Alternative mutual funds are a type of publicly offered, SEC-registered mutual fund that uses non-traditional investments or complex investment and trading strategies to achieve their investment objectives. These funds have gained popularity among investors as they provide access to a wider range of investments and offer potential benefits such as diversification and higher returns. Alternative mutual funds differ from traditional mutual funds in several ways. Traditional mutual funds typically invest in a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash, while alternative mutual funds invest in non-traditional assets such as real estate, commodities, or startup companies. Additionally, alternative mutual funds use more complex investment strategies, such as derivatives and short-selling, than traditional mutual funds. Alternative mutual funds have unique characteristics that differentiate them from traditional mutual funds. The key characteristics of alternative mutual funds include: Alternative mutual funds aim to fulfill different investment requirements with diverse investment objectives. Some funds strive to lessen investment value fluctuations and risks through diversification across various assets or via complicated trading strategies. Meanwhile, other funds aim to generate better-than-market returns compared to similar mutual funds. Alternative mutual funds aim to achieve their investment goals by investing in non-traditional assets, which traditional mutual funds do not invest in. Non-traditional assets may include global real estate, start-up companies, or commodities such as gold or oil. Although these investments may provide diversification or different returns compared to traditional investments, they may also carry additional risks. Alternative mutual funds tend to employ complex investment and trading strategies that go beyond traditional mutual funds. They may use techniques such as selling stocks short, derivatives, or following "absolute return" or “market neutral” strategies that aim to generate positive returns even when stock markets decline. Nevertheless, these methods may entail greater risks and costs than those of traditionally managed funds. Alternative mutual funds often have higher risk and return characteristics than traditional mutual funds. The higher risk associated with alternative mutual funds is due to their investments in non-traditional assets and their use of complex investment strategies. The potential higher return of alternative mutual funds is also due to their investments in non-traditional assets that may have higher potential returns. Alternative mutual funds are required to disclose their holdings and investment strategies, just like traditional mutual funds. This provides investors with transparency and helps them to understand the risks and potential rewards associated with investing in the fund. Alternative mutual funds can be less liquid than traditional mutual funds due to their investments in illiquid assets such as private equity or real estate. This can make it difficult for investors to sell their shares quickly. Alternative mutual funds generally have higher expenses than traditional mutual funds due to their use of more complex investment strategies and the need for specialized management. These higher expenses can eat into potential returns for investors. Investing in alternative mutual funds requires a different process than investing in traditional mutual funds. The first step in investing in alternative mutual funds is to select a fund that meets your investment objectives. Investors should research the various alternative mutual funds available and choose a fund that aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance. They should also review the prospectus of the funds and annual reports to understand the investment objectives, strategies, and fees of the funds. Once an investor has selected a fund, they need to open an account with the investment advisor of the funds. The investment advisor will provide the necessary paperwork to open an account, typically including an application and investment agreement. It is common for alternative mutual funds to have higher minimum investment requirements than traditional mutual funds due to their higher expenses and the need for specialized management. However, the exact minimum investment required for alternative mutual funds can vary depending on the investment objectives, strategies, and expenses of the funds. Some alternative mutual funds may require a minimum investment of only a few thousand dollars, while others may require several hundred thousand dollars or more. Investors should carefully review the prospectus of the funds and annual reports to determine the minimum investment required for a particular fund. After opening an account and meeting the minimum investment requirement, investors can make investments in the alternative mutual fund. The investment advisor of the funds will provide instructions on how to make investments, which typically involves wiring funds or writing a check. Investing in alternative mutual funds can be complex, and many investors may benefit from working with a financial advisor specializing in alternative investments. A financial advisor can help investors understand the risks and potential rewards of investing in alternative mutual funds and provide guidance on selecting a fund that aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance. Additionally, financial advisors can monitor the performance of the fund and make recommendations for changes to the portfolio of the investor as needed. Alternative mutual funds offer several potential benefits for investors, including: Alternative mutual funds often invest in non-traditional asset classes, such as commodities, real estate, and private equity, which can provide diversification benefits to the portfolio of an investor. By investing in various asset classes, investors can reduce their overall portfolio risk and increase their potential for returns. Alternative mutual funds often pursue higher returns than traditional mutual funds by investing in higher-risk asset classes or using complex investment strategies. These funds may offer the potential for higher returns than traditional investments, such as stocks and bonds. Some alternative mutual funds seek to reduce market risk by using hedging strategies or investing in non-correlated asset classes. By reducing market risk, these funds may be able to generate positive returns even when the broader market is experiencing a downturn. Some alternative mutual funds offer tax benefits to investors, such as the ability to defer or reduce taxes on capital gains or dividends. Investors should consult a tax professional to understand the tax implications of investing in alternative mutual funds. While alternative mutual funds offer potential benefits, they also come with certain risks. These risks include: Alternative mutual funds often have higher fees than traditional mutual funds due to their specialized management and complex investment strategies. These fees can reduce the returns of an investor over time and may outweigh the potential benefits of investing in these funds. Some alternative mutual funds may have limited liquidity, meaning that investors may not be able to sell their shares at any time. This can make it difficult for investors to access their money when they need it. Alternative mutual funds can be complex and difficult to understand, particularly for individual investors. Investors may need to do significant research and seek the help of financial advisors to fully understand these funds and make informed investment decisions. Alternative mutual funds may be subject to changes in regulation that could impact their investment strategies or performance. Investors should be aware of the potential impact of regulatory changes on their investments. Alternative mutual funds and hedge funds share similarities in their investment strategies and holdings, but there are several important differences between these two types of investment vehicles. Investors considering investing in either alternative mutual funds or hedge funds should carefully consider these differences to determine which type of investment is best suited for their individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation. Alternative mutual funds are publicly offered, SEC-registered mutual funds that are regulated under the Investment Company Act of 1940. This act provides certain protections for investors, such as limits on illiquid investments, restrictions on borrowings and debt, and requirements to allow investors to sell their shares at any time. On the other hand, hedge funds are not required to follow these regulations and may pursue non-traditional strategies and investments without the same regulatory safeguards. As a result, investors in hedge funds may be exposed to greater risks and have fewer protections compared to investors in alternative mutual funds. Alternative mutual funds are open to all investors, while hedge funds are only available to accredited investors or those with a high income or assets. This is to protect investors in hedge funds who are financially sophisticated and can handle the risks. Therefore, alternative mutual funds are a more accessible option for a broader range of investors. Investors in alternative mutual funds generally pay lower fees than hedge fund investors. Many alternative mutual funds have an annual fee equal to 2% or less of the assets of the funds. In contrast, investors in hedge funds generally pay advisory fees at a similar level plus a percentage of any profits earned, with the typical fee structure being 2% assets of the funds plus a 20% fee of any profits earned. As a result, alternative mutual funds are generally more cost-effective for investors, particularly those who may not have a significant amount of capital to invest. Alternative mutual funds offer a variety of potential benefits for investors, including diversification, higher returns, and reduced market risk. However, they also have potential downsides, such as higher fees and limited liquidity. Investing in alternative mutual funds requires a different process than investing in traditional mutual funds, including selecting a fund that aligns with the investment goals and risk tolerance of the investor, opening an account, and making investments. When considering investing in alternative mutual funds, investors should also be aware of the differences between alternative mutual funds and hedge funds. While alternative mutual funds may be suitable for some investors, they are not suitable for everyone. Investors should carefully consider their individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation before investing in these funds. Seeking the help of wealth management services can provide guidance on selecting a fund that aligns with the goals and risk tolerance of the investor and help manage the risks associated with investing in alternative mutual funds.What Are Alternative Mutual Funds?
Characteristics of Alternative Mutual Funds
Wide Range of Investment Objectives
Non-Traditional Investments
Complex Investment and Trading Strategies
Risk and Return Characteristics
Transparency
Liquidity
High Expenses

How to Invest in Alternative Mutual Funds
Selecting a Fund
Opening an Account
Complying With the Minimum Investment
Making Investments
Working With a Financial Advisor

Advantages of Investing in Alternative Mutual Funds
Diversification
Higher Returns
Reduced Market Risk
Tax Benefits
Disadvantages of Investing in Alternative Mutual Funds
Higher Fees
Limited Liquidity
Complexity
Regulatory Changes
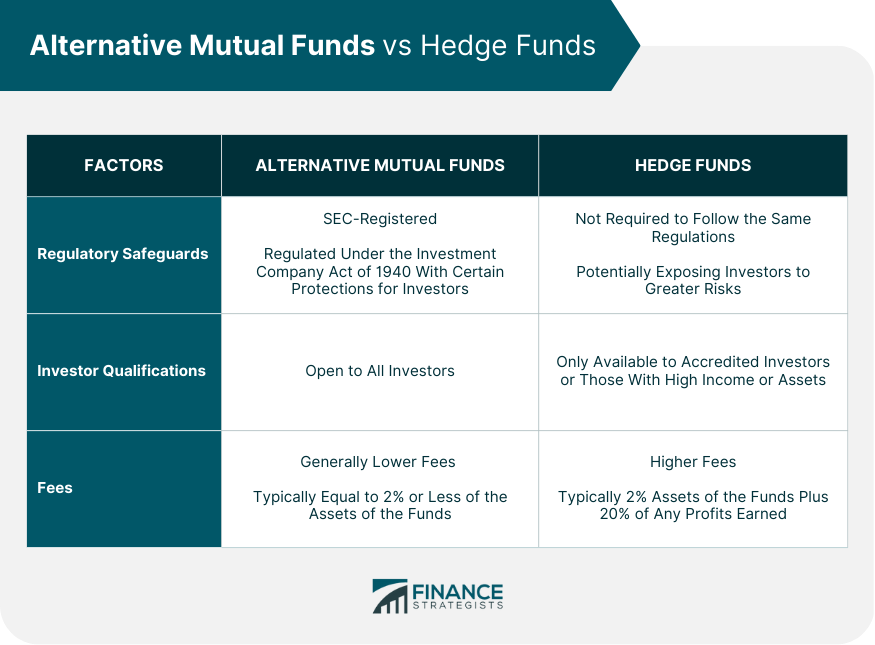
Alternative Mutual Funds vs Hedge Funds
Regulatory Safeguards
Investor Qualifications
Fees
Final Thoughts
Alternative Mutual Funds FAQs
Alternative mutual funds are SEC-registered mutual funds that invest in non-traditional assets or use complex investment strategies to achieve their investment objectives. They differ from traditional mutual funds in several ways, such as their investment strategies and types of assets invested in.
Alternative mutual funds can offer potential benefits such as diversification, higher returns, and reduced market risk. They may also offer potential tax benefits, depending on the investment strategy of the funds.
Alternative mutual funds generally have higher fees than traditional mutual funds, and some funds may have limited liquidity or be difficult to understand for individual investors. Additionally, these funds may be subject to regulatory changes that could impact their investment strategies or performance.
Investing in alternative mutual funds requires selecting a fund that aligns with your investment objectives and risk tolerance, opening an account with the investment advisor of the funds, and meeting the minimum investment requirement. Working with a financial advisor specializing in alternative investments may be beneficial.
Alternative mutual funds are publicly offered, SEC-registered mutual funds that are regulated under the Investment Company Act of 1940 and generally have lower fees than hedge funds. On the other hand, hedge funds are not subject to the same regulatory safeguards and may only be purchased by accredited investors or qualified purchasers who meet certain financial qualifications.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











