Currency swaps are financial derivatives that involve the exchange of principal and interest payments in one currency for equivalent amounts in another currency between two parties. These transactions typically involve the exchange of fixed or floating interest rates and are used for various purposes, such as hedging currency risk, obtaining lower borrowing costs, and accessing new financial markets. Currency swaps are used by businesses, financial institutions, and governments to manage their exposure to fluctuations in currency exchange rates, reduce borrowing costs, and diversify their funding sources. The main participants in currency swap transactions include commercial banks, investment banks, multinational corporations, and central banks. Fixed-for-fixed currency swaps involve the exchange of fixed interest rate payments in one currency for fixed interest rate payments in another currency. Fixed-for-floating currency swaps entail the exchange of fixed interest rate payments in one currency for floating interest rate payments in another currency. Floating-for-floating currency swaps involve the exchange of floating interest rate payments in one currency for floating interest rate payments in another currency. The currency swap agreement process begins with two parties agreeing on the principal amounts, interest rates, and other terms of the swap. The agreement is then documented in a formal contract, usually referred to as a swap confirmation or master agreement. At the start of the swap, the two parties exchange the agreed-upon principal amounts in their respective currencies at the prevailing spot exchange rate. Throughout the life of the swap, the parties exchange interest payments at agreed-upon intervals, typically quarterly or semi-annually. The interest payments are calculated based on the principal amounts and the agreed-upon interest rates. At the end of the swap agreement, the parties re-exchange the original principal amounts at the initial exchange rate, effectively unwinding the transaction. Currency swaps allow businesses and investors to hedge their exposure to fluctuations in currency exchange rates, reducing the risk of adverse currency movements affecting their financial position. By using currency swaps, companies can obtain lower borrowing costs by accessing funds in foreign markets, where interest rates may be more favorable than in their domestic market. Currency swaps enable businesses to access funding in foreign currencies, helping them expand their operations into new markets and diversify their funding sources. Investors can use currency swaps to diversify their portfolios by gaining exposure to foreign currency assets, thereby reducing concentration risk. Counterparty risk refers to the possibility that one party in a currency swap transaction may default on its payment obligations, leading to financial losses for the other party. Interest rate risk arises from changes in market interest rates, which can affect the value of floating-rate payments and lead to fluctuations in the market value of the swap. Exchange rate risk is the potential for losses resulting from adverse movements in currency exchange rates during the life of the swap. Liquidity risk refers to the risk that a party may be unable to find a counterparty to unwind or offset a currency swap position, potentially leading to financial losses. The pricing of currency swaps is influenced by various factors, including interest rate differentials between the two currencies, credit risk of the counterparties, and market liquidity. The valuation of currency swaps typically involves the use of present value calculations, where the future cash flows of the swap are discounted to determine the current market value. Various models, such as the Black-Scholes model and the Heath-Jarrow-Morton model, can be used to estimate the fair value of a currency swap. Central banks often engage in currency swap agreements with other central banks to provide liquidity and stabilize financial markets during times of stress or crisis. These arrangements can help to prevent contagion and maintain financial stability. Currency swaps play a vital role in international trade and investment by allowing businesses to manage their currency risks, access foreign funding, and hedge their exposure to fluctuations in exchange rates. Currency swaps can influence foreign exchange markets by affecting the supply and demand for the currencies involved in the transaction. Large-scale currency swap transactions can lead to changes in exchange rates and affect the relative value of currencies. Currency swaps are subject to regulation and oversight by various authorities, such as central banks, securities regulators, and financial market supervisors. These regulators aim to ensure the stability and integrity of currency swap markets and protect market participants from undue risk. Market participants involved in currency swap transactions may be subject to reporting and disclosure requirements, depending on the jurisdiction and the specific regulations in place. These requirements can include transaction reporting, position limits, and margin requirements, among others. Currency swaps play a crucial role in global finance by enabling businesses, investors, and governments to manage their currency risks, access foreign funding, and diversify their financial exposures. They also play a significant role in international trade, investment, and central bank operations. While currency swaps offer numerous benefits, they also involve various risks, such as counterparty risk, interest rate risk, exchange rate risk, and liquidity risk. It is essential for market participants to understand and manage these risks effectively to maximize the benefits of currency swap transactions. The currency swap market continues to evolve, driven by changes in technology, regulation, and market dynamics. As the landscape changes, market participants need to stay informed and adapt to new developments to capitalize on the opportunities and mitigate the risks associated with currency swaps.What Are Currency Swaps?
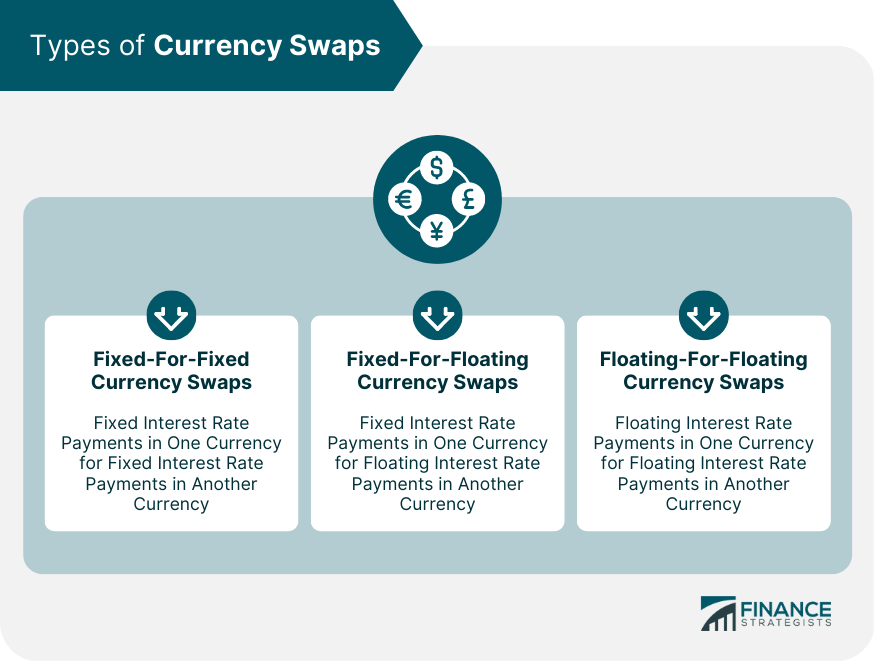
Types of Currency Swaps
Fixed-For-Fixed Currency Swaps
Fixed-For-Floating Currency Swaps
Floating-For-Floating Currency Swaps
Mechanics of Currency Swaps
Initiation of Swap Agreement
Exchange of Principal Amounts
Exchange of Interest Payments
Termination of Swap Agreement
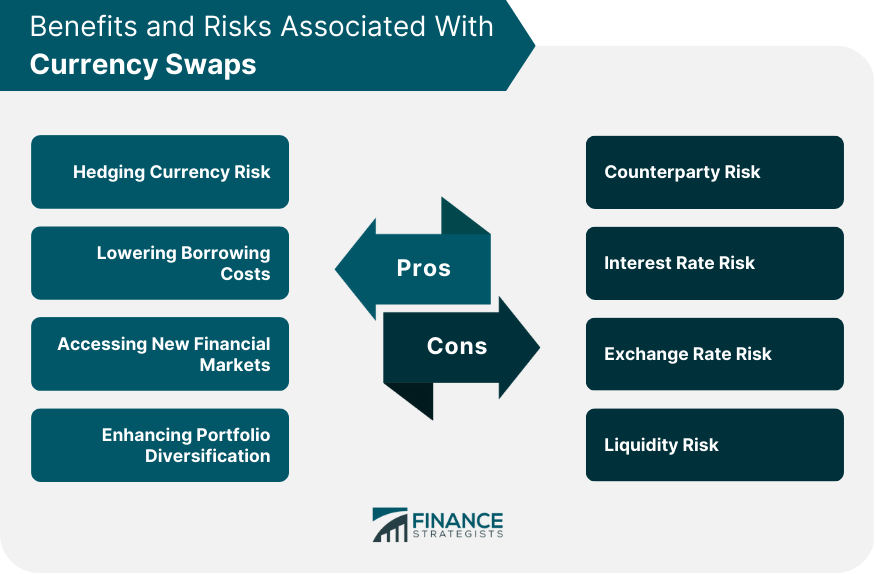
Benefits of Currency Swaps
Hedging Currency Risk
Lowering Borrowing Costs
Accessing New Financial Markets
Enhancing Portfolio Diversification
Risks Associated With Currency Swaps
Counterparty Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Exchange Rate Risk
Liquidity Risk
Pricing and Valuation of Currency Swaps
Factors Affecting Currency Swap Pricing
Valuation Methodologies
Role of Currency Swaps in International Finance
Central Banks and Currency Swaps
Use in International Trade and Investment
Impact on Foreign Exchange Markets
Regulation and Oversight of Currency Swaps
Regulatory Authorities
Reporting and Disclosure Requirements
Conclusion
Importance of Currency Swaps in Global Finance
Balancing Benefits and Risks
The Evolving Landscape of Currency Swaps
Currency Swaps FAQs
A currency swap is a financial instrument that allows two parties to exchange a set amount of one currency for another at an agreed-upon exchange rate. Currency swaps are often used to hedge against currency risk, as they allow parties to access foreign currency without having to purchase it directly.
Currency swaps are primarily used by corporations, banks, and institutional investors to hedge against currency risk or to access foreign currency at a more favorable rate than they could obtain in the open market. Governments may also use currency swaps as part of their international economic policies.
In a currency swap, two parties agree to exchange a set amount of one currency for another at an agreed-upon exchange rate. The parties then agree to exchange the currencies back at a later date, typically at the same exchange rate. The exchange rate is determined by the prevailing market rate at the time of the swap.
The primary benefit of a currency swap is that it allows parties to access foreign currency without having to purchase it directly, which can be costly and may expose them to currency risk. Currency swaps can also be used to obtain financing at a more favorable rate than would be available in the open market.
Like any financial instrument, currency swaps carry risks. The primary risk associated with currency swaps is the risk that the counterparty may default on the swap, leaving one party exposed to currency risk. Additionally, currency swaps may be subject to fluctuations in exchange rates, which can impact the value of the swap.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











