Portfolio reporting refers to the process of gathering, analyzing, and presenting relevant information about a portfolio's performance, risks, and other attributes. This information is typically compiled into a comprehensive report and distributed to stakeholders to facilitate informed decision-making and continuous improvement. Portfolio reporting serve several critical purposes: It helps stakeholders assess the performance of the portfolio against its objectives and benchmarks. It provides insights into the effectiveness of the portfolio's management and decision-making processes. It enables stakeholders to identify potential risks and opportunities for improvement. It ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. Various stakeholders are involved in the portfolio reporting process, including portfolio managers, analysts, investors, clients, regulators, and other interested parties. There are different types of portfolios that require reporting, each with its unique set of characteristics and requirements. Investment portfolios consist of a collection of financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. Portfolio reporting for investment portfolios typically focuses on financial performance, risk management, and asset allocation. Project portfolios comprise a group of projects managed collectively to achieve strategic objectives. Reporting for project portfolios typically includes project status, resource allocation, and progress towards organizational goals. Product portfolios consist of a range of products or services offered by a company. Reporting for product portfolios often involves evaluating product performance, market share, and profitability. Art and design portfolios showcase an individual's creative work, such as illustrations, photographs, or graphic designs. Reporting for these portfolios may involve evaluating the quality and impact of the creative pieces, as well as their potential market value. Portfolio reports typically include several key components that provide a comprehensive view of the portfolio's performance and status. These metrics evaluate the financial performance of the portfolio, such as return on investment, net asset value, and total returns. Risk metrics assess the level of risk associated with the portfolio, including measures such as volatility, value at risk, and risk-adjusted performance. Operational metrics provide insights into the management and administration of the portfolio, such as turnover, expense ratios, and trading costs. Portfolio reports often include comparisons to relevant benchmarks, such as market indices or industry standards, to evaluate the portfolio's performance relative to its peers. This component of portfolio reporting presents the distribution of assets within the portfolio and assesses the level of diversification to manage risk effectively. Portfolio reports are typically produced at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, to ensure stakeholders receive timely and relevant information. Effective portfolio reporting requires adherence to several best practices to ensure accurate, insightful, and actionable information. Setting Clear Objectives and Goals: Establishing well-defined objectives and goals for the portfolio is crucial for guiding the reporting process and evaluating performance. Ensuring Data Accuracy and Consistency: Accurate and consistent data is the foundation of reliable portfolio reporting. This involves maintaining a robust data management system and validating the data used in the reports. Effective Communication and Visualization: Clear communication and visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, and tables, help convey complex information in an easily digestible format. Leveraging Technology and Automation: Embracing technology and automation tools can streamline the portfolio reporting process, reduce manual effort, and minimize the risk of errors. Portfolio reporting must comply with various regulations and standards to ensure transparency, accountability, and investor protection. Different jurisdictions and industries have specific regulations and standards that govern portfolio reporting, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations for investment portfolios in the United States. Portfolio managers must adhere to reporting requirements and deadlines specified by regulatory bodies to maintain compliance and avoid penalties. Protecting the confidentiality and security of sensitive portfolio information is critical to prevent unauthorized access and maintaining stakeholder trust. Portfolio reporting faces several challenges that can impact the effectiveness and efficiency of the process. Integrating data from multiple sources and maintaining data quality can be a complex and time-consuming task, particularly for large and diverse portfolios. Producing timely and frequent reports is essential to keep stakeholders informed, but it can also strain resources and lead to information overload. Balancing the diverse needs and expectations of various stakeholders can be challenging, as different parties may prioritize different aspects of the portfolio. Regulatory environments are constantly evolving, and portfolio managers must adapt their reporting processes to comply with new rules and requirements. The field of portfolio reporting is continually evolving as technology advances and new trends emerge. AI and machine learning technologies can help automate and enhance portfolio reporting by providing more accurate data analysis, predictive insights, and tailored recommendations. As technology continues to improve, real-time reporting and analytics will become more accessible, allowing stakeholders to access up-to-date information and make faster, more informed decisions. There is a growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in portfolio management, leading to increased demand for ESG-related reporting and analytics. Innovations in data visualization and user experience design will enable more intuitive and engaging portfolio reports, making complex information more accessible to a wider audience. Portfolio reporting is a crucial process that helps stakeholders make informed decisions and drive success. Effective portfolio reporting involves gathering, analyzing, and presenting relevant information about a portfolio's performance, risks, and other attributes. Different types of portfolios require different reporting approaches, each with its unique set of characteristics and requirements. Portfolio reports typically include several key components, such as performance metrics, benchmarking, asset allocation, and reporting frequency. Adherence to best practices and compliance with regulatory requirements are essential for producing reliable and actionable portfolio reports. Portfolio reporting faces several challenges, such as data management, stakeholder expectations, and regulatory changes. Future trends in portfolio reporting, such as the integration of AI and machine learning, real-time reporting and analytics, sustainability and ESG reporting, and advancements in data visualization and user experience design, offer exciting opportunities for enhancing the reporting process.Definition of Portfolio Reporting
Importance and Purpose of Portfolio Reporting
Key Stakeholders Involved in Portfolio Reporting
Types of Portfolios
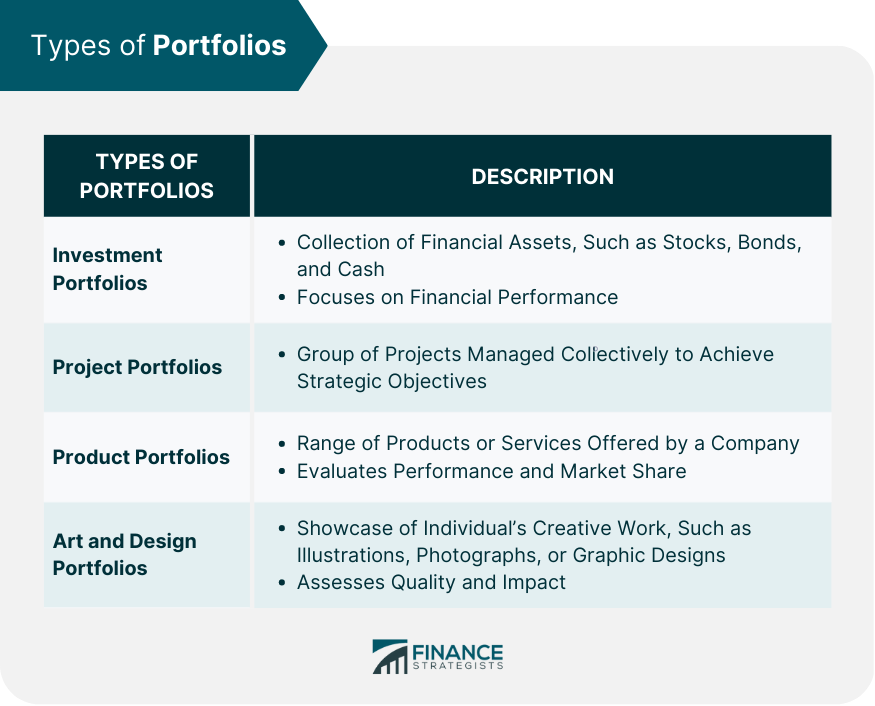
Investment Portfolios
Project Portfolios
Product Portfolios
Art and Design Portfolios
Components of Portfolio Reporting
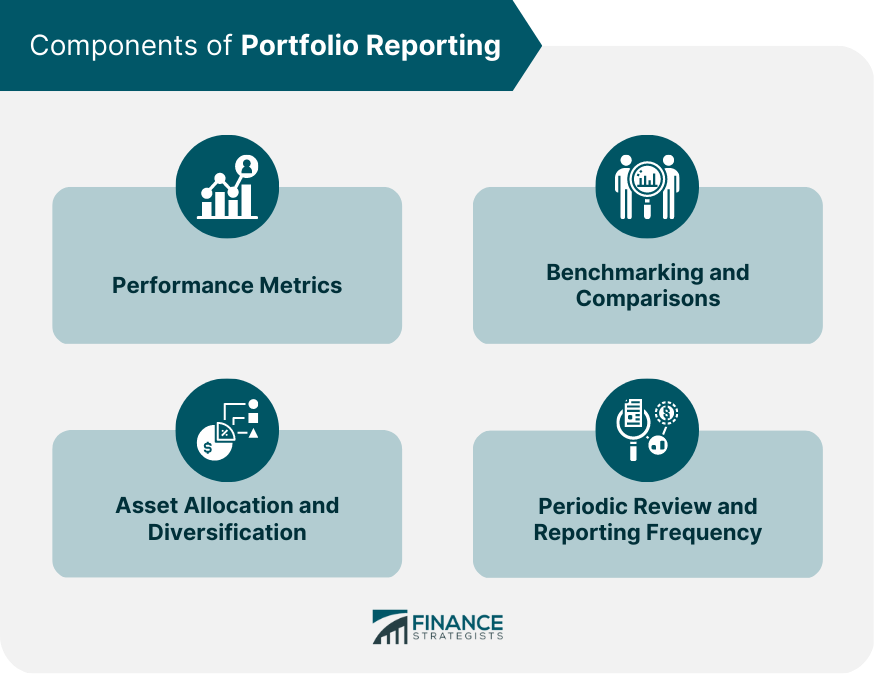
Performance Metrics
Financial Metrics
Risk Metrics
Operational Metrics
Benchmarking and Comparisons
Asset Allocation and Diversification
Periodic Review and Reporting Frequency
Portfolio Reporting Best Practices
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Relevant Regulations and Standards
Reporting Requirements and Deadlines
Ensuring Confidentiality and Security
Challenges in Portfolio Reporting
Data Management and Integration
Timeliness and Frequency of Reporting
Managing Stakeholder Expectations
Adapting to Regulatory Changes
Future Trends in Portfolio Reporting
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Enhanced Real-Time Reporting and Analytics
Increased Focus on Sustainability and ESG Reporting
Advancements in Data Visualization and User Experience
Final Thoughts
Portfolio Reporting FAQs
Portfolio Reporting serves to gather, analyze, and present relevant information about a portfolio's performance, risks, and other attributes to stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
The frequency of Portfolio Reporting depends on the type of portfolio and stakeholder requirements. Typically, reports are produced at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, to ensure stakeholders receive timely and relevant information.
The main components of Portfolio Reporting include performance metrics (financial, risk, and operational metrics), benchmarking and comparisons, asset allocation and diversification, and periodic review and reporting frequency.
To ensure effective Portfolio Reporting, it is essential to set clear objectives and goals, ensure data accuracy and consistency, use effective communication and visualization techniques, and leverage technology and automation tools to streamline the process.
Portfolio Reporting is continually evolving to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning for better insights, offer enhanced real-time reporting and analytics, focus more on sustainability and ESG reporting, and leverage advancements in data visualization and user experience design.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











