Mutual Fund Taxation refers to the tax implications associated with investing in mutual funds, a critical aspect for investors to understand for effective financial planning. This taxation varies based on the type of mutual fund, such as equity or debt funds, and the duration of the investment, distinguishing between short-term and long-term holdings. The tax treatment of mutual funds is influenced by factors like the nature of returns – whether as capital gains or dividends – and the investor's income tax bracket. Understanding mutual fund taxation is essential for investors to optimize their post-tax returns and make informed decisions. It involves navigating complex tax laws, which can significantly impact the overall profitability of mutual fund investments. When you invest in mutual funds, you may receive periodic dividend distributions and capital gains. These distributions are subject to taxation, and the tax treatment depends on several factors, including the type of income (qualified or non-qualified) and the holding period of your shares. Qualified dividends, which meet specific criteria, are generally taxed at a lower rate than non-qualified dividends. On the other hand, capital gains from the sale of mutual fund shares are categorized as short-term or long-term, each with its tax rates. To minimize the tax impact on your mutual fund investments, it's essential to employ tax-efficient strategies. One common approach is to consider the holding period of your investments. Long-term investments are typically subject to lower capital gains tax rates than short-term ones. Therefore, holding onto your mutual fund shares for an extended period can lead to tax savings. Additionally, choosing tax-managed funds or tax-efficient ETFs can help reduce tax liabilities. These funds are designed to minimize taxable events within the fund, potentially resulting in lower tax obligations for investors. Different types of mutual funds, such as equity funds, bond funds, and international funds, may have varying tax implications. Equity mutual funds, for instance, often generate capital gains, which can impact your tax liability. Bond mutual funds, on the other hand, primarily produce interest income, subject to different tax treatment. Understanding how taxation varies among fund types can help you make informed investment decisions. Tax laws are subject to change, and recent updates can affect how mutual fund investments are taxed. Staying informed about these changes is crucial to adapt your investment strategy accordingly. Recent tax reforms may impact the taxation of dividends, capital gains, and other aspects of mutual fund investments. Keeping abreast of legislative updates ensures that you make tax-efficient decisions and optimize your returns. One of the primary benefits of mutual fund taxation is the ability to defer taxes on investment gains until you sell your mutual fund shares. This deferral allows your investments to grow more rapidly since you're not immediately reducing your returns through taxation. Over time, the compounding effect of tax-deferred growth can significantly enhance your wealth. Mutual funds provide investors with diversification benefits by pooling money from multiple investors and investing in a diversified portfolio of securities. This diversification can help spread risk and reduce the impact of poor-performing assets. From a tax perspective, it can also be advantageous because gains in some investments may offset losses in others, potentially reducing your overall tax liability. Another advantage of mutual funds is the professional management they offer. Experienced fund managers make investment decisions on behalf of investors, selecting securities and adjusting the portfolio to achieve the fund's objectives. This expertise can lead to more tax-efficient investment strategies, such as tax-loss harvesting, which individual investors might find challenging to implement effectively. Certain types of capital gains, known as long-term capital gains, are subject to preferential tax rates, which are typically lower than ordinary income tax rates. Mutual funds often generate long-term capital gains, providing investors with the opportunity to benefit from these lower tax rates when they sell their shares. This can be particularly advantageous for investors in higher tax brackets. While mutual fund dividends are a source of income for investors, they are also subject to taxation. The tax rate applied to dividends depends on whether they are qualified or non-qualified. Non-qualified dividends are typically taxed at higher ordinary income tax rates, reducing the after-tax return on your investment. Understanding the tax treatment of dividends is essential for assessing the impact on your overall return. When you sell mutual fund shares, any capital gains generated from the sale are subject to taxation. These capital gains can be categorized as short-term or long-term, with different tax rates. Short-term capital gains are typically taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can be substantially higher than the tax rate for long-term capital gains. Managing your capital gains tax liability by considering your holding period is essential to minimize taxes. Actively managed mutual funds frequently engage in buying and selling securities within the portfolio. While this active approach can potentially enhance returns, it can also lead to more taxable events, resulting in increased tax liability for investors. In contrast, passively managed index funds or ETFs tend to have lower turnover and can be more tax-efficient. If you frequently buy and sell mutual fund shares, you may incur capital gains taxes with each transaction. Short-term trading can trigger short-term capital gains, subject to higher tax rates. Additionally, frequent trading can lead to higher transaction costs, which can erode your overall returns. It's essential to consider the tax consequences of your trading activity and assess whether it aligns with your long-term investment goals. Managing mutual fund investments often involves keeping detailed records of transactions, dividend distributions, and capital gains. Failing to maintain accurate records can lead to reporting errors when filing taxes, potentially triggering audits or penalties. Staying organized and understanding the documentation required for tax purposes is crucial for a smooth tax filing process. The duration for which you hold your mutual fund shares can significantly impact your tax liability. Generally, investments held for more than one year qualify for long-term capital gains tax rates, typically lower than short-term rates. Therefore, adopting a long-term investment horizon can lead to tax savings over time. Choosing tax-efficient mutual funds can help minimize your tax liabilities. Tax-managed funds and index funds tend to generate fewer taxable events within the fund due to lower turnover. This can result in reduced capital gains distributions, making them suitable options for tax-conscious investors. Tax-managed funds are specifically designed to minimize tax consequences for investors. Fund managers employ strategies such as tax-loss harvesting, offsetting gains with losses within the fund, and selecting securities with lower tax implications. Investing in tax-managed funds can lead to more tax-efficient outcomes. Tax loss harvesting involves strategically selling investments that have declined in value to offset capital gains in your portfolio. By realizing losses, you can reduce your taxable income and, in turn, your tax liability. This technique requires careful planning and adherence to tax regulations to ensure its effectiveness. When it comes time to withdraw funds from your mutual fund investments, adopting a tax-efficient withdrawal strategy can help you minimize tax liabilities. This may involve selecting specific shares to sell, managing your income sources in retirement, and considering tax brackets to optimize your withdrawals. When tax season arrives, mutual fund investors should be prepared to receive Form 1099-DIV and Form 1099-B from their fund providers. Form 1099-DIV reports dividend distributions and capital gains received during the year, while Form 1099-B provides information about the sale of mutual fund shares. These forms are essential for accurately reporting your investment income and transactions on your tax return. Understanding the tax reporting deadlines is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure compliance with tax regulations. The deadline for filing federal income tax returns is typically April 15th, but it may vary based on specific circumstances. Additionally, extensions may be available for individuals who need more time to prepare their taxes. Staying informed about the deadlines and extensions is essential to meet your tax obligations. Preparing your taxes for mutual fund investments can be complex, especially if you have multiple funds or a significant portfolio. Utilizing tax software or seeking professional assistance from a tax advisor or certified public accountant (CPA) can streamline the process and help you maximize tax efficiency. Tax professionals can provide valuable insights, ensuring you take advantage of available deductions and credits while minimizing your tax liability. Understanding mutual fund taxation is crucial for investors seeking to optimize their returns and navigate the complexities of tax laws. Mutual funds, whether equity or debt, come with distinct tax implications based on the nature of returns and investment duration. Key points include the different tax treatments for dividends and capital gains, with qualified dividends often taxed at a lower rate and capital gains categorized as short-term or long-term. Employing tax-efficient strategies, such as considering holding periods and selecting tax-managed funds, can significantly reduce tax liabilities. It's also important to stay informed about changes in tax laws, as these can impact mutual fund investments. Ultimately, effective tax planning and understanding the nuances of mutual fund taxation can lead to more informed investment decisions and enhanced post-tax returns. This knowledge empowers investors to take control of their financial future, making the most of their mutual fund investments.What Is Mutual Fund Taxation?
How Mutual Fund Taxation Works
Taxation of Mutual Fund Dividends and Capital Gains
Tax-Efficient Investing Strategies
Taxation of Different Types of Mutual Funds
Recent Changes in Mutual Fund Taxation Laws
Benefits of Mutual Fund Taxation
Tax Deferral
Diversification Benefits
Professional Management
Capital Gains Tax Rate Advantage
Drawbacks of Mutual Fund Taxation
Tax Impact on Dividend Distributions
Capital Gains Tax Liability
Tax Inefficiency in Active Funds
Tax Consequences of Frequent Trading
Tax Documentation and Recordkeeping Requirements

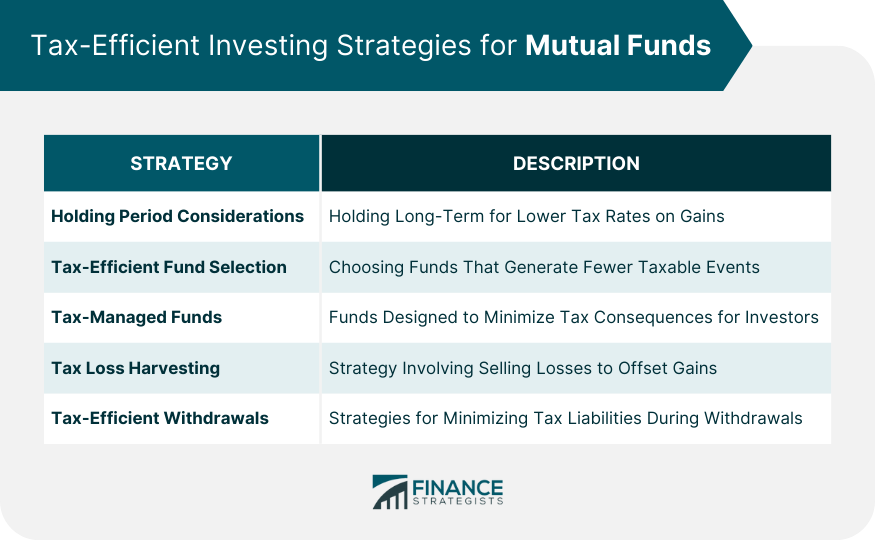
Tax-Efficient Investing Strategies for Mutual Funds
Holding Period Considerations
Tax-Efficient Fund Selection
Tax-Managed Funds
Tax Loss Harvesting
Tax-Efficient Withdrawal Strategies
Reporting and Filing Taxes for Mutual Fund Investments
Form 1099-DIV and 1099-B
Tax Reporting Deadlines
Tax Software and Professional Assistance
Conclusion
Mutual Fund Taxation FAQs
Mutual fund taxation refers to the set of rules and regulations governing the taxation of mutual fund investments, including the taxation of dividends and capital gains generated by mutual funds.
Mutual fund dividends are typically subject to taxation. The tax rate depends on whether the dividends are qualified or non-qualified. Qualified dividends often enjoy lower tax rates, while non-qualified dividends are taxed at ordinary income tax rates.
Capital gains resulting from the sale of mutual fund shares can be subject to taxation. These gains may be categorized as short-term or long-term, with different tax rates applied. Long-term capital gains often enjoy more favorable tax rates.
There are tax-efficient strategies for mutual fund investments. These strategies include holding investments for the long term to benefit from lower long-term capital gains tax rates, choosing tax-efficient funds, and employing tax-loss harvesting to offset gains with losses.
Recent changes in taxation laws can impact the taxation of mutual fund investments. Staying informed about these changes is essential for adjusting your investment strategy accordingly to optimize tax efficiency.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











