-supported cheaper version. Similarly, YouTube has a free, ad-supported version and a premium, ad-free subscription service. This approach allows platforms to cater to different consumer preferences and increase potential revenue streams. OTT platforms generate revenue primarily through subscriptions, advertising, and transactions. Subscription services involve recurring payments, providing a predictable revenue stream. Advertising-based services generate revenue from ad placements within their content. Transaction-based services earn money from users purchasing or renting individual pieces of content. The cost structure of OTT businesses largely revolves around content acquisition, technology infrastructure, and marketing. Content acquisition can be particularly costly, especially for platforms that invest in original content. Maintaining robust and secure technology infrastructure for seamless content delivery is another significant expense. Lastly, marketing costs are essential for attracting and retaining users in a highly competitive market. Profitability in the OTT industry is influenced by various factors such as the chosen business model, user base size, and cost control measures. Monetization strategies can include enhancing subscription offerings, introducing tiered pricing, expanding into new markets, and partnering with other businesses for cross-promotion. The OTT market has been experiencing rapid growth, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. As of 2023, the global OTT market is estimated to be worth $171.99 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of around 15.2%% over the next five years. The OTT industry is dominated by major players like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Hulu in video streaming; Spotify and Apple Music in music streaming; and WhatsApp, Messenger, and WeChat in OTT messaging. The OTT market is highly competitive, with platforms vying for market share through content offerings, pricing strategies, and user experience enhancements. In recent years, there has been a surge in the production of original content as a strategy to attract and retain subscribers. In the U.S., OTT services are subject to regulations by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Regulations cover areas like content standards, advertising practices, and data privacy. Internationally, OTT regulations vary by country. They can encompass issues such as content censorship, data localization, and taxation. Regulations can impact various aspects of OTT business, from the type of content that can be offered to how user data is managed. Companies must stay updated and compliant with regulations to avoid penalties and safeguard their reputation. With the proliferation of OTT platforms, market saturation, and competition are significant challenges. Companies must continually innovate to differentiate their offerings and attract subscribers. Technological challenges such as maintaining streaming quality, ensuring data security, and adapting to new technologies are constant concerns for OTT providers. Despite the challenges, there are ample opportunities for growth in the OTT space. These include exploring new content formats, leveraging data analytics for personalized experiences, expanding into emerging markets, and integrating with other digital platforms. Over-the-Top (OTT) services have revolutionized media and entertainment by delivering content directly to consumers via the internet, thereby bypassing traditional distribution channels. The diverse forms of OTT services, such as video and music streaming, messaging apps, VoIP services, and gaming, provide an array of on-demand experiences. OTT platforms leverage various business models—subscription-based, advertisement-based, transaction-based, and hybrid—to generate revenue. Despite challenges like market saturation and technological demands, these platforms have created a dynamic, rapidly expanding market, expected to reach $171.99 billion by 2023. Key players in this industry continuously innovate to stand out, with strategies often centered on unique content offerings, advanced user experiences, and strategic market expansions. Compliance with domestic and international regulations is crucial for these platforms, given the integral role they play in data handling and content distribution. Overall, the OTT landscape presents an exciting interplay of technology, regulation, and consumer preference, driving the future of global digital consumption.What Is Over-the-Top (OTT)?
Different Forms of Over-the-Top (OTT) Services
Video Streaming Services
Music Streaming Services
Messaging Apps
VoIP Services
OTT in Gaming

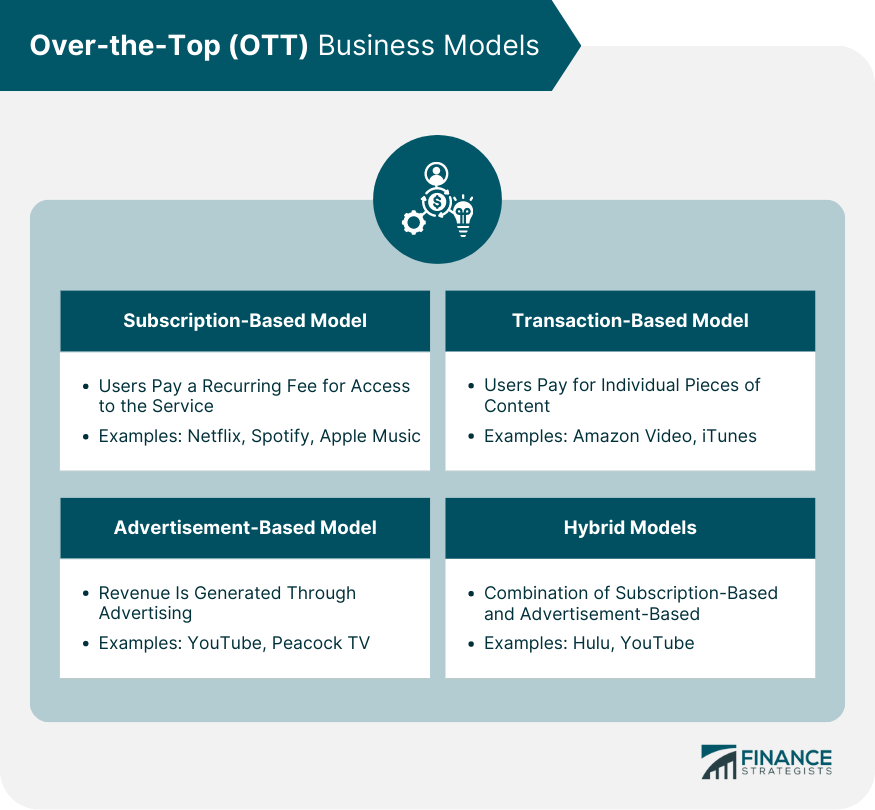
Over-the-Top (OTT) Business Models
Subscription-Based Model
Advertisement-Based Model
Transaction-Based Model
Hybrid Models
Financial Aspects of Over-the-Top (OTT) Services
Revenue Generation in OTT
Cost Structure of OTT Businesses
Profitability and Monetization in the OTT Industry
Market Analysis of Over-the-Top (OTT) Services
Current Market Size and Growth Trends
Major Players in the OTT Industry
Competitive Landscape in the OTT Market
Over-the-Top (OTT) Regulatory Environment
Domestic Regulations
International Regulations
Impact of Regulations on OTT Business
Challenges and Opportunities in Over-the-Top (OTT) Services
Market Saturation and Competition
Technological Challenges
Opportunities for Innovation and Growth in OTT

Final Thoughts
Over-the-Top (OTT) FAQs
OTT refers to the delivery of film and TV content via the internet, bypassing traditional cable or satellite TV service providers.
OTT services generate revenue through subscriptions, advertising, and transactions.
Major players in the OTT industry include Netflix, Amazon Prime Vdeo, and Disney+ for video streaming; Spotify and Apple Music for music streaming, and WhatsApp and Messenger for messaging services.
Challenges for OTT services include market saturation, competition, and technological challenges.
The OTT market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of around 14% over the next five years, making it a significant segment of the digital economy.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











