Exchange rate risk refers to the potential for loss that arises from fluctuations in the exchange rate between two currencies. This risk arises when an investor or business conducts transactions in a foreign currency or holds assets denominated in a foreign currency. Exchange rate risk is an essential concept in finance and investment, particularly for those who operate in international markets or conduct transactions in foreign currencies. Understanding and managing exchange rate risk is critical to minimizing potential losses and maximizing returns. Exchange rate risk plays a significant role in risk management. Investors and businesses must manage exchange rate risk to protect against potential losses and ensure the stability of their investments and operations. The exchange rate between two currencies represents the value of one currency in terms of the other. Exchange rates are determined by market forces of supply and demand and can be influenced by various economic, political, and social factors. Economic factors that can impact exchange rates include interest rates, inflation rates, and trade balances. Changes in these factors can lead to changes in the demand for a currency, which can impact its value and the exchange rate. Political factors can also impact exchange rates, such as changes in government policies or political instability. These factors can lead to changes in the perception of a country's economic prospects and impact the demand for its currency. Market sentiment, or the overall mood and attitude of investors towards a particular currency, can also impact exchange rates. Positive market sentiment can lead to an increase in demand for a currency, while negative sentiment can lead to a decrease in demand. Transaction risk is the risk that arises from fluctuations in exchange rates between the time a transaction is initiated and the time it is settled. This risk can impact the cost of imports and exports and can lead to potential losses for businesses. Translation risk is the risk that arises from fluctuations in exchange rates when a company has assets or liabilities denominated in a foreign currency. This risk can impact the financial statements of a company and can lead to potential losses. For example, if a US company has a subsidiary in Europe and the euro depreciates against the US dollar, the company's financial statements may show lower profits due to the translation of the subsidiary's financial statements into US dollars. Economic risk is the risk that arises from changes in exchange rates that impact the value of an investment or portfolio. This risk can impact the returns of foreign investments and can lead to potential losses for investors. For example, if a US investor buys shares in a European company and the euro depreciates against the US dollar, the value of the investment in US dollar terms will decrease, leading to potential losses for the investor. Forward contracts are agreements between two parties to exchange a specified amount of currency at a future date and at a fixed exchange rate. By using forward contracts, businesses and investors can lock in an exchange rate and minimize potential losses. For example, a business may use a forward contract to lock in the exchange rate for a future invoice payment to a foreign supplier. This can help the business manage exchange rate risk and ensure predictable costs. Options contracts give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified price at a future date. This provides flexibility and protection against potential losses. For example, an investor may use an options contract to protect against potential losses in a foreign investment due to unfavorable exchange rate movements. If the exchange rate moves in a favorable direction, the investor can choose not to exercise the option and benefit from the movement. Currency swaps involve the exchange of cash flows in different currencies over a specified period. This can help businesses and investors manage exchange rate risk by exchanging fixed-rate cash flows for variable-rate cash flows. For example, a business may enter into a currency swap agreement to exchange fixed-rate interest payments in one currency for variable-rate interest payments in another currency. This can help the business manage exchange rate risk and ensure predictable costs. Diversification involves spreading investments across different currencies and markets to reduce exposure to any single currency or market. This can help investors manage exchange rate risk by diversifying their portfolio and reducing their exposure to any single currency. For example, an investor may hold investments in multiple currencies and markets to spread out their exchange rate risk. Forecasting and analysis can help businesses and investors anticipate potential changes in exchange rates and manage exchange rate risk effectively. By analyzing economic, political, and market factors, businesses and investors can make informed decisions about managing exchange rate risk. For example, an investor may use technical analysis to analyze exchange rate trends and make decisions about when to enter or exit a foreign investment. Exchange rate risk can impact the returns of foreign investments, particularly when the exchange rate changes significantly. This can lead to potential losses for investors. Exchange rate risk can impact the overall risk of a portfolio, particularly when the portfolio includes investments denominated in multiple currencies. Exchange rate risk can impact asset allocation decisions, as investors may need to adjust their portfolio allocations to manage potential risks and maximize returns. Exchange rate risk is a critical concept in finance and investment, with significant implications for businesses and investors operating in international markets. Understanding and managing exchange rate risk is essential for minimizing potential losses and maximizing returns. There are various strategies that businesses and investors can use to manage exchange rate risk, including forward contracts, options contracts, currency swaps, diversification, and forecasting and analysis. It is also essential for investors to consider the potential impact of exchange rate risk on their portfolio risk and asset allocation decisions. Overall, effective management of exchange rate risk is critical for success in the global marketplace.Definition of Exchange Rate Risk
How Exchange Rate Works
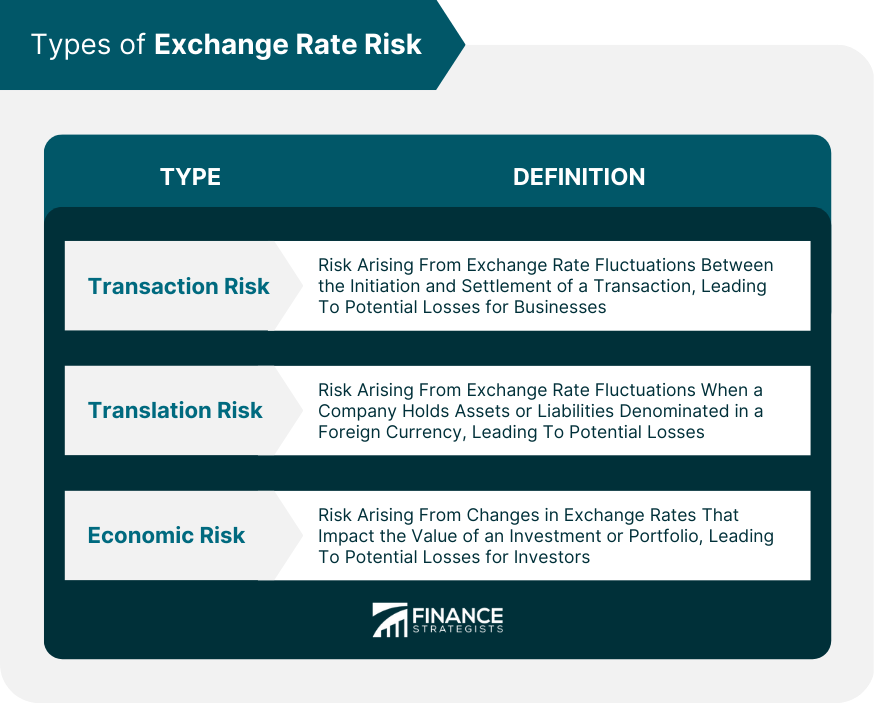
Types of Exchange Rate Risk
Transaction Risk
For example, if a US business buys goods from a supplier in Europe and the exchange rate changes between the time the order is placed and the time the payment is made, the business may end up paying more than expected due to the change in the exchange rate.Translation Risk
Economic Risk
Managing Exchange Rate Risk
Forward Contracts
Options Contracts
Currency Swaps
Diversification
Forecasting and Analysis
Impact of Exchange Rate Risk on Investments
Foreign Investment Returns
Portfolio Risk
Asset Allocation
Conclusion
Exchange Rate Risk FAQs
Exchange rate risk is the potential for an investment's value to be affected by fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
The two main types of exchange rate risk are transaction risk and translation risk. Transaction risk is the risk of losses from a transaction denominated in a foreign currency, while translation risk is the risk of losses from translating financial statements from a foreign currency to the home currency.
Exchange rate risk can be managed through various strategies such as hedging, diversification, netting, and pricing strategies.
Exchange rate risk can impact businesses by affecting their revenues, expenses, and profitability. It can also impact their competitiveness in international markets.
Investors can mitigate the effects of exchange rate risk by investing in hedged funds, investing in domestic stocks, or using currency futures and options to hedge against currency fluctuations.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











