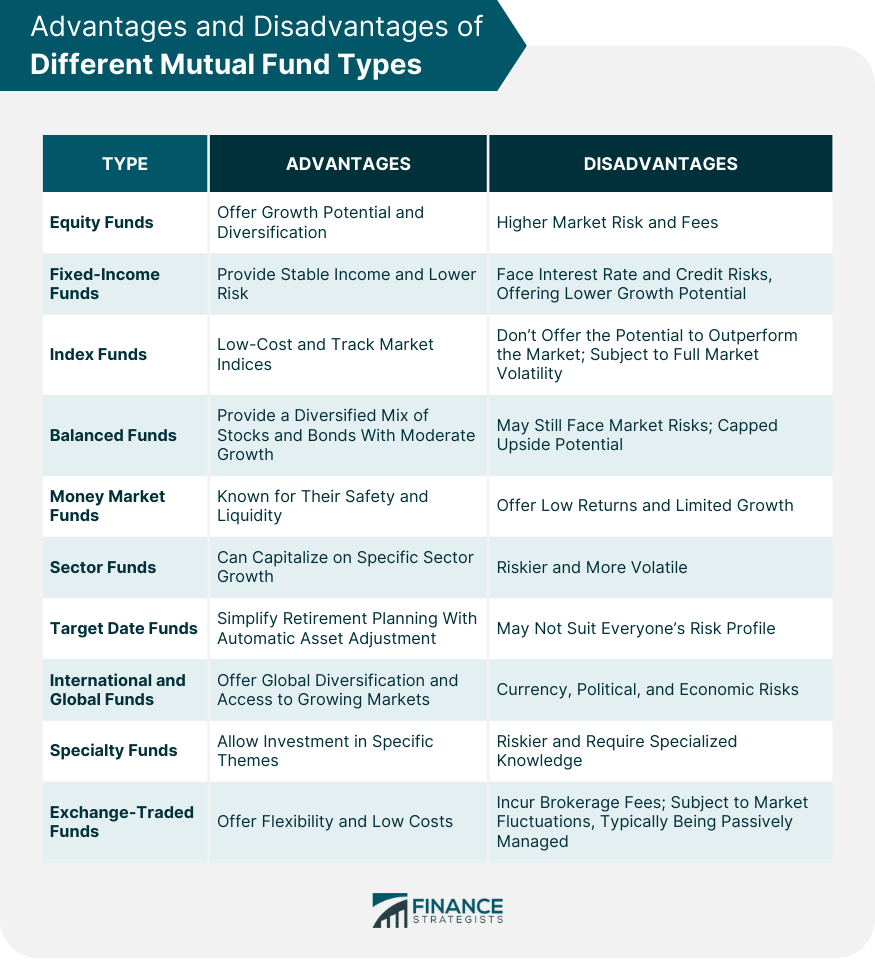
Mutual funds have emerged as a pivotal component in the arsenal of modern investment strategies, serving as a conduit for individual investors to tap into professionally managed, diversified portfolios. The essence of mutual funds lies in their ability to pool resources from multiple investors, thereby facilitating access to a variety of assets that might be otherwise unattainable for an individual investor. Equity funds primarily invest in stocks and are often the go-to choice for investors targeting capital growth. Their categorization is multi-dimensional, focusing on aspects like company size (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap), geographical market (domestic, international), or investment approach (growth, value). Large-Cap Funds: Tailored for investors inclined towards risk aversion, these funds focus on well-established corporations known for their market stability and potential for consistent, albeit moderate, growth. Small-Cap Funds: These funds venture into the terrain of smaller companies, offering a high-risk, high-reward scenario. They are particularly attractive to investors who are willing to tolerate market volatility in pursuit of substantial growth prospects. Fixed-income funds invest in an array of debt securities, providing investors with a more predictable income stream. These funds are segmented based on issuer types (like government bonds, and corporate bonds) and the duration of the bonds (short, medium, or long-term). Index funds strive to emulate the performance of designated market indices (such as the S&P 500), offering an investment approach that is more passive and typically associated with lower management fees compared to actively managed funds. Balanced funds blend both equities and fixed-income securities, aiming to strike a balance between risk mitigation and potential growth. They are suited for investors seeking a middle ground between the aggressiveness of pure equity funds and the conservative nature of bond funds. Investing in short-term, highly liquid securities, money market funds are often regarded as the safest category within the mutual fund spectrum. They cater to investors who prioritize capital preservation and liquidity over higher returns. Sector funds concentrate their investments in specific industry sectors (like technology, healthcare, or energy), providing an opportunity to capitalize on the growth potential of these sectors. However, this specialization also introduces a higher degree of risk due to the lack of diversification across different sectors. These funds are tailored for retirement planning, automatically adjusting their asset allocation over time. As the target date (typically the investor's retirement year) approaches, the fund gradually shifts towards a more conservative asset mix. International and global funds enable investors to diversify their portfolios by investing in markets outside their home country. International funds exclusively focus on foreign markets, while global funds invest both domestically and internationally. This category encompasses funds that invest in specific niches like real estate, commodities, or those adhering to socially responsible investment principles (Environmental, Social, and Governance - ESG funds). Although technically not mutual funds, ETFs are often discussed alongside them due to their shared characteristics. ETFs combine the diversification benefits of mutual funds with the flexibility of being traded like stocks on an exchange. The selection of an appropriate mutual fund is a nuanced process, requiring a deep understanding of one’s financial objectives, risk tolerance, and investment time frame. Investors must recognize the importance of diversification not just across asset classes, but also within mutual fund categories. However, factors like expense ratios and management fees should not be overlooked, as they can significantly impact the net returns on investments. Equity funds offer growth potential and diversification but come with higher market risk and fees. Fixed income funds provide stable income and lower risk, yet they face interest rate and credit risks, offering lower growth potential. Index funds are low-cost and track market indices but don't offer the potential to outperform the market and are subject to full market volatility. Balanced funds provide a diversified mix of stocks and bonds with moderate growth but may still face market risks and have capped upside potential. Money market funds are known for their safety and liquidity, but they offer low returns and limited growth. Sector funds can capitalize on specific sector growth but are riskier and more volatile. Target date funds simplify retirement planning with automatic asset adjustment but may not suit everyone's risk profile. International and global funds offer global diversification and access to growing markets but carry currency, political, and economic risks. Specialty funds allow investment in specific themes but are often riskier and require specialized knowledge. Lastly, ETFs offer flexibility and low costs but incur brokerage fees and are subject to market fluctuations, typically being passively managed. Each fund type has unique characteristics and should be chosen based on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. The journey into mutual fund investments begins with setting up an investment account, either through a brokerage or directly with a mutual fund company. The key to successful investing lies in conducting thorough research to identify funds that resonate with your investment profile and continuously monitoring and adjusting your portfolio to ensure alignment with your evolving financial goals. Understanding the diverse landscape of mutual funds is an essential first step toward making informed and effective investment decisions. While this article provides a foundational overview, the complexity of financial markets and individual circumstances necessitate personalized advice from financial advisors. Armed with the right knowledge and strategic planning, mutual funds can serve as a robust tool in the pursuit of your financial aspirations.What Are Mutual Funds?
Types of Mutual Funds
Equity Funds
Fixed-Income Funds
Index Funds
Balanced Funds
Money Market Funds
Sector Funds
Target Date Funds
International and Global Funds
Specialty Funds
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
Choosing the Right Type of Mutual Fund
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Mutual Fund Types
How to Invest in Mutual Funds
Conclusion
Types of Mutual Funds FAQs
There are several main types of mutual funds, including equity funds, which invest in stocks; fixed income funds, focusing on bonds; balanced funds, combining stocks and bonds; money market funds, investing in short-term debt securities; sector funds, targeting specific industry sectors; target date funds, adjusting assets based on a retirement date; international and global funds, investing in non-domestic markets; and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), which are similar to mutual funds but traded like stocks.
Equity funds primarily invest in stocks and are distinct from other types of mutual funds in terms of their higher growth potential and market risk. They differ from fixed-income funds, which focus on bonds and offer more stable income, and from balanced funds, which combine the characteristics of both stocks and bonds for a diversified portfolio.
Index funds, a specific type of mutual fund, offer the advantages of low expense ratios, simplicity, and a passive investment strategy designed to replicate the performance of a market index, like the S&P 500. They stand out among other types of mutual funds for their cost-effectiveness and straightforward approach to market performance tracking.
International and global funds are unique types of mutual funds that invest in markets outside the investor’s home country. International funds exclusively focus on foreign markets, while global funds invest both domestically and internationally, offering diversification and exposure to different economic environments and growth opportunities.
Sector funds, which concentrate on specific sectors like technology or healthcare, can be considered a riskier choice among types of mutual funds due to their focus on a single sector. This concentration can lead to higher volatility and susceptibility to sector-specific risks, as opposed to more diversified fund types.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











