A trading house is a business that specializes in facilitating transactions between different parties in the global marketplace. It acts as an intermediary in buying and selling a variety of goods, commodities, and financial instruments. Trading houses can play a critical role in both international and domestic trade, connecting suppliers, manufacturers, and consumers. Their operations range from identifying market opportunities and managing risks to handling logistics and finances. With their strong networks and relationships, trading houses help in bridging gaps between local and global markets, thereby streamlining trade operations and promoting economic growth. Trading houses play a critical role in international trade. They act as intermediaries, facilitating import/export operations between countries and industries. For instance, Japanese trading houses, known as "sogo shosha," play a key role in global supply chains, linking suppliers in one country with consumers in another. They source raw materials globally, distribute them to manufacturers, and then export the finished goods worldwide. On the domestic front, trading houses streamline wholesale and retail operations, connecting manufacturers with consumers. They bridge the gap between production and consumption, ensuring that goods reach the right place at the right time. In the US, for example, agricultural trading houses play an essential role in moving produce from farms to markets and grocery stores. Trading houses can be classified based on their area of operation. Commodity trading houses, such as Glencore and Cargill, specialize in the trade of physical commodities like grains, oil, metals, and minerals. Financial trading houses, on the other hand, deal with financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives. Industrial trading houses like Mitsubishi Corporation operate across various sectors, including energy, machinery, chemicals, and food. A trading house's operations involve identifying market opportunities, risk management, and transaction facilitation. Trading houses identify potential markets for specific products or services and negotiate deals on behalf of their clients. They manage risks by diversifying their portfolios, insuring against potential losses, and using hedging instruments. They also handle logistics, finance, and other transaction-related tasks. The success of a trading house largely depends on its network and relationships. Trading houses need to build strong relationships with suppliers, buyers, logistics providers, financial institutions, and government agencies. These relationships help them to gain market intelligence, secure deals, manage risks, and navigate regulatory landscapes. International trade is governed by a complex set of laws and regulations, including customs regulations, trade agreements, anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations. Trading houses must comply with these laws to avoid legal troubles and maintain their reputation in the market. The World Trade Organization (WTO) is a key international body overseeing these regulations. Domestic trade also has its legal and regulatory aspects. Trading houses need to secure necessary licenses and permits, comply with domestic trade laws, and regularly report their activities to regulatory bodies. In the US, trading houses are regulated by agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). Price fluctuations in commodities, exchange rates, and interest rates can drastically impact the profitability of trading houses. Dealing with these instabilities necessitates sophisticated risk management strategies, including portfolio diversification and the use of hedging instruments. Tariffs, quotas, and other trade policy shifts can disrupt business operations and create uncertainty. The ongoing trade tensions between the U.S. and China exemplify such disruptions that trading houses have to navigate. As the trading business evolves and becomes more digital, substantial investments are required to upgrade systems and processes. While technology can streamline operations and reduce costs, it can threaten traditional business models. Present significant opportunities due to their rapid economic growth, increasing consumer demand, and market liberalization. Countries like India, China, and Brazil, are increasingly attracting trading houses looking to capitalize on these burgeoning markets. Digitalization, e-commerce, and blockchain technology are revolutionizing trading house operations. Online marketplaces and digital platforms enable trading houses to reach global markets more efficiently, while blockchain technology promises to enhance transparency and efficiency in trade operations. Growing consumer consciousness and stringent regulatory demands for sustainable practices provide opportunities for trading houses to embrace and invest in sustainable practices, thereby contributing to responsible trading. Trading houses are pivotal agents in the global marketplace, facilitating transactions and serving as crucial links in both international and domestic commerce. They connect suppliers, manufacturers, and consumers, while adeptly managing market opportunities and inherent risks. Navigating through intricate regulatory landscapes, they maintain stringent compliance with international and domestic trading laws. Despite facing challenges such as market volatility, trade policy shifts, and technological disruptions, trading houses adapt and thrive. They seize opportunities in emerging markets and harness technological innovations, like digitalization and blockchain. Moreover, their increasing focus on sustainability signals their commitment to responsible trading practices.What Are Trading Houses?
Importance and Role of Trading Houses in Commerce
Trading Houses in International Trade
Trading Houses in Domestic Trade
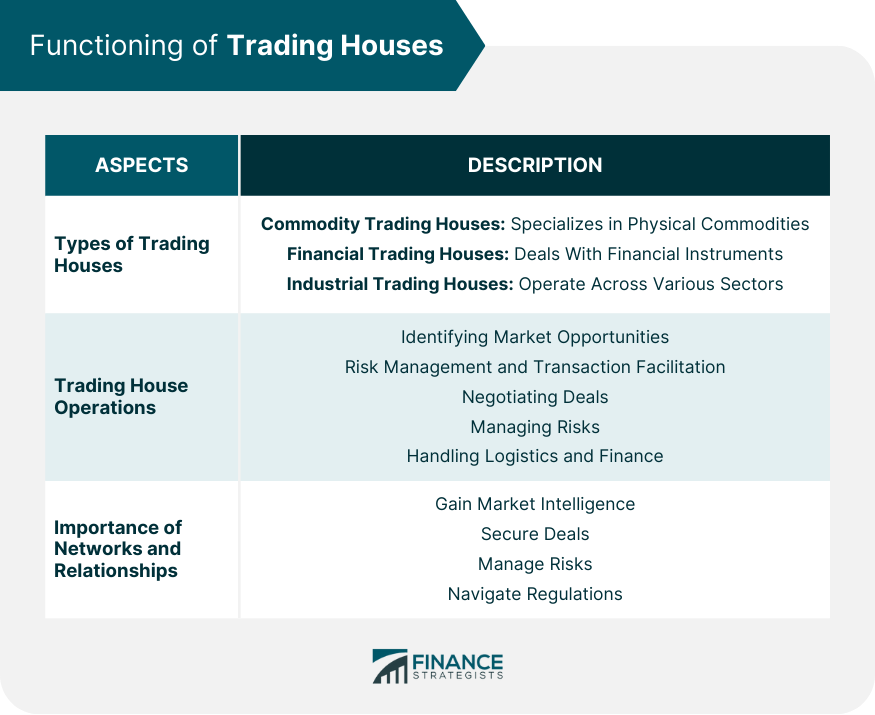
Functioning of Trading Houses
Types of Trading Houses
Trading House Operations
Importance of Networks and Relationships
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Trading Houses
International Trading Laws
Domestic Trading Laws
Risks in the Trading House Business
Market Volatility
Trade Policy Changes
Technological Disruptions
Opportunities in the Trading House Business
Emerging Markets
Technological Innovations
Sustainability

Conclusion
Trading Houses FAQs
A trading house is a business that acts as an intermediary in buying and selling a variety of goods, commodities, and financial instruments. It plays a crucial role in both international and domestic trade by connecting suppliers, manufacturers, and consumers. Through strong networks and relationships, trading houses help bridge gaps between local and global markets.
Trading houses manage market volatility and risk through diversification of their portfolios, insurance against potential losses, and the use of hedging instruments. They also leverage their network and relationships to gain market intelligence and secure deals, further mitigating risks.
Trading houses face challenges such as market volatility, trade policy changes, and technological disruptions. However, they also have opportunities in emerging markets with rapid economic growth and increasing consumer demand. Furthermore, technological innovations like digitalization and blockchain present new avenues for growth and efficiency.
Trading houses are leveraging digitalization and e-commerce to reach global markets. They are using online marketplaces and digital platforms for their operations. Additionally, they are exploring blockchain technology and smart contracts to bring transparency and efficiency to their operations.
As sustainability becomes a key focus area in global trade, trading houses are increasingly embracing sustainable practices. These include investing in renewable energy, adopting fair trade practices, and adhering to regulations and guidelines pertaining to environmental and social issues.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











