Market share represents the portion of a specific market or industry that is controlled or held by a business, product, or brand. Expressed as a percentage, it provides a snapshot of a company's competitiveness and dominance in a particular segment. Understanding market share offers insights not just into a company's current standing but also into market trends, consumer preferences, and potential areas for growth or improvement. Market share is complementary with a company growing or shrinking. When the market share of a company increases or decreases, it gives analysts information on how competitive that company's goods or services are at that particular time. If the total market for a product or service grows, and a company maintains its market share, it means it is growing revenues at the same rate as the total market. If it is growing its market share, its revenue is growing faster than the total market revenue. The purpose of this metric is to give a general idea of the size of a company relative to its direct competitors. Additionally, investors use market share data when assessing the opportunity of a business for growth. Market share can provide a distinct competitive advantage. Companies with a higher market share often benefit from economies of scale, which can reduce production costs and bolster profit margins. Moreover, a significant market share can serve as a deterrent for new entrants eyeing the same market segment, since establishing a foothold becomes challenging against well-entrenched competitors. Furthermore, a dominant market position can enhance brand visibility and recognition, leading to increased consumer trust and loyalty – crucial assets in fiercely competitive markets. Those with significant market shares are often seen as industry leaders or giants, wielding considerable influence over market trends, pricing, and even regulatory matters. Such positioning can lead to preferential treatment from suppliers, better negotiation leverage, and increased investor confidence. Conversely, companies with declining market shares might face skepticism from stakeholders and be viewed as less influential or relevant in their industry. A company's market share directly correlates with its growth opportunities. With a higher market share, businesses have a clearer path to expand, innovate, and diversify. They have a proven track record, which can be instrumental in securing partnerships, collaborations, and investments. On the other hand, companies with smaller market shares, while facing challenges, aren’t without growth opportunities. They can identify market niches, innovate, and challenge industry norms to carve out a space for themselves. Overall market share pertains to the total sales of a company as a percentage of the sales of the entire market. It gives a broad perspective of the company's position in the entire industry landscape. It’s an essential metric for large corporations and conglomerates operating in multiple sectors. Relative market share is a more specific measure, comparing a company's market share to that of its nearest competitor. It offers a more refined understanding of competitive positioning, especially in industries where the top two or three players dominate. Segment market share narrows the focus even further, analyzing a company's dominance in a specific segment of the market. For instance, a tech company might examine its market share in the tablet segment, independent of its performance in other device categories. This metric is calculated by taking the company's sales over a specified period of time and dividing it by the total sales of the industry over the same period of time. The formula is: This straightforward calculation provides a percentage that indicates the company's share of the market. Imagine a company, Brand X, which sold 500,000 units of its product last year. If the total sales in the industry for that year were 5 million units, the market share for Brand X would be: Market Share (%) = (500,0005,000,000) x 100 Market Share = 10% Thus, Brand X holds 10% of the market share in that industry. A primary driver for market share is product quality and innovation. Companies that consistently produce high-quality products that meet or exceed consumer expectations are likely to command a higher market share. Additionally, businesses that invest in research and development to introduce innovative products can capture more market share. Competitive pricing, discounts, and promotions can attract customers, but if done excessively, it can also erode profit margins. Conversely, premium pricing can establish a product as high-end but might alienate cost-conscious consumers. Brands that resonate with consumers, communicate their value proposition effectively, and build strong emotional connections typically enjoy higher market loyalty and, by extension, market share. Happy customers are repeat customers. Companies that prioritize customer satisfaction, address grievances promptly, and create value can foster loyalty, ensuring a stable and potentially growing market share. When a company increases its market share, they have more room to improve operations and profitability. Market shares assume a fixed market size but can be grown. Some tactics that companies use to grow their market size include advertising, lowering prices, adding new products, or appealing to unique and specific demographics. Tapping into new geographies or enhancing presence in existing markets can boost market share. This might involve setting up new retail outlets, expanding online sales channels, or even entering international markets. Diversifying the product range to cater to a broader audience or meet varying consumer needs can attract a larger customer base. However, diversification should be done after thorough market research to ensure demand. Acquiring or merging with other companies can be a swift way to increase market share. This strategy not only brings in the acquired company's customer base but also its resources, technologies, and expertise. Strategically pricing products, offering discounts, or introducing loyalty programs can entice customers. While it's essential to ensure profitability, competitive pricing can be a useful tool to capture a larger share of the market. Market share is usually calculated within specific countries, however investors can obtain market share data from other independent sources, and often from the companies themselves. In some industries, it can be difficult to accurately measure when comparing across countries. Market Share is the percentage of a market controlled by a business or brand, reflecting competitiveness and dominance. It offers insights into trends, preferences, and growth potential. A growing or shrinking market share indicates a company's competitiveness. A company maintaining share while the market grows shows proportional growth; exceeding it implies faster expansion. Market share's purpose is gauging a company's size relative to competitors and aiding investor assessments. It yields a competitive advantage, influencing economies of scale, brand visibility, and trust. Dominant shares position companies as industry leaders, influencing trends and negotiations. A larger share expands growth opportunities through partnerships and innovation. Factors like quality, pricing, marketing, and customer satisfaction impact share. Growing strategies encompass diversification, expansion, mergers, competitive pricing, and international presence. Market share data, though mainly country-specific, can provide valuable insights for investors.Define Market Share in Simple Terms
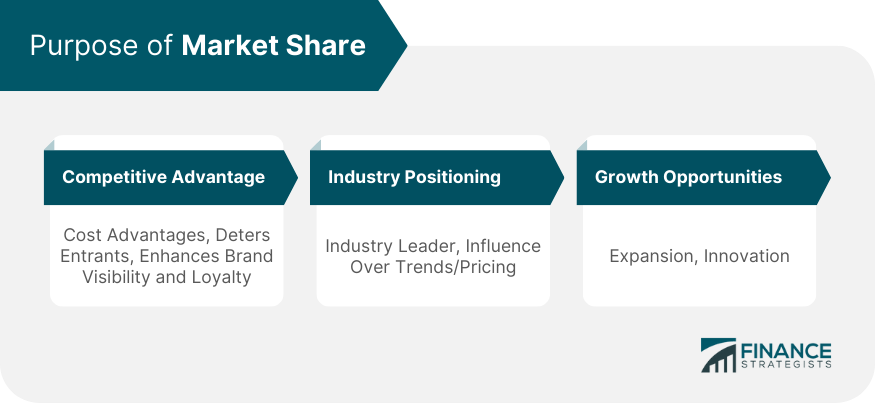
The Purpose of Market Share
Competitive Advantage
Industry Positioning
Growth Opportunities
Types of Market Share
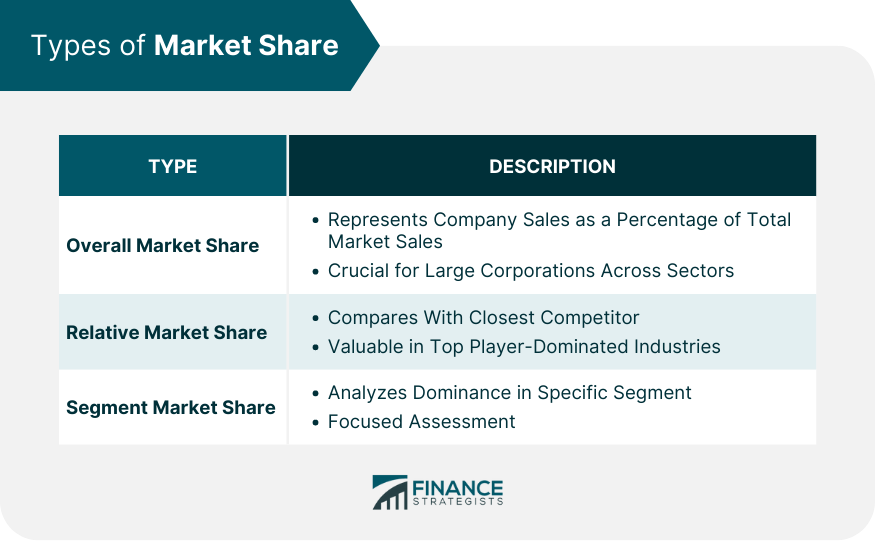
Overall Market Share
Relative Market Share
Segment Market Share
Formula for Market Share Calculation
Factors Affecting Market Share
Product Quality and Innovation
Pricing Strategies
Marketing and Advertising Efforts
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty

Growing a Company's Market Share
Expansion and Penetration
Product Diversification
Mergers and Acquisitions
Competitive Pricing

International Market Share
Conclusion
Market Share FAQs
Market share is the percent of total sales in an industry generated by a given company or product.
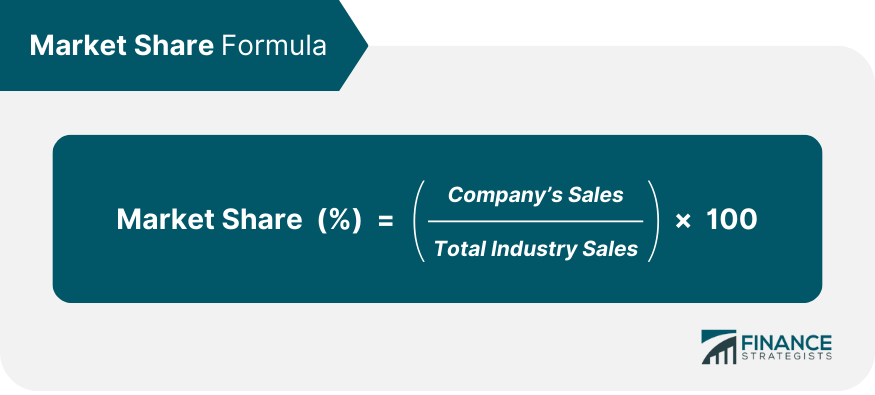
This metric is calculated by taking the company’s sales over a specified period of time and dividing it by the total sales of the industry over the same period of time.
The purpose of this metric is to give a general idea of the size of a company relative to its direct competitors.
If the total market for a product or service grows, and a company maintains its market share, it means it is growing revenues at the same rate as the total market.
Market share is usually calculated within specific countries, however, investors can obtain market share data from other independent sources and often from the companies themselves. In some industries, it can be difficult to accurately measure when comparing across countries.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











