Monopolistic competition is a market structure where there are many small firms that produce differentiated products. Unlike perfect competition, each firm has some market power due to product differentiation, which allows them to charge slightly higher prices than their competitors. However, because there are many firms producing similar but not identical products, consumers have a range of choices and can switch to another product if the price of one becomes too high. As a result, firms in a monopolistically competitive market must engage in non-price competition, such as advertising and product differentiation, to attract customers. Monopolistic competition is characterized by several key features: Large Number of Small Firms. There are many firms operating in the market, none of which dominates the market. Differentiated Products. Each firm produces a product that is distinct from its competitors' products, either through quality, design, or branding. Some Market Power. Each firm has some control over the price of its product due to product differentiation, but this control is limited because there are many substitutes available to consumers. Non-price Competition. Firms in a monopolistically competitive market compete using advertising, product development, and other marketing strategies to attract customers rather than relying on lower prices. Monopolistic competition can be observed in a variety of industries, but here are some examples: These are a good example of monopolistically competitive markets because they offer different types of cuisine, ambiance, and price range, which creates a range of options for consumers. This differentiation allows each restaurant to have some control over its pricing strategy, but not enough to eliminate competition. Clothing companies differentiate their products through design, quality, and brand image. This differentiation creates a range of options for consumers, giving each clothing company some market power over its pricing strategy. Consumers often choose clothing based on brand image, style, and quality, rather than just the price. Companies producing electronics such as smartphones, laptops, and televisions are also good examples of monopolistically competitive markets. These companies differentiate their products through technology, features, and design. For example, Apple's iPhone and Samsung's Galaxy phones have different designs, features, and operating systems, which create a range of options for consumers. These industries have many firms competing for market share and offering slightly different products, making them good examples of monopolistically competitive markets. Monopolistic competition offers several benefits to both consumers and firms: In a monopolistically competitive market, consumers have a range of options to choose from, leading to greater consumer satisfaction and utility. Firms in a monopolistically competitive market differentiate their products, which encourages innovation and leads to a greater variety of products for consumers. The need for product differentiation in a monopolistically competitive market drives firms to innovate and create new products, technologies, and marketing strategies to attract consumers. This can lead to technological advancements and greater efficiency in the market. Overall, monopolistic competition encourages competition, innovation, and variety, benefiting both consumers and firms in the market. While monopolistic competition offers some benefits, it also presents several challenges: The product differentiation in monopolistically competitive markets can make it difficult for new firms to enter the market and compete with established firms. This can lead to reduced competition and market inefficiencies. Firms in a monopolistically competitive market have some market power, which allows them to charge slightly higher prices than in a perfectly competitive market. This can lead to higher prices for consumers and reduced consumer surplus. Monopolistic competition can lead to an inefficient allocation of resources, as firms may spend resources on advertising and product differentiation rather than on improving their production process. This can result in less efficient use of resources and higher costs for consumers. Monopolistic competition has several practical applications in business and government policies: Firms in a monopolistically competitive market must focus on product differentiation and non-price competition to attract customers. This can include investing in research and development, creating unique brand identities, and developing marketing campaigns to promote their products. Because monopolistic competition can lead to market inefficiencies and reduced competition, governments may regulate these markets to promote fair competition and protect consumers. Antitrust laws may be used to prevent monopolistic practices, such as price-fixing, collusion, or abuse of market power. Understanding the characteristics and implications of monopolistic competition can help businesses make strategic decisions and help governments develop effective policies to promote competition and protect consumers. Monopolistic competition is just one of several market structures, each with its unique features: In a perfectly competitive market, many small firms sell identical products with no market power. Prices are determined by supply and demand, and there are no barriers to entry or exit. Unlike the monopolistic competition, there is no product differentiation or non-price competition. In a monopoly, there is only one firm in the market with complete market power. The firm can set prices and restrict output without facing competition. There are significant barriers to entry, making it difficult for new firms to enter the market. Monopolistic competition sits between the extreme market structures of perfect competition and monopoly, with some market power due to product differentiation but still facing competition from other firms. In an oligopoly, there are only a few firms in the market, each with a significant market share. The firms may have some market power and engage in non-price competition, but there are significant barriers to entry and exit, making it difficult for new firms to enter the market. Oligopoly is similar to monopolistic competition in that there are barriers to entry and a small number of firms, but with more market power and less product differentiation. Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which many small firms produce differentiated products, leading to some market power and non-price competition. This market structure offers benefits such as consumer choice, product differentiation, and innovation but also presents challenges such as barriers to entry, higher prices for consumers, and inefficient allocation of resources. Understanding the characteristics and implications of monopolistic competition can help businesses make strategic decisions and help governments develop effective policies to promote competition and protect consumers. It is important to note that monopolistic competition is just one of several market structures, each with unique features and implications. You can speak to a wealth management professional to learn more about monopolistic competition.What Is Monopolistic Competition?
Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition
These characteristics create a market structure that combines elements of both monopoly and perfect competition, resulting in a market where firms have some market power, but not enough to eliminate competition altogether.
Examples of Monopolistic Competition
Restaurants
Clothing
Electronics
Benefits of Monopolistic Competition
Consumer Choice
Product Differentiation
Innovation
Challenges of Monopolistic Competition
Barriers to Entry
Higher Prices for Consumers
Inefficient Allocation of Resources
Applications of Monopolistic Competition
Business Strategy and Marketing
Government Regulation and Antitrust Policies
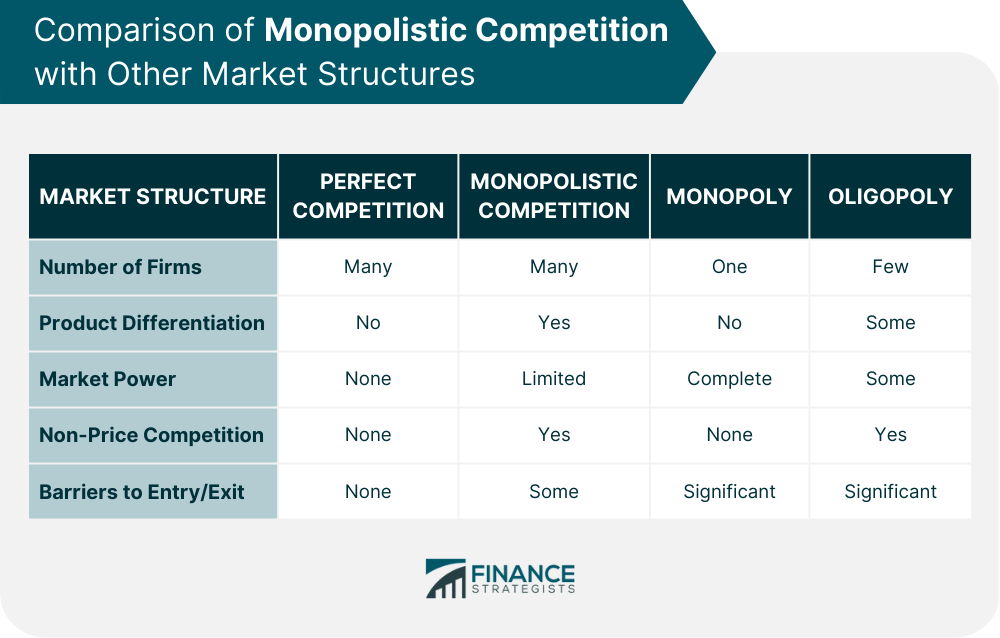
Comparison of Monopolistic Competition with Other Market Structures
Perfect Competition
Monopoly
Oligopoly
Final Thoughts
Monopolistic Competition FAQs
Monopolistic competition is a market structure where many small firms produce differentiated products, creating some market power but still facing competition. Unlike perfect competition, firms have some control over the price of their product due to product differentiation.
Monopolistic competition can be observed in industries such as restaurants, clothing, and electronics, where firms differentiate their products through features, design, and branding to attract customers.
Monopolistic competition offers benefits such as consumer choice, product differentiation, and innovation, as firms must constantly develop new products, technologies, and marketing strategies to remain competitive.
The need for product differentiation can create barriers to entry, making it difficult for new firms to enter the market and compete with established firms. This can lead to market inefficiencies and higher prices for consumers. Furthermore, monopolistic competition can result in an inefficient allocation of resources.
Understanding the characteristics, benefits, and challenges of monopolistic competition is essential for businesses and policymakers seeking to navigate this market structure effectively. This includes investing in research and development, creating unique brand identities, and developing marketing campaigns to promote their products. Governments may also regulate these markets to promote fair competition and protect consumers through antitrust laws.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











