QDII is a program introduced by various emerging economies, particularly China, that permits domestic institutional investors to invest in foreign securities markets within certain regulatory limits. This initiative aims to diversify domestic investors' portfolios, promote cross-border investments, and reduce the impact of domestic economic fluctuations. The QDII program was first launched in China in April 2006 by the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), the People's Bank of China (PBOC), and the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE). Initially, the program allowed only domestic commercial banks to invest in foreign fixed-income securities, but it has since expanded to include other institutional investors such as insurance companies, securities firms, and fund management companies. Under the QDII scheme, eligible domestic institutional investors are granted quotas to invest in foreign securities markets. These quotas are determined by the regulatory authorities and are subject to periodic review. Once an institution receives its quota, it can invest in various types of foreign securities, such as stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments, subject to regulatory guidelines and investment restrictions. Several key players are involved in the QDII program, including: Regulatory authorities, such as the CSRC, PBOC, and SAFE, which oversee the program, grant quotas, and enforce compliance. Domestic institutional investors, such as banks, insurance companies, securities firms, and fund management companies, which participate in the program. Foreign securities markets and investment products, which provide the investment opportunities for domestic institutional investors. The QDII program is regulated by a set of rules and guidelines established by the relevant regulatory authorities. These rules and guidelines govern various aspects of the program, including eligibility criteria, investment allocation, compliance requirements, and risk management strategies. The QDII program offers several benefits to domestic investors, including: Diversification: By allowing domestic investors to invest in foreign markets, QDII reduces their reliance on domestic markets and helps them diversify their portfolios. Access to international markets: QDII provides domestic investors with access to a wider range of investment opportunities, enabling them to benefit from global economic growth. Risk reduction: Investing in foreign securities can help domestic investors mitigate risks associated with domestic economic fluctuations. The QDII program can also have significant effects on international markets, such as: Increased capital flows: The QDII program promotes cross-border investments, increasing the flow of capital between participating countries. Improved market liquidity: As more domestic investors participate in foreign markets, market liquidity can improve, making it easier for investors to buy and sell securities. Enhanced global economic integration: The QDII program fosters stronger economic ties between participating countries, contributing to global economic integration. The eligibility criteria for becoming a QDII vary by country. However, the common thread among all these criteria is the financial stability and integrity of the institution. Regulators require that these institutions have a solid risk management system, a strong balance sheet, and good corporate governance. Investor eligibility often depends on the type of QDII product. In some cases, only institutional investors can participate, while in others, retail investors can invest too. The regulatory requirements usually consider the investor's financial knowledge, investment experience, and risk tolerance. The types of overseas investments that a QDII can make are specified by the regulators. These may include equities, bonds, derivatives, and other investment vehicles. The regulations typically ensure that the investments align with the country's economic and financial stability goals. The QDII program allows for a variety of investments, including equities, fixed income, commodities, real estate, and various types of derivative products. The specific types of investments allowed depend on the regulations of the country implementing the QDII program. Each QDII is assigned a quota, which is the maximum amount of funds that can be invested overseas. This quota is determined by the relevant regulatory authorities based on several factors, including the size of the institution, its risk management capabilities, and the overall economic conditions. To ensure the stability of the financial system, QDIIs are required to employ robust risk management strategies. These may include diversification across different types of investments, regions, and industries, as well as the use of derivatives to hedge against potential losses. While QDII enables domestic institutions to invest overseas, QFII allows foreign institutions to invest in domestic markets. Both programs aim to increase cross-border investments and diversify portfolios. However, QFII is more focused on attracting foreign capital, while QDII seeks to encourage domestic capital to invest overseas. RQFII is a variant of the QFII scheme, allowing foreign institutional investors to use offshore RMB funds to invest in the Chinese mainland securities market. Compared to QDII, RQFII aims to internationalize the RMB and promote its use in global trade and finance. There are numerous other global investment schemes similar to QDII, such as India's Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS) and Brazil's Investimento no exterior (Overseas Investment) scheme. While the specifics of each program vary, their common goal is to promote cross-border investments and facilitate global economic integration. In the case of China, three main regulatory bodies oversee the QDII program: The People's Bank of China (PBOC), the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), and the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE). These bodies are responsible for establishing and enforcing the rules and regulations governing the program. Several key regulations and policies govern the QDII program, including the Guidelines for Internal Control of Commercial Banks and the Measures for the Administration of Overseas Investments by Qualified Domestic Institutional Investors. It also includes Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Measures for the Administration of Overseas Investments by Qualified Domestic Institutional Investors. These regulations establish the eligibility criteria for QDIIs, set the investment quotas, and prescribe the risk management strategies that QDIIs must follow. QDIIs must comply with a host of requirements. They must submit regular reports to the regulatory authorities, comply with the investment restrictions, and adhere to the risk management guidelines. In case of non-compliance, they may face penalties, including reduction of their investment quotas or suspension of their QDII status. The QDII program can have a significant impact on the domestic capital market. By allowing capital outflows, it can relieve pressure on the domestic currency and contribute to its stability. Moreover, it can lead to a more efficient allocation of resources, as domestic investors can seek better returns overseas. By facilitating capital outflows, the QDII program can impact the domestic currency's valuation. If significant amounts of domestic currency are converted into foreign currencies for overseas investments, it may put downward pressure on the domestic currency. However, the regulatory authorities manage this risk by controlling the quotas assigned to QDIIs. The QDII program plays a crucial role in economic development. By encouraging cross-border investments, it contributes to the integration of the domestic economy with the global economy. This can lead to increased trade and investment flows, contributing to economic growth and development. The QDII program is an investment initiative that allows domestic institutional investors in emerging economies to invest in foreign securities markets within certain regulatory limits. This program promotes cross-border investments, helps domestic investors diversify their portfolios, and contributes to global economic integration. The QDII program works by granting quotas to eligible domestic institutional investors to invest in foreign securities. This program has significant effects on both domestic investors and international markets, as it promotes diversification, provides access to international markets, and enhances global economic integration. The QDII program is regulated by a set of rules and guidelines that govern eligibility criteria, investment allocation, compliance requirements, and risk management strategies. For investors, the QDII program offers a unique opportunity to diversify their portfolios and gain exposure to international markets. For policymakers, this program serves as a tool to manage capital flows, stabilize the domestic currency, and promote economic development. If you are considering investing in foreign securities through the QDII program, it is important to seek professional advice. This can help you understand the potential risks and rewards, navigate the regulatory requirements, and make informed investment decisions. What Is the Qualified Domestic Institutional Investor (QDII)?
Mechanics of the QDII Scheme
How the Scheme Works
Key Players Involved
Regulatory Oversight
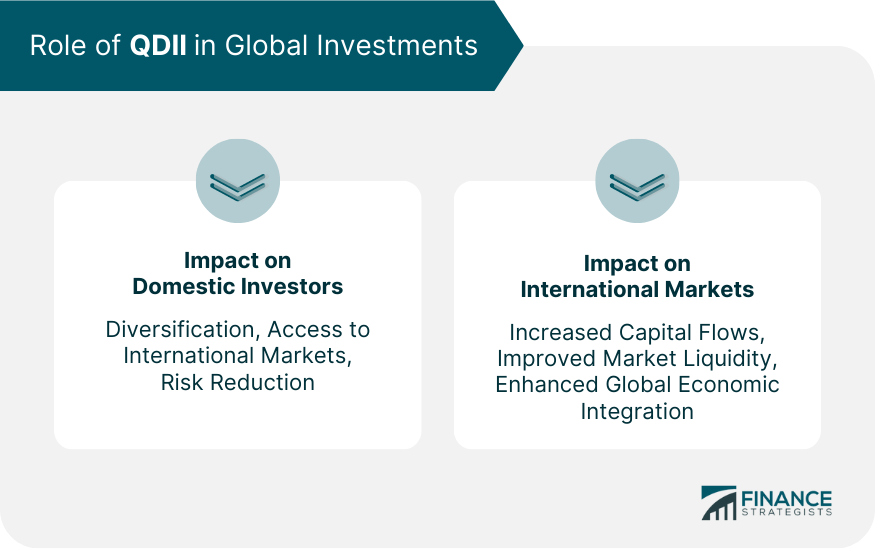
Role of QDII in Global Investments
Impact on Domestic Investors
Impact on International Markets
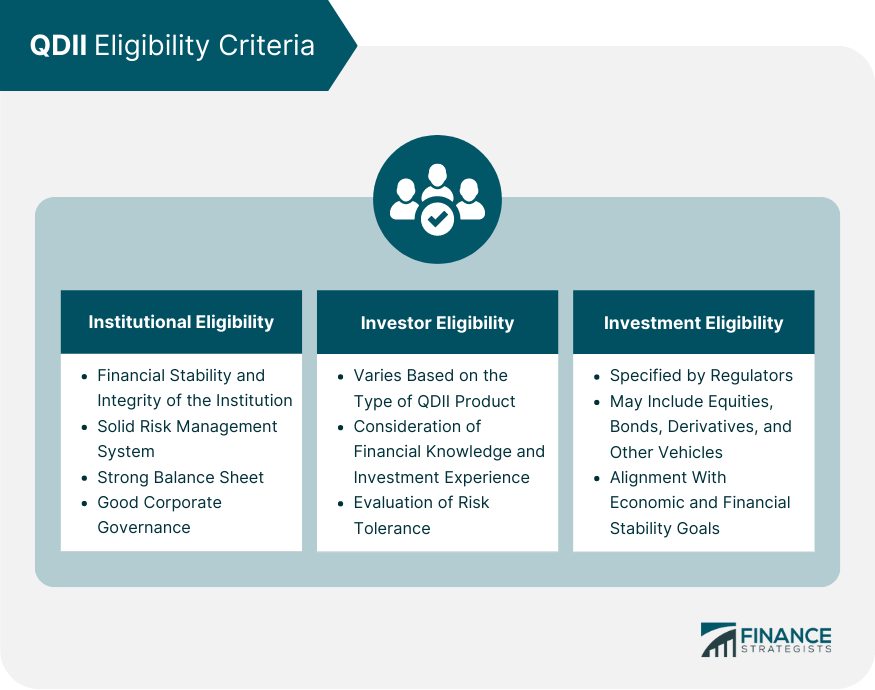
QDII Eligibility Criteria
Institutional Eligibility
Investor Eligibility
Investment Eligibility
QDII Investment Allocation
Types of Investments Allowed
Allocation Limits
Risk Management Strategies
Comparison of QDII With Other Investment Schemes
QDII vs QFII (Qualified Foreign Institutional Investor)
QDII vs RQFII (RMB Qualified Foreign Institutional Investor)
QDII vs Other Global Investment Schemes
Regulatory Framework Governing QDII
Main Regulatory Bodies
Key Regulations and Policies
Compliance Requirements
Impact of QDII on Domestic Economy
Influence on Domestic Capital Market
Effect on Currency Valuation
Role in Economic Development
Final Thoughts
Qualified Domestic Institutional Investor (QDII) FAQs
QDII is a program introduced by the Chinese government that allows domestic institutional investors, such as mutual funds, insurance companies, and securities firms, to invest in offshore financial markets.
The QDII program was established to provide Chinese investors with opportunities to diversify their investment portfolios by investing in international markets. It aims to enhance the efficiency and competitiveness of China's domestic financial markets.
Eligible participants in the QDII program include domestic institutional investors that meet specific criteria set by the regulatory authorities. These criteria typically include a minimum net asset value, operational experience, risk management capabilities, and regulatory compliance.
Investing through the QDII program offers several benefits. It allows domestic investors to access a wider range of investment opportunities in international markets, diversify their portfolios, and potentially earn higher returns. Additionally, it helps promote the development and internationalization of China's financial industry.
Yes, there are certain restrictions and limitations in place for the QDII program. These may include limits on the amount of funds that can be invested overseas, regulatory requirements regarding the types of financial products that can be invested in, and periodic reviews of participating institutions' compliance with investment guidelines. These measures are put in place to manage risks and ensure the stability of China's financial system.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











