Transaction exposure, also known as transaction risk, refers to the potential risk that businesses face when their financial obligations denominated in foreign currencies fluctuate due to changes in exchange rates. These financial obligations typically stem from international trade and can include payables and receivables, dividends, and loan repayments. Managing transaction exposure is crucial for businesses engaged in international trade. It helps maintain the financial stability of the company by protecting it from unexpected losses due to currency fluctuations. Effective management ensures that the company's profits are not eroded by unfavorable exchange rate movements, thereby aiding in the accurate forecasting of future cash flows and enhancing overall business performance. Contractual exposure arises from contracts entered into by a firm that entail future cash flows denominated in foreign currencies. These include purchase agreements, sales contracts, and loan agreements. This refers to the exposure a firm has to exchange rate fluctuations based on expected future cash flows from foreign transactions, which are not contractually bound yet. Competitive exposure, also known as strategic exposure, arises when exchange rate changes affect the competitive position of the firm in the global market. Translation exposure, also known as accounting exposure, occurs when a firm's financial statements need to be consolidated from foreign currencies to the reporting currency, leading to potential exchange rate risk. Exchange rate fluctuations are a primary cause of transaction exposure. They are influenced by various factors, including inflation rates, interest rates, political instability, economic performance, and speculation. The longer the duration between the initiation of a transaction and its settlement, the greater the transaction exposure. This is due to the increased probability of exchange rate fluctuations within this period. Companies with international operations are naturally exposed to transaction risk due to their dealings in various foreign currencies. This method measures transaction exposure by revaluing the foreign currency contract at current market rates. The difference between the contract value and the market value represents the potential gain or loss. VaR estimates the potential loss in value of a risky asset or portfolio over a defined period for a given confidence interval. This method examines how different values of an independent variable impact a particular dependent variable under a given set of assumptions. Transaction exposure can affect the cash flow of a company due to exchange rate movements. It could lead to an increase or decrease in the cash flow depending on the direction of the exchange rate movement. Changes in exchange rates can affect the profitability of a company. If the domestic currency depreciates against the foreign currency, it could lead to a decrease in profitability. Transaction exposure can affect a company's competitive position. If a firm fails to manage its exposure effectively, it may suffer financial losses, which could adversely affect its competitive position. In risk sharing, the parties involved in a transaction agree to share the risk of exchange rate fluctuations. This involves adjusting the timing of payments or receipts in anticipation of changes in exchange rates. Netting is a method where a company consolidates its receivables and payables from different subsidiaries to reduce multiple currency exposures. Firms can adjust their pricing policies to pass on the exchange rate risk to the customer or absorb it themselves. Matching involves offsetting anticipated inflows and outflows in each foreign currency to minimize exposure. A forward contract is a contractual agreement between two parties to buy or sell a specified amount of a currency at a specified exchange rate on a specified future date. Currency futures are standardized contracts to buy or sell a particular currency at a future date at a price fixed on the purchase date. Currency options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific currency at a specific price within a specified time. Money market hedging involves borrowing or lending a foreign currency amount equal to the present value of the future foreign currency cash flow. Currency swaps involve two parties exchanging specific amounts of different currencies at the outset and repaying over time according to agreed-upon terms. One of the major advantages of using transaction exposure management techniques is the ability to shield a company from sudden and unexpected exchange rate fluctuations. This protection means companies can conduct their international business activities without fearing drastic financial impacts due to fluctuating currencies. The predictability of cash flow is a significant factor in a company's sustainability and growth. Companies can better forecast their future cash flows by managing transaction exposure effectively. This advantage helps in making informed decisions and budget planning. Effective transaction exposure management can provide valuable insights for strategic planning. With an understanding of potential currency risks, companies can develop strategies that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance. This can lead to an optimized business model that can weather global financial challenges. By mitigating the risk of fluctuating exchange rates, companies can improve their overall financial health. When a company's cash flow is stable, it can invest in growth strategies, increase market competitiveness, and ensure long-term profitability. While hedging can be an effective tool for managing transaction exposure, it comes with associated costs. Companies must invest resources to set up and maintain hedging strategies. These costs include premiums for financial instruments like options and forward contracts, as well as the costs of managing these tools effectively. By using hedging techniques to manage transaction exposure, companies might miss out on potential profit opportunities. If exchange rates shift favorably, hedging strategies can prevent companies from fully benefiting from these positive changes. While this is part of the risk management process, it is a notable disadvantage. Implementing and managing transaction exposure techniques require a high level of expertise. The complexity of these methods can be daunting for companies without a specialized finance team. Additionally, poorly executed strategies can lead to ineffective risk management, thereby potentially exacerbating financial risks. This necessitates investment in personnel training or hiring experienced professionals, which can be costly. Transaction exposure plays a significant role in international business, reflecting the risk that arises from fluctuations in exchange rates impacting foreign currency-denominated financial obligations. It's essential to understand its various components, including contractual, non-contractual, competitive, and translation exposures, each with distinct characteristics and implications. These exposures stem from several causes, notably exchange rate variations, the time gap between transaction initiation and settlement, and the very nature of international operations. Accurate measurement of this exposure is vital for effective financial risk management, achieved through methods like Mark-to-Market, Value at Risk (VaR), and Sensitivity Analysis. Recognizing and comprehending these aspects of transaction exposure are crucial steps in managing financial risk and ensuring the resilience of businesses in the dynamic global market.Definition of Transaction Exposure
Components of Transaction Exposure
Contractual Exposure
Non-Contractual Economic Exposure
Competitive Exposure
Translation Exposure
Causes of Transaction Exposure
Fluctuation in Exchange Rates
Time Duration Between Transaction Initiation and Settlement
International Operations
Measurement of Transaction Exposure
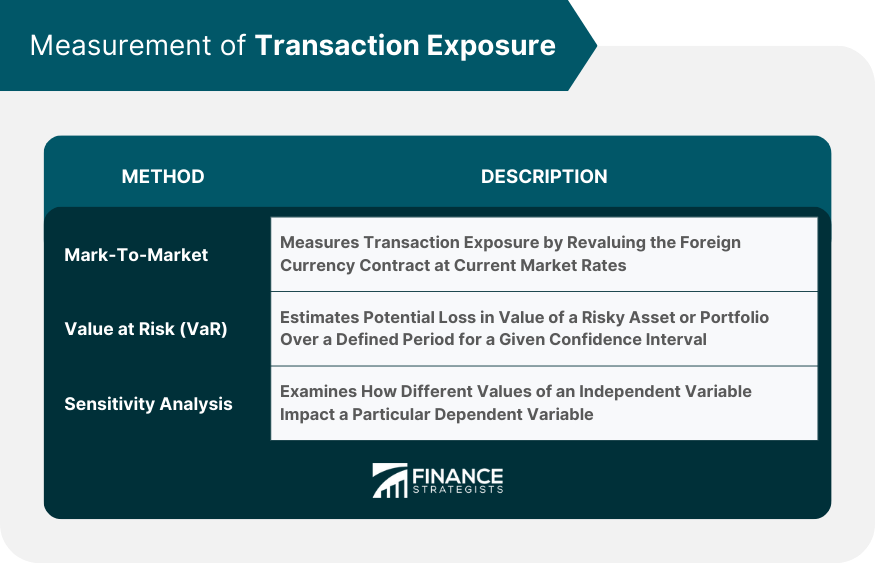
Mark-to-Market Method
Value at Risk (VaR) Method
Sensitivity Analysis Method
Impacts of Transaction Exposure
Impact on Cash Flow
Impact on Profitability
Impact on Competitive Position
Management of Transaction Exposure
Internal Techniques
Risk Sharing
Leading and Lagging
Netting
Pricing Policy
Matching
External Techniques
Forward Contracts
Currency Futures
Currency Options
Money Market Hedging
Currency Swaps
Advantages of Transaction Exposure Management Techniques
Protection From Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Increase in Cash Flow Predictability
Enhanced Strategic Planning
Improvement in Overall Financial Health
Disadvantages of Transaction Exposure Management Techniques
Costs of Hedging Techniques
Missed Profit Opportunities
Expertise and Complexity
Final Thoughts
Transaction Exposure FAQs
Transaction exposure is the risk that businesses face when their financial obligations denominated in foreign currencies fluctuate due to changes in exchange rates.
Managing transaction exposure is crucial for maintaining financial stability, protecting the company from unexpected losses due to currency fluctuations, and enhancing overall business performance.
Techniques include risk sharing, leading and lagging, netting, pricing policy, matching, forward contracts, currency futures, currency options, money market hedging, and currency swap
Future trends include the use of technological advancements like blockchain technology and big data analytics and adaptation to regulatory changes.
Transaction exposure can impact the cash flow, profitability, and competitive position of a company. It can either lead to an increase or decrease in cash flow and profitability, depending on the direction of the exchange rate movement.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











