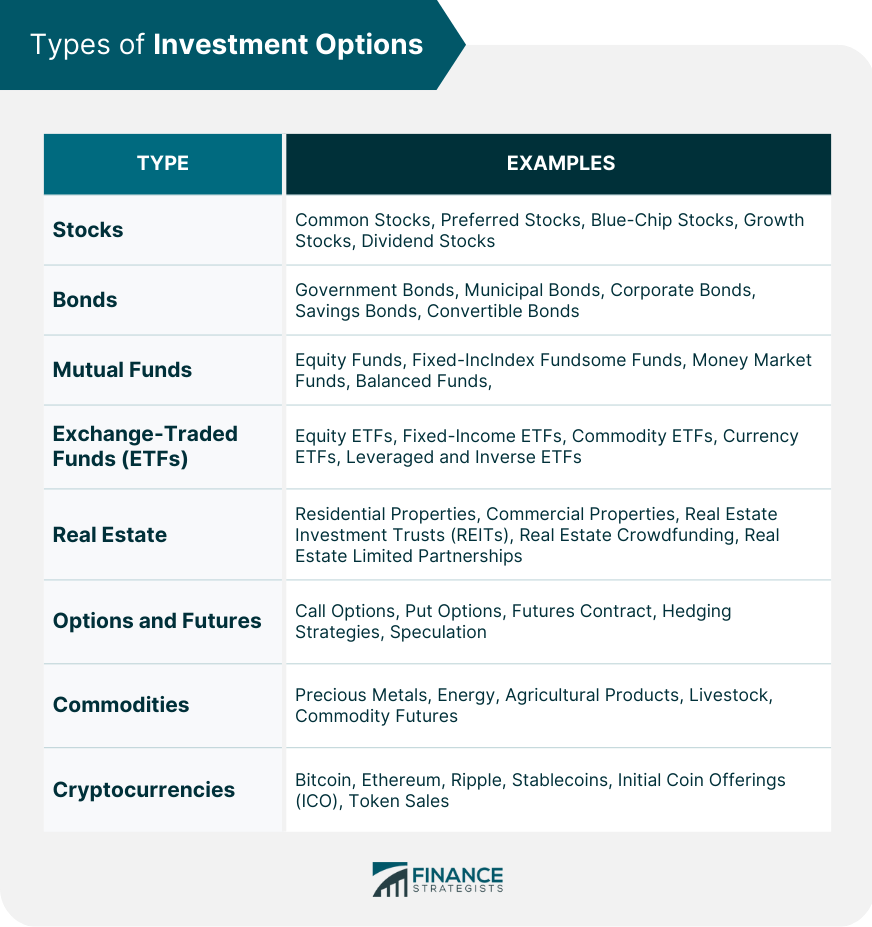
Investment options are financial assets that individuals or institutions can invest in to generate returns. These can include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, and more. Investing is the process of allocating resources, often money, with the expectation of generating a profit or income over time. Investments play a crucial role in financial growth by allowing individuals and businesses to achieve their financial goals and create wealth. Before diving into specific investment options, it's essential to understand the factors that influence investment decisions. These include: Risk tolerance is an individual's ability to withstand potential losses on an investment. It's essential to assess your risk tolerance before investing, as it helps determine which investment options are best suited for you. Your investment goals determine your investment strategy. For example, if your goal is to accumulate funds for retirement, you'll likely choose long-term, relatively low-risk investments. The time horizon refers to the period you plan to hold an investment before needing to access the funds. Shorter time horizons may require more conservative investments, while longer time horizons may allow for greater risk-taking. Diversification involves investing in a mix of assets to spread risk and reduce potential losses. A well-diversified portfolio can help mitigate the impact of poor-performing investments. Liquidity is the ease with which an investment can be converted to cash. Investments with higher liquidity are generally more accessible and can be sold quickly when needed. Taxes can significantly affect your investment returns. It's crucial to consider the tax implications of your investment choices and seek professional advice when needed. Numerous investment options are available, each with its own set of risks and rewards. Understanding these options can help you build a diversified and tailored investment portfolio. Stocks, or shares, represent partial ownership in a company. They are often categorized based on their characteristics, such as: Common stocks are the most common type of stock and provide shareholders with voting rights and dividends. Preferred stocks pay fixed dividends and have priority over common stocks in dividend payments and asset distribution in case of liquidation. Blue-chip stocks are shares of large, well-established, and financially stable companies with a history of consistent dividends. Growth stocks are shares of companies with high potential for revenue and earnings growth but may not pay dividends. Dividend stocks are shares of companies with a consistent history of paying dividends, providing steady income to shareholders. Bonds are debt securities governments, municipalities, or corporations issued to raise capital. They typically pay periodic interest and return the principal upon maturity. Types of bonds include: National governments issue government bonds and are generally considered low-risk investments. Local governments or agencies issue municipal bonds to fund public projects and are usually exempt from federal taxes. Companies issue corporate bonds to raise capital for business purposes and carry varying degrees of risk depending on the issuer's creditworthiness. Savings bonds are low-risk, government-issued bonds that pay interest over a fixed term and are often used for long-term savings goals. Convertible bonds can be converted into a predetermined number of common shares, allowing investors to participate in the potential appreciation of the underlying stock. Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. There are several types of mutual funds, including: Equity funds invest primarily in stocks, aiming to achieve long-term capital appreciation. Fixed-income funds invest in bonds and other debt securities, focusing on generating regular income for investors. Money market funds invest in short-term, high-quality debt securities and are considered a low-risk investment option. Balanced funds invest in a mix of stocks and bonds, seeking to balance growth potential and income generation. Index funds track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500, and aim to replicate its performance. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are investment funds traded on stock exchanges, similar to stocks. They offer diversification and can be bought or sold throughout the trading day. Types of ETFs include: Equity ETFs invest in stocks and may track a specific market index, sector, or investment style. Fixed-income ETFs invest in bonds and other debt securities, aiming to provide regular income and capital preservation. Commodity ETFs invest in commodities, such as precious metals, energy, or agricultural products. Currency ETFs invest in foreign currencies, allowing investors to gain exposure to global currency markets. Leveraged ETFs aim to provide a multiple of the daily return of an underlying index, while inverse ETFs seek to deliver the opposite of the index's daily return. Real estate investments involve purchasing property to generate income or capital appreciation. Real estate investment options include: Residential properties like single-family homes or apartments can generate rental income and potential capital appreciation. Commercial properties, including office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial properties, offer income and appreciation potential. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are companies that own, operate or finance income-generating real estate properties. Investors can buy shares in REITs, providing exposure to the real estate market. Real estate crowdfunding platforms allow investors to pool funds to invest in property development or ownership projects. Real estate limited partnerships involve a general partner managing a property portfolio and limited partners providing capital. Options and futures are financial contracts that allow investors to speculate on or hedge against price movements in various assets. These include: Call options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a specified price before a certain date. Put options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a specified price before a certain date. Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specified future date. Hedging strategies involve using options or futures to offset potential losses from other investments. Speculation involves using options and futures to profit from anticipated price movements in an underlying asset. Commodities are physical goods, such as metals, energy, or agricultural products. Investors can gain exposure to commodities through various methods, including: Investors can invest in precious metals, such as gold or silver, through physical ownership, ETFs, or mining company stocks. Investing in energy commodities, such as oil or natural gas, can be done through futures contracts, ETFs, or stocks of energy companies. Agricultural products, such as crops or livestock, can be invested in through futures contracts, ETFs, or stocks of agribusiness companies. Livestock investments involve exposure to the price movements of animals, such as cattle or hogs, which can be accessed through futures contracts or agribusiness stocks. Commodity futures allow investors to speculate on or hedge against price movements in various commodities without directly owning the physical goods. Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security and operate on decentralized networks. Some popular cryptocurrencies and related investment options include: Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, which can be bought, sold, or held as a long-term investment. Ethereum is a decentralized platform that enables smart contracts and has its native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), which can be invested in. Ripple is a cryptocurrency and digital payment network designed to facilitate cross-border transactions, and its native currency is XRP. Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to a stable asset, such as a fiat currency, to minimize price volatility. Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and token sales involve raising funds for new cryptocurrency projects by issuing and selling digital tokens to investors. Investment options tailored for retirement savings often provide tax advantages and long-term growth potential. These include: Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) are tax-advantaged accounts that allow individuals to save for retirement. Types of IRAs include: Contributions to a traditional IRA may be tax-deductible, and earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal in retirement. Roth IRA contributions are made with after-tax dollars, but qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free. A rollover IRA allows individuals to transfer assets from a previous employer-sponsored retirement plan into an IRA. A Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA is designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners to save for retirement. A Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE) IRA is a retirement plan designed for small businesses to provide employees with retirement savings options. Employer-sponsored retirement plans are tax-advantaged savings plans provided by employers. Some common types include: A 401(k) plan allows employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income to a retirement account, often with employer-matching contributions. A 403(b) plan is similar to a 401(k) but is designed for employees of non-profit organizations, public schools, and certain religious institutions. A 457(b) plan is a non-qualified deferred compensation plan for certain state and local government employees and non-governmental tax-exempt organizations. A Thrift Savings Plan (TSP) is a retirement savings plan for federal employees and members of the uniformed services. Profit-sharing plans allow employers to contribute a portion of company profits to employees' retirement accounts. Annuities are insurance products that provide a stream of income in exchange for an upfront premium payment. Types of annuities include: Immediate annuities begin paying income shortly after the premium is paid, providing immediate income to the annuitant. Deferred annuities accumulate earnings until a specified date, at which point the annuity begins paying income. Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed fixed income, regardless of market conditions. Variable annuities offer income that varies based on the performance of the underlying investments. Indexed annuities tie their returns to a market index, providing potential for higher returns while still offering some protection against market downturns. In conclusion, investment options are financial assets that individuals or institutions can invest in to generate returns. Investing plays a crucial role in financial growth by allowing individuals and businesses to achieve their financial goals and create wealth. Before choosing among various investment options, it's essential to consider factors such as risk tolerance, investment goals, time horizon, diversification, liquidity, and tax considerations. There are numerous investment options available, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, options and futures, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Retirement investment options are tailored for retirement savings and often provide tax advantages and long-term growth potential. These include individual retirement accounts (IRAs), employer-sponsored retirement plans, profit-sharing plans, and annuities. By understanding the various investment options and factors to consider, individuals can build a diversified and tailored investment portfolio that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance.What Are Investment Options?
Factors to Consider Before Choosing an Investment Option
Risk Tolerance
Investment Goals
Time Horizon
Diversification
Liquidity
Tax Considerations

Types of Investment Options
Stocks
Common Stocks
Preferred Stocks
Blue-Chip Stocks
Growth Stocks
Dividend Stocks
Bonds
Government Bonds
Municipal Bonds
Corporate Bonds
Savings Bonds
Convertible Bonds
Mutual Funds
Equity Funds
Fixed-Income Funds
Money Market Funds
Balanced Funds
Index Funds
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Equity ETFs
Fixed-Income ETFs
Commodity ETFs
Currency ETFs
Leveraged and Inverse ETFs
Real Estate
Residential Properties
Commercial Properties
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Real Estate Crowdfunding
Real Estate Limited Partnerships
Options and Futures
Call Options
Put Options
Futures Contracts
Hedging Strategies
Speculation
Commodities
Precious Metals
Energy
Agricultural Products
Livestock
Commodity Futures
Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin
Ethereum
Ripple
Stablecoins
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Token Sales
Retirement Investment Options
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Traditional IRA
Roth IRA
Rollover IRA
SEP IRA
SIMPLE IRA
Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans
401(k)
403(b)
457(b)
Thrift Savings Plan (TSP)
Profit-Sharing Plans
Annuities
Immediate Annuities
Deferred Annuities
Fixed Annuities
Variable Annuities
Indexed Annuities
Conclusion
Investment Options FAQs
Investment options refer to various types of financial assets that individuals or institutions can invest in to generate returns on their investments. These assets include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, commodities, etc.
The most popular investment options include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate. Each investment option has unique characteristics, risks, and potential rewards.
When choosing investment options, you should consider factors such as your investment goals, risk tolerance, investment time horizon, and liquidity needs. You should also thoroughly research the investment options and seek professional advice before making investment decisions.
Yes, some low-risk investment options include savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and government bonds. These investments offer lower returns but have a lower risk of loss of principal.
Yes, it is generally advisable to diversify your investment portfolio by investing in multiple investment options. This can help reduce your overall risk and potentially increase your returns. However, you should ensure that you have a well-thought-out investment strategy and do not over-diversify.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











