Unlimited Risk refers to a financial situation in which an investor or trader faces the potential for infinite losses. Unlike scenarios with limited risk where the maximum potential loss is capped and known in advance, in cases with unlimited risk, there's no predetermined maximum loss. This risk often arises in certain trading strategies, such as selling options, short selling, and high-leverage forex trading, where market movements against the investor's position can lead to losses exceeding their initial investment. These losses can continue to accumulate until the investor is able to close out the position, which could potentially result in financial ruin. Furthermore, in the context of an extremely volatile market, such positions can generate losses far more quickly than one might anticipate, leaving little to no time for corrective action. Therefore, it's crucial that investors engaging in high-risk strategies have a solid understanding of the potential implications and have risk management measures in place. Leverage allows investors to control large positions with a relatively small amount of capital. While high leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses, contributing to unlimited risk. If a trade moves in the wrong direction, the loss could exceed the investor's initial capital, leading to a debt to the broker. The risk is particularly high in highly leveraged forex trading or contracts-for-difference (CFDs) where leverage ratios can reach up to 500:1. Short-selling involves selling a borrowed asset with the hope of buying it back at a lower price and pocketing the difference. It carries unlimited risk because there is no cap on how high a stock's price can rise. If the stock price rises significantly, the short-seller may need to buy back the asset at an extremely high price, leading to substantial losses that could exceed the initial investment. Participating in specific forms of derivative trading, like the sale of options, can result in the existence of boundless risk. A prime illustration is an act of selling naked call options, in which the trader, lacking ownership of the underlying asset, becomes vulnerable to the possibility of incurring losses that have the potential to extend infinitely. If the price of the underlying asset skyrockets, the seller of the call options is obligated to provide the asset at the pre-agreed price, potentially leading to massive losses. Market volatility refers to the rate at which the price of an asset increases or decreases. High volatility means the price of an asset can change dramatically in a short time, making potential returns unpredictable. While volatility can offer trading opportunities, it can also expose investors to unlimited risk, especially when combined with high leverage, short-selling, or risky derivative trades. An ineffective risk management strategy can also contribute to unlimited risk. This could involve placing too much capital on a single trade, failing to set stop-loss orders, or not diversifying investments. Without a sound risk management strategy, an unexpected market move could lead to devastating losses that exceed the initial investment. Lack of knowledge and experience is another significant factor contributing to unlimited risk. Novice traders or investors may not fully understand the instruments they are trading or the risks involved. They might also have difficulty interpreting market signals or managing emotions during volatile periods. This can lead to poor decision-making and expose them to unlimited risk. Derivatives are financial contracts whose value derives from an underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies. Engaging in specific derivative trading strategies, like option selling, involves the presence of boundless risk, whereby the trader faces the potential of incurring losses surpassing the initial investment by a significant margin. Short selling stocks involves borrowing shares and selling them in the hope of buying them back at a lower price. However, if the price of the stock rises instead of falling, the short seller may face unlimited losses, as there's no upper limit to how high a stock's price can go. Forex trading, which involves buying and selling currencies, also carries unlimited risk, particularly when using leverage. Fluctuations in exchange rates can lead to substantial losses, exceeding the initial investment. Venture capital and private equity investments also pose an unlimited risk. These investments involve funding startups and private companies, which have a higher risk of failure. If the company fails, the investor could lose their entire investment. Stop-loss orders are a tool that traders can use to limit their losses. This is an order placed with a broker to sell a security when it reaches a specific price. Diversifying investments across different asset classes and sectors can also help mitigate unlimited risk. By spreading investments, the impact of a single failing investment is reduced. Implementing risk management techniques such as adjusting position sizes and employing appropriate leverage is vital in mitigating potential losses. Additionally, it is essential to conduct comprehensive research and analysis prior to engaging in a trade or investment. Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in mitigating unlimited risk. By enforcing rules and regulations, they aim to ensure market integrity and protect investors. The potential for unlimited risk can significantly impact investor behavior. The fear of substantial losses can lead to stress, anxiety, and poor decision-making. Risk tolerance refers to the degree of variability in investment returns that an investor is willing to withstand. Understanding one's risk tolerance is crucial in managing unlimited risk. Stress and anxiety resulting from high-risk scenarios can impair decision-making abilities. It's important to maintain emotional composure and make decisions based on careful analysis rather than fear or greed. Unlimited risk encapsulates situations where potential losses could be infinite, a concept starkly different from limited risk scenarios where the maximum loss is known. This risk often arises from factors such as high leverage, short selling, certain derivative trading activities, and market volatility. These elements, when coupled with poor risk management strategies or lack of experience, can expose investors to a higher degree of vulnerability. Contexts where unlimited risk commonly arises include trading financial derivatives, short-selling stocks, forex trading, and venture capital or private equity investments. These areas, characterized by their inherent unpredictability and complexity, amplify the potential for losses beyond initial investments. Thus, understanding unlimited risk and the contexts in which it arises is crucial for informed decision-making and effective risk management in financial dealings.Definition of Unlimited Risk
Key Factors Contributing to Unlimited Risk
High Leverage
Short Selling
Derivative Trading
Market Volatility
Poor Risk Management Strategies
Lack of Knowledge and Experience

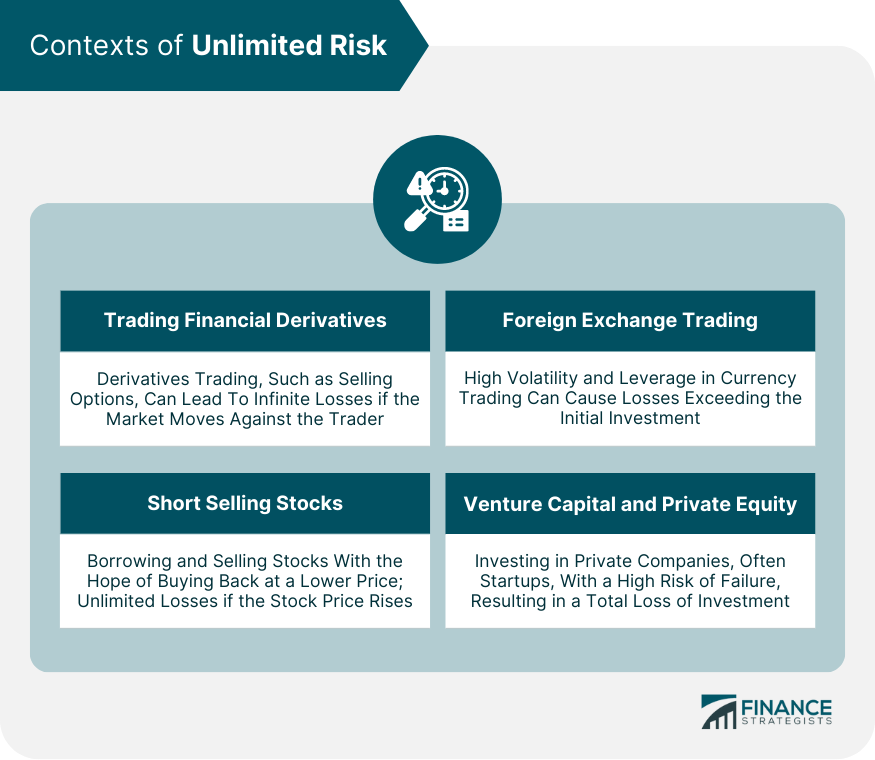
Contexts of Unlimited Risk
Trading Financial Derivatives
Short Selling Stocks
Foreign Exchange (Forex) Trading
Venture Capital and Private Equity Investments
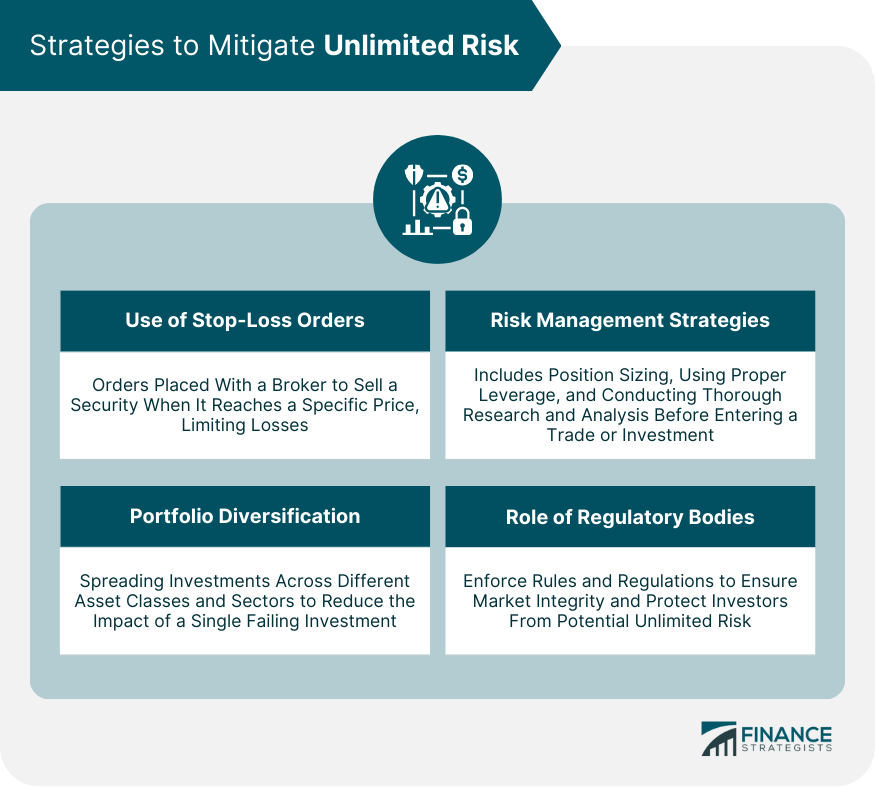
Mitigating Unlimited Risk
Use of Stop-Loss Orders
Portfolio Diversification
Risk Management Strategies
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Psychological Aspect of Unlimited Risk
Impact on Investor Behavior
Concept of Risk Tolerance
Stress and Decision-Making in High-Risk Scenarios
Final Thoughts
Unlimited Risk FAQs
Unlimited risk refers to a financial scenario where potential losses can be infinite, often arising in certain trading strategies or investment scenarios.
Certain types of derivative trading, short selling, forex trading with high leverage, and venture capital or private equity investments can carry unlimited risk.
Unlimited risk can be mitigated through the use of stop-loss orders, portfolio diversification, proper risk management strategies, and adherence to regulations set by financial regulatory bodies.
The potential for unlimited risk can lead to stress and anxiety, which can impact decision-making. Understanding one's risk tolerance and maintaining emotional composure is crucial in managing unlimited risk.
Yes, in certain trading scenarios, such as short selling or trading on margin, losses can exceed the trader's initial investment, potentially leading to debt.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











