Investing in commodities involves buying or trading raw materials like gold, oil, and agricultural products. Commodities can provide diversification to your portfolio and act as a hedge against inflation, but they also come with risks such as price volatility. There are several ways to invest in commodities, including buying physical commodities, investing in futures contracts, or investing in commodity-related stocks or ETFs. Before investing, it's essential to research and analyze the market thoroughly. There are various types of commodities, which can be broadly categorized into energy, metals, and agricultural commodities. Energy commodities are crucial for powering the world's economies and are traded on a global scale. Crude Oil: Crude oil is the most widely traded energy commodity, and its prices significantly influence global economic activity Natural Gas: generation, heating, and cooking Coal: Although facing a decline due to environmental concerns, coal is still an important commodity for electricity generation in several countries Uranium: Uranium is a key commodity for nuclear power generation Metals are categorized into precious metals and base metals. Precious metals are valued for their rarity and include gold, silver, platinum, and palladium. Gold: considered a safe-haven investment and is often used as a hedge against inflation and currency fluctuations Silver: has both industrial and investment demands, making it a popular choice among investors Platinum: used in various industries, including automotive, jewelry, and electronics Palladium: primarily used in the automotive industry for catalytic converters Base metals are widely used in construction, manufacturing, and other industries. Copper: essential for electrical wiring, plumbing, and electronics manufacturing Aluminum: used in the transportation, construction, and packaging industries Zinc: is primarily used for galvanizing steel and in the production of brass and bronze Nickel: used in the production of stainless steel and various other alloys Agricultural commodities include grains, soft commodities, and livestock. Grains are essential food commodities and include corn, wheat, and soybeans. Corn: used for food, animal feed, and ethanol production Wheat: a staple food commodity used in the production of bread, pasta, and other food items Soybeans: used for food, animal feed, and as a source of vegetable oil Soft commodities are primarily agricultural products that are not grains or livestock. Sugar: a widely traded soft commodity used for food and beverage production Cotton: an essential commodity for the textile industry Coffee: one of the most popular beverages worldwide and is an important traded commodity Cocoa: the primary ingredient in chocolate production Livestock commodities include cattle, hogs, and poultry. Cattle: are raised for meat and dairy production Hogs: are raised for pork production Poultry: including chickens and turkeys, is raised for meat and egg production Commodity markets facilitate the buying and selling of commodities through standardized contracts. Major commodity exchanges include the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), London Metal Exchange (LME), and New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). Various participants engage in commodity trading, including producers, consumers, speculators, and regulators. Producers are companies that extract or produce commodities, such as miners, farmers, and oil companies. Consumers are companies or individuals that use commodities as inputs for their businesses or for personal consumption. Speculators are traders who buy and sell commodities to profit from price fluctuations. Regulators oversee the commodity markets to ensure fair trading practices and maintain market stability. Investors can gain exposure to commodities through direct and indirect investment methods. Direct investment involves owning the physical commodity or participating in the futures market. Investors can buy and store physical commodities, such as gold bars or bags of coffee beans. Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell a specific commodity at a predetermined price and date. Futures contracts allow investors to lock in a price for a commodity today for delivery at a future date. Investors must maintain a minimum amount of capital, called margin, in their accounts to participate in futures trading. Futures trading involves risks, such as leverage and price volatility, but also offers potential benefits, such as hedging and speculation opportunities. Indirect investment methods include investing in commodity stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), exchange-traded notes (ETNs), and mutual funds. Investors can gain exposure to commodities by investing in the stocks of companies that produce or consume commodities. For example, mining and energy companies extract and produce commodities like oil, gold, and copper. Meanwhile, agricultural firms are involved in the production and processing of agricultural commodities, such as grains and livestock. ETFs and ETNs provide investors with exposure to commodities through diversified and liquid investment vehicles. Commodity-Focused ETFs track the performance of a single commodity, such as gold or oil. Commodity index ETFs track the performance of a basket of commodities, providing diversified exposure. Investing in ETFs and ETNs involves risks, such as counterparty risk and tracking errors, but also offers benefits, like liquidity and diversification. Mutual funds provide investors with exposure to commodities through actively managed investment strategies. Commodity-Focused Mutual Funds invest primarily in commodities or commodity-related securities. Diversified commodity funds invest in a broad range of commodities and related assets to provide a balanced exposure. Various factors influence commodity prices, including supply and demand, geopolitical events, macroeconomic factors, weather, and government policies. Production levels, consumption patterns, and inventory levels affect commodity prices. Geopolitical events, such as wars and political instability, can disrupt commodity supplies and influence prices. Macroeconomic factors, such as inflation, interest rates, and currency fluctuations, can impact the demand for and prices of commodities. Commodities often serve as a hedge against inflation, as their prices tend to rise when the value of money decreases. Changes in interest rates can affect the cost of borrowing and investment in commodities. Currency fluctuations can influence the prices of commodities, as they are often priced in US dollars. Weather patterns and natural disasters, such as droughts, hurricanes, and earthquakes, can significantly impact the production and transportation of commodities, affecting prices. Government policies, such as subsidies, tariffs, and environmental regulations, can influence commodity production and prices. Investing in commodities can provide portfolio diversification, as they often have low correlations with traditional asset classes, such as stocks and bonds. Commodities can serve as a hedge against inflation, protecting the purchasing power of investors' capital. Commodities can offer potentially high returns due to their inherent volatility and the potential for significant price movements. Investing in commodities provides exposure to emerging markets and growing industries, such as renewable energy and electric vehicles. Commodity prices can be highly volatile, influenced by factors such as weather, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. The use of leverage in futures trading can amplify gains but also magnify losses. Political instability and changes in regulations can impact commodity prices and the performance of commodity-related investments. Indirect investments, such as ETFs and ETNs, involve counterparty risk, as investors rely on the financial stability of the issuing institutions. Successful commodity investing requires a combination of fundamental analysis, technical analysis, portfolio diversification, and risk management. Fundamental analysis involves evaluating supply and demand factors and macroeconomic indicators to determine the fair value of a commodity. Analyzing production levels, consumption patterns, and inventory data can help investors predict price trends. Monitoring macroeconomic indicators, such as inflation, interest rates, and currency fluctuations, can provide insight into the potential impact on commodity prices. Technical analysis involves studying price charts and using indicators and oscillators to identify trends and potential trading opportunities. Chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles, can provide clues about future price movements. Indicators and oscillators, such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and stochastic oscillators, can help identify trends and overbought or oversold conditions. Investors should allocate a portion of their portfolio to commodities to achieve diversification and reduce overall portfolio risk. Effective risk management involves position sizing and the use of stop-loss orders. Investors should determine the appropriate size of their commodity positions based on their risk tolerance and overall portfolio size. Stop-loss orders can help limit losses by automatically closing a position if the commodity price reaches a predetermined level. Newcomers to commodity investing should remember these tips to enhance their chances of success and reduce potential risks. Before investing in commodities, it is essential to understand the basics of commodity markets, trading, and various investment vehicles. Reading books, articles, and attending webinars or seminars can help build a strong foundation. Consider your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and available capital when choosing the appropriate investment vehicle, such as futures contracts, ETFs, or mutual funds. Establish a trading plan that outlines your investment goals, risk tolerance, preferred strategies, and risk management techniques. Stick to your trading plan and maintain discipline in your trading decisions. Avoid emotional decision-making, as it can lead to impulsive trades and increased risk. Stay updated on the latest news and developments that can impact commodity prices, such as geopolitical events, weather, and changes in government policies. Regularly review your commodity investments and make adjustments as needed to maintain your desired level of diversification and risk exposure. If you are unsure about your investment decisions or need assistance developing a trading plan, consider consulting with a commodity trading or financial advisor. As with any investment, learning from your successes and failures is essential for growth and improvement. Reflect on your trades, identify areas for improvement, and apply those lessons to future investments. Even experienced investors can make mistakes when investing in commodities. Being aware of these common pitfalls can help you minimize risk and improve your overall investment performance. Overtrading, or executing too many trades in a short period, can result in increased transaction costs and decrease your overall returns. It's essential to maintain discipline and adhere to your trading plan. Investing a large portion of your portfolio in a single commodity can expose you to significant risk. Maintain diversification by spreading your investments across different commodities and investment vehicles. Focusing solely on technical analysis without considering the underlying fundamentals can lead to poor investment decisions. Keep an eye on supply and demand dynamics, macroeconomic factors, and geopolitical events that may affect commodity prices. Not implementing risk management techniques, such as position sizing and stop-loss orders, can lead to substantial losses. Always consider your risk tolerance and use appropriate strategies to protect your capital. Jumping on trends without proper analysis can result in buying high and selling low. Be patient and wait for suitable entry points based on your analysis before entering a trade. Allowing emotions to drive your investment decisions can lead to impulsive trades and poor risk management. Practice emotional control and make decisions based on rational analysis. Failing to keep detailed records of your trades can make tracking your performance and learning from your mistakes difficult. Maintain a trading journal to record your trades, strategies, and outcomes. Commodity investing can be a valuable addition to any investor's portfolio, providing exposure to a diverse range of assets with potential benefits like portfolio diversification, inflation hedging, and the potential for high returns. However, it is important to understand the risks involved, such as price volatility, leverage, and counterparty risk, and to develop a solid trading plan that includes effective risk management strategies. Investors should also stay informed about the factors that impact commodity prices and monitor their investments regularly to ensure they are achieving their investment objectives. By following the tips provided in this article and avoiding common mistakes, investors can enhance their chances of success and enjoy the potential rewards that commodity investing can offer. Remember, commodity investing requires patience, discipline, and a commitment to continuous learning and improvement. With the right approach and strategies, investors can capitalize on the opportunities that this exciting and dynamic asset class provides.Overview of Investing in Commodities
Types of Commodities to Invest In
Energy Commodities
Metals
Precious Metals
Base Metals
Agricultural Commodities
Grains
Soft Commodities
Livestock
Commodity Markets and Exchanges to Invest In
Commodity Market Participants
Producers
Consumers
Speculators
Regulators
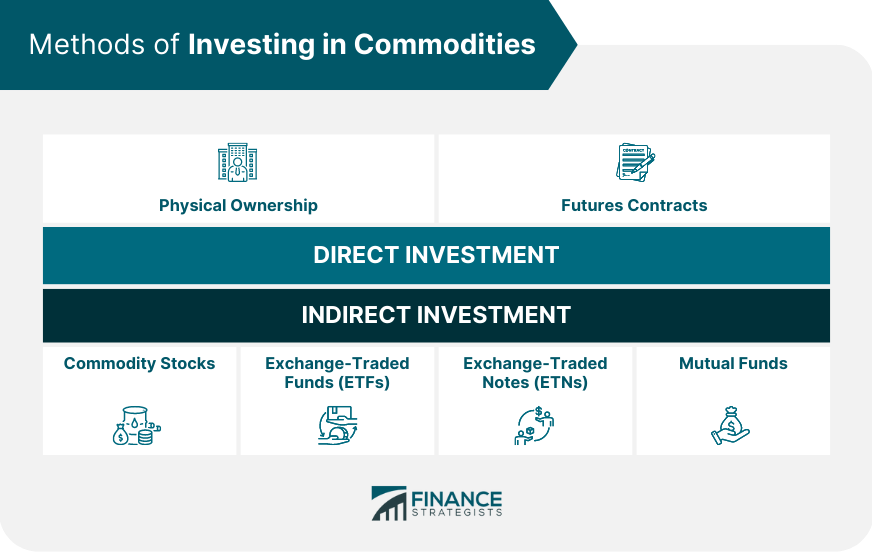
Methods of Investing in Commodities
Direct Investment
Physical Ownership
Futures Contracts
Indirect Investment
Commodity Stocks
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and Exchange-Traded Notes (ETNs)
Mutual Funds
Factors Affecting Commodity Prices
Supply and Demand
Geopolitical Events
Macroeconomic Factors
Inflation
Interest Rates
Currency Fluctuations
Weather and Natural Disasters
Government Policies and Regulations
Benefits of Investing in Commodities
Diversification
Inflation Hedge
Potential for High Returns
Access to Growing Markets
Risks of Investing in Commodities
Volatility
Leverage
Political and Regulatory Risks
Counterparty Risk

Strategies for Successful Investing in Commodities
Fundamental Analysis
Supply and Demand Analysis
Macroeconomic Indicators
Technical Analysis
Chart Patterns
Indicators and Oscillators
Portfolio Diversification and Asset Allocation
Risk Management
Position Sizing
Stop-Loss Orders
Tips for Successful Investing in Commodities
Start With Education
Choose the Right Investment Vehicle
Develop a Trading Plan
Use a Disciplined Approach
Stay Informed
Monitor Your Portfolio Regularly
Seek Professional Advice
Learn From Experience
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Investing in Commodities
Overtrading
Overexposure to a Single Commodity
Ignoring the Fundamentals
Failing to Manage Risk
Chasing Trends
Lack of Emotional Control
Inadequate Record-Keeping
Conclusion
Investing in Commodities FAQs
Commodities are raw materials or primary products that are used in the production of goods and services. Investing in commodities can provide diversification to your portfolio and can act as a hedge against inflation.
There are several ways to invest in commodities, including buying physical commodities such as gold or silver, investing in commodity futures or options contracts, investing in commodity-related stocks or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and investing in commodity mutual funds.
Investing in commodities can be risky, as commodity prices can be volatile and subject to fluctuations based on supply and demand factors, geopolitical events, and other economic factors. Additionally, some commodity investments may involve high fees and expenses.
Commonly traded commodities include precious metals such as gold and silver, energy commodities such as oil and natural gas, agricultural commodities such as wheat and corn, and industrial metals such as copper and aluminum.
To research and analyze commodity investments, you can utilize a variety of resources, including financial news websites, market research reports, commodity-specific industry publications, and expert opinions from financial advisors and analysts. It's important to conduct thorough research and analysis before making any investment decisions.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











