What Is Risk Management?
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing potential risks, followed by implementing strategies to minimize or mitigate their impact. This proactive approach helps organizations protect their assets, reputation, and long-term success.
Effective risk management is crucial in business and finance, as it enables organizations to navigate uncertainty, maintain stability, and seize opportunities while minimizing potential threats.
By addressing risks proactively, businesses can protect their assets, maintain stakeholder confidence, and ensure long-term growth.
The primary objectives of risk management are to identify and assess potential risks, develop strategies to mitigate or control them and monitor and review the effectiveness of these strategies.
Ultimately, risk management aims to support informed decision-making, protect the organization, and ensure long-term success.
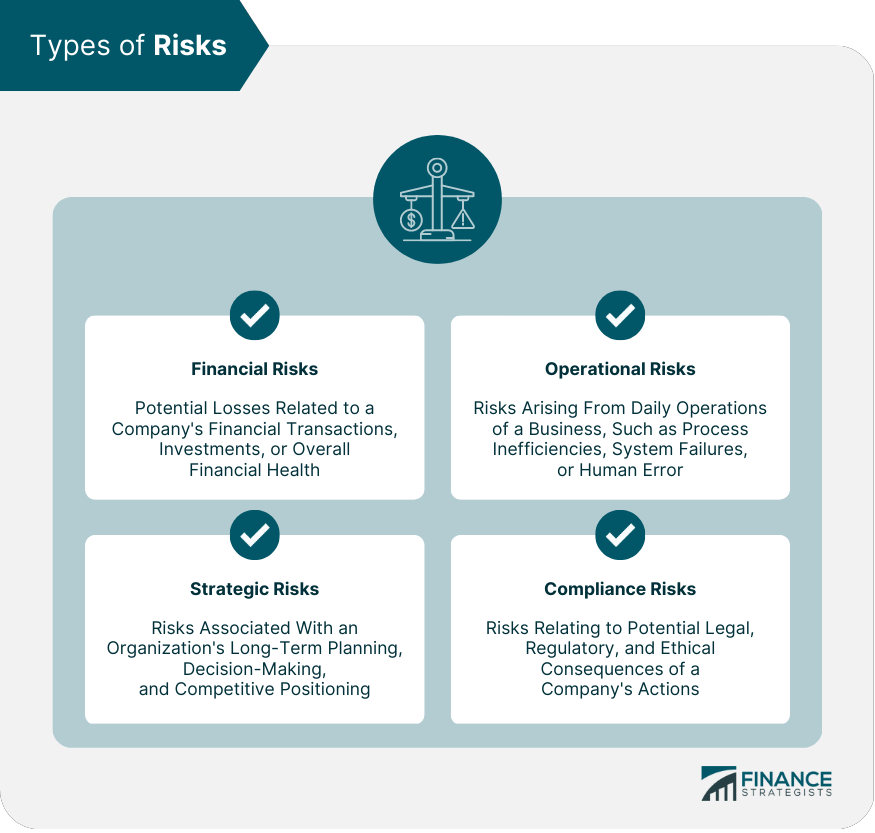
Types of Risks
Financial Risks
Financial risks involve potential losses related to a company's financial transactions, investments, or overall financial health. Examples include credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, and foreign exchange risk.
Operational Risks
Operational risks arise from the daily operations of a business, such as process inefficiencies, system failures, or human error. These risks can impact productivity, revenue, and overall business performance.
Strategic Risks
Strategic risks are associated with an organization's long-term planning, decision-making, and competitive positioning. These risks can stem from changes in market conditions, technological advancements, or shifts in consumer preferences.
Compliance Risks
Compliance risks relate to the potential legal, regulatory, and ethical consequences of a company's actions. Non-compliance with laws and regulations can lead to fines, penalties, and reputational damage.
Risk Assessment Techniques
Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative risk analysis involves the use of expert judgment, historical data, and subjective assessments to evaluate potential risks. This approach considers factors such as likelihood, impact, and vulnerability to prioritize risks and inform decision-making.
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative risk analysis employs mathematical and statistical techniques to estimate risks' probability and potential impact. This data-driven approach provides objective insights and supports more accurate decision-making.
Risk Mapping and Prioritization
Risk mapping is the process of visualizing potential risks based on their likelihood and impact. This tool helps organizations identify high-priority risks, allocate resources effectively, and focus on the most significant threats to their success.
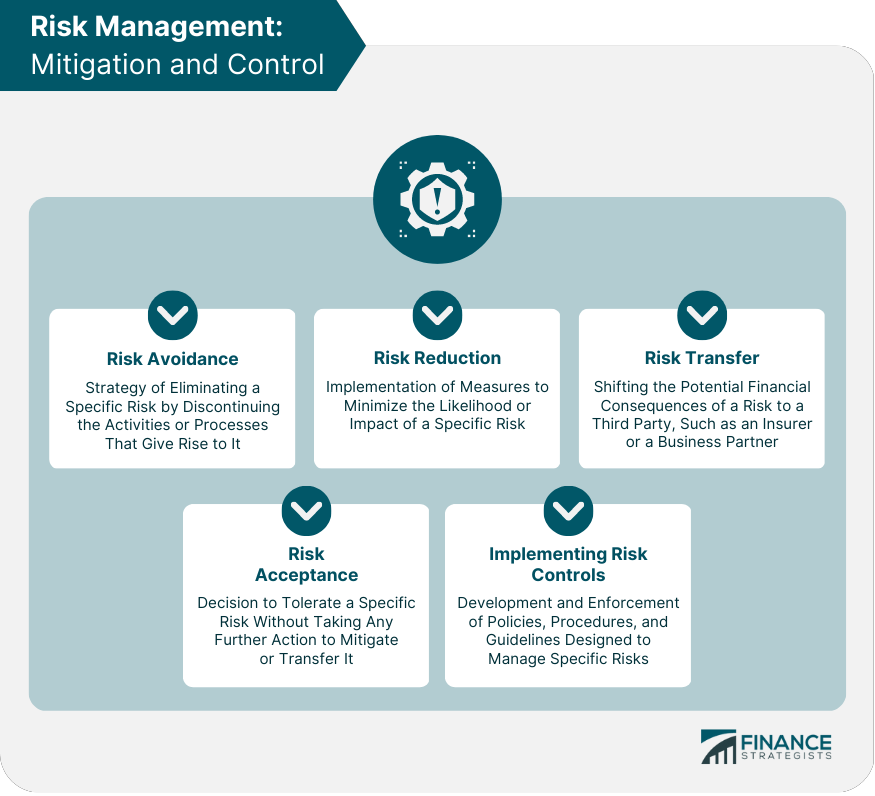
Risk Mitigation and Control
Risk Avoidance
Risk avoidance is the strategy of eliminating a specific risk by discontinuing the activities or processes that give rise to it. This approach is often used for high-impact risks that cannot be effectively managed through other means.
Risk Reduction
Risk reduction involves implementing measures to minimize the likelihood or impact of a specific risk. This strategy can include process improvements, technology upgrades, training, and other preventive actions.
Risk Transfer
Risk transfer involves shifting the potential financial consequences of a risk to a third party, such as an insurer or a business partner. Common examples of risk transfer include insurance policies, contracts, and hedging strategies.
Risk Acceptance
Risk acceptance is the decision to tolerate a specific risk without taking any further action to mitigate or transfer it.
This strategy is typically used when the cost of addressing the risk outweighs the potential benefits or when the risk is considered an inherent part of the organization's operations.
Implementing Risk Controls
Implementing risk controls involves the development and enforcement of policies, procedures, and guidelines designed to manage specific risks.
Effective risk controls help organizations reduce the likelihood or impact of risks and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Risk Monitoring and Reporting
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) are metrics that help organizations monitor and measure the effectiveness of their risk management efforts. KRIs provide early warning signals, enabling timely identification of emerging risks and proactive response to potential threats.
Risk Reporting and Communication
Risk reporting and communication involve regularly sharing risk-related information among stakeholders, such as employees, management, and board members.
Effective communication ensures that all parties are aware of the organization's risk landscape and can make informed decisions based on current risk exposures.
Continuous Monitoring and Review
Continuous monitoring and review are essential components of effective risk management. By regularly evaluating the effectiveness of risk controls and adjusting strategies as needed, organizations can stay ahead of emerging risks and maintain a strong risk management culture.
Risk Management Framework and Governance
Establishing a Risk Management Framework
A risk management framework provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and managing risks across an organization.
Establishing a framework involves defining the organization's risk appetite, setting risk management objectives, and developing policies and procedures to guide risk management activities.
Risk Management Policies and Procedures
Risk management policies and procedures outline the organization's approach to managing risks and detail the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders.
These documents serve as a foundation for risk management activities and ensure consistency and accountability across the organization.
Roles and Responsibilities
Board of Directors
The board of directors is responsible for setting the organization's risk appetite, overseeing risk management activities, and ensuring that risks are effectively managed in line with strategic objectives.
Senior Management
Senior management plays a crucial role in implementing risk management strategies, allocating resources, and promoting a risk-aware culture within the organization.
Risk Management Committee
A risk management committee is responsible for coordinating risk management activities, monitoring risk exposures, and advising the board of directors on risk-related matters.
Risk Managers and Analysts
Risk managers and analysts are responsible for identifying, assessing, and monitoring risks and developing and implementing risk mitigation strategies to protect the organization.
Risk Management Training and Awareness
Risk management training and awareness programs help to promote a risk-aware culture within the organization.
These programs ensure that employees at all levels understand their roles and responsibilities in managing risks and are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Integrating Risk Management With Business Strategy
Aligning Risk Appetite with Business Goals
Aligning risk appetite with business goals ensures that risk management activities support the organization's strategic objectives.
By establishing a clear risk appetite, organizations can make informed decisions about which risks to accept, mitigate, or transfer, aligning with their overall goals.
Risk Management in Decision-Making
Incorporating risk management into decision-making processes helps organizations make informed choices that consider both potential opportunities and threats.
This approach enables organizations to balance risk and reward, optimize resource allocation, and achieve their strategic objectives.
Building a Risk-Aware Culture
A risk-aware culture promotes a shared understanding of the organization's risk landscape and encourages proactive risk management at all levels.
Organizations can strengthen their risk management capabilities by fostering open communication, accountability, and continuous learning and driving long-term success.
Risk Management Tools and Techniques
Risk Management Software
Risk management software offers organizations a centralized platform for identifying, assessing, and monitoring risks. These tools can automate processes, improve data accuracy, and provide real-time insights to support informed decision-making.
Scenario Analysis and Stress Testing
Scenario analysis and stress testing involve simulating potential risk events to evaluate their potential impact on the organization.
These techniques help organizations assess their resilience to extreme events and identify areas where additional risk mitigation efforts may be required.
Risk Management Models
Risk management models, such as Value at Risk (VaR) or Monte Carlo simulations, provide quantitative insights into potential risk exposures.
These models help organizations estimate risk events' probability and potential impact, supporting more informed decision-making and resource allocation.
Final Thoughts
Effective risk management is essential for organizations to navigate uncertainty, protect their assets, and achieve long-term success.
By proactively identifying, assessing, and addressing potential risks, organizations can maintain stability, seize opportunities, and minimize threats to their operations.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, organizations must adapt their risk management practices to stay ahead of emerging risks and challenges.
Risk management plays a critical role in achieving business success by supporting informed decision-making, optimizing resource allocation, and fostering a risk-aware culture.
By integrating risk management with business strategy, organizations can balance risk and reward and drive long-term growth.
Organizations seeking to improve their risk management capabilities should consider engaging in wealth management services.
These professionals can provide valuable insights, tools, and support to help organizations develop and implement effective risk management strategies, optimize resource allocation, and achieve their strategic objectives.
Risk Management FAQs
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing potential risks, followed by implementing strategies to minimize or mitigate their impact.
Effective risk management is crucial in business and finance, as it enables organizations to navigate uncertainty, maintain stability, and seize opportunities while minimizing potential threats.
The types of risks in risk management include financial risks, operational risks, strategic risks, and compliance risks.
Risk management's risk mitigation and control strategies include risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, and risk acceptance.
Organizations seeking to improve their risk management capabilities should consider engaging in wealth management services. These professionals can provide valuable insights, tools, and support to help organizations develop and implement effective risk management strategies, optimize resource allocation, and achieve their strategic objectives.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











