Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure of the value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders during a specified period, adjusted for inflation. It is a critical indicator of economic performance as it reflects the changes in the volume of goods and services produced in an economy, independent of changes in the overall price level. The value of Real GDP is expressed in constant dollars, meaning the effect of inflation has been removed from the value of goods and services produced. This allows for more accurate comparisons of economic performance over time, as it reflects changes in the volume of goods and services produced rather than just changes in their nominal value due to inflation. The Real GDP is a crucial measure of economic performance as it provides insight into the growth or decline of an economy. Real GDP is used to measure economic growth or contraction, and its trends can provide information about the economic health of a country. Additionally, it provides policymakers, analysts, and investors with valuable information on which to base their economic decisions. Real GDP is often compared with Nominal GDP, which is the current value of goods and services produced without being adjusted for inflation. Nominal GDP provides an estimate of the value of goods and services produced in an economy; however, it does not provide a clear picture of the economy's growth or decline due to changes in the overall price level. The calculation of Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is an essential step in understanding the economic growth or contraction of a country. To calculate Real GDP, the nominal GDP is adjusted for inflation, with the result expressed in constant dollars. The calculation involves three primary steps: Nominal GDP refers to the total value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders during a specific period, expressed in current market prices. However, nominal GDP does not account for the impact of inflation, which can distort the true value of economic output. Therefore, to calculate Real GDP, inflation needs to be taken into account. To adjust for inflation, a base year is chosen where prices are stable and reflect the market's real values. The base year is used as a reference point to measure the change in prices over time. The choice of the base year is critical, as it affects the comparison of Real GDP across different periods. Typically, a base year is chosen every five years, and the Real GDP of other years is calculated by adjusting the nominal GDP of that year with the price level of the base year. The formula to calculate Real GDP involves dividing the nominal GDP by the inflation rate, which is expressed as a decimal, to get the Real GDP in constant dollars. The formula for calculating Real GDP is as follows: Nominal GDP is the total value of goods and services produced in current prices, and the price index is a measure of inflation, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or the Gross Domestic Product Deflator (GDP Deflator). The calculation of Real GDP provides a more accurate measure of economic output as it removes the effects of price changes from the GDP measure, enabling the comparison of the volume of goods and services produced across different time periods. Real GDP is a crucial measure used in economic policy-making, economic forecasting, and international comparisons. Real GDP plays an important role in the formulation of economic policies such as monetary policy and fiscal policy. Policymakers use Real GDP to assess the state of the economy and decide on policies to improve it. For example, if Real GDP is declining, policymakers may implement expansionary monetary and fiscal policies to stimulate the economy. Economists and analysts use Real GDP to forecast the economic performance of a country. By analyzing the trends in Real GDP, analysts can determine whether an economy is growing, contracting, or remaining stagnant. This information can be used to predict future economic trends, such as inflation, job growth, and business activity. Real GDP is used to compare the economic performance of different countries or regions. It provides a basis for measuring the relative size of economies and comparing their growth rates. By using Real GDP as a common measure, policymakers can evaluate the performance of different countries and regions and make informed decisions about international trade, investment, and cooperation. Despite its importance, Real GDP has limitations as a measure of economic well-being and as a sole indicator of economic performance. Some of the criticisms of Real GDP include: Real GDP measures the production of goods and services within a country, but it does not consider other factors that affect the well-being of citizens. For example, it does not account for income distribution, the quality of life, and environmental sustainability. Therefore, a country with a high Real GDP may not necessarily have a high standard of living for all citizens. Real GDP is a comprehensive measure of economic activity but it does not capture all economic activities. It does not consider the underground economy, which is a significant contributor to economic activity in many countries. Additionally, Real GDP does not account for the value of leisure time, volunteer work, or the benefits of technological innovations. Therefore, Real GDP may not provide a complete picture of the economy's performance. Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is an essential measure of economic performance. It measures the production of goods and services within a country, adjusted for inflation. Real GDP is used to measure economic growth or contraction and provides policymakers, analysts, and investors with valuable information on which to base their economic decisions. However, Real GDP has limitations as a measure of economic well-being and as a sole indicator of economic performance. Despite these limitations, Real GDP remains a critical measure of economic performance and is widely used in economic analysis and policymaking. As Real GDP is a crucial measure of economic performance, it is essential to understand its importance, calculation, uses, and criticisms. By gaining a deeper understanding of Real GDP, individuals can make more informed decisions about economic policy-making, investment, and forecasting. Keep learning and exploring to gain a comprehensive understanding of Real GDP's role in shaping the economy.Real Gross Domestic Product: Definition
Importance of Real GDP
Calculation of Real GDP
Nominal GDP and Inflation
Importance of Base Year
Real GDP Formula

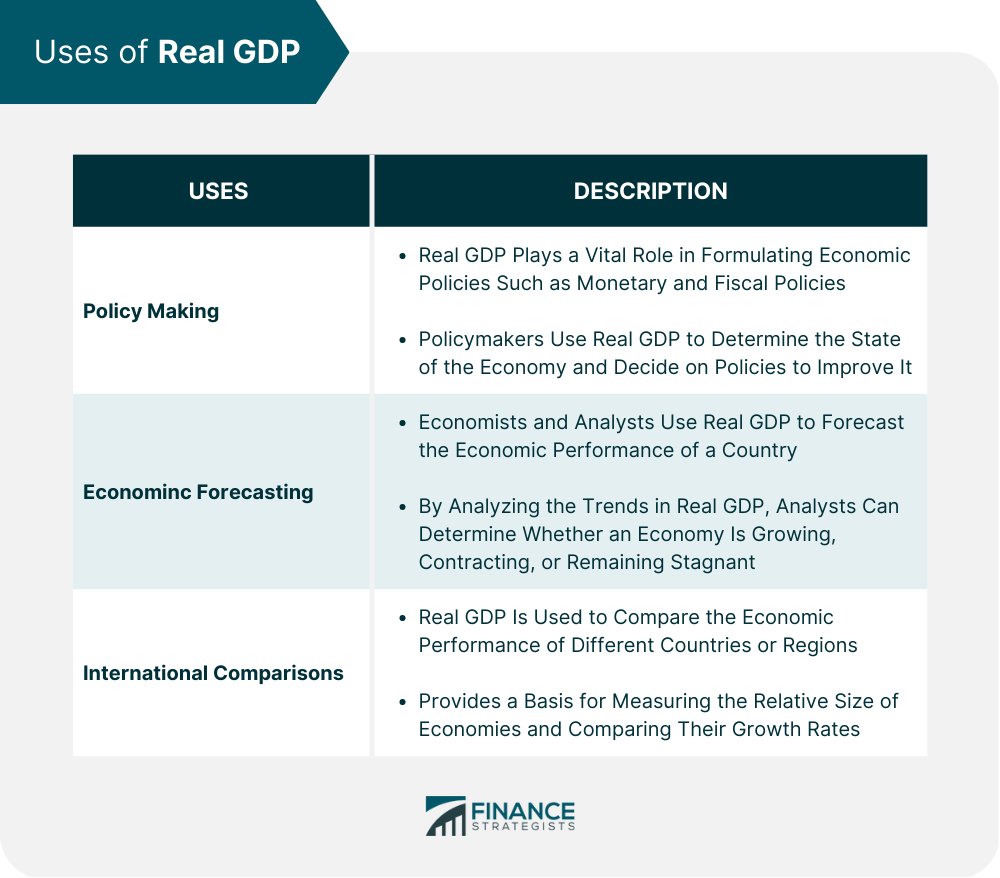
Uses of Real GDP
Importance of Real GDP in Policy-Making
Use of Real GDP in Economic Forecasting
Role of Real GDP in International Comparisons
Criticisms of Real GDP
Limitations of Real GDP as a Measure of Economic Well-Being
Criticisms of Real GDP as a Sole Indicator of Economic Performance
Final Thoughts
Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) FAQs
Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure of the value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders during a specified period, adjusted for inflation.
Real GDP is calculated by adjusting the nominal GDP (the current value of goods and services produced) for inflation using a price index such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or the Gross Domestic Product Deflator (GDP Deflator).
Real GDP is a critical measure of economic performance as it provides insight into the growth or decline of an economy. It is used to measure economic growth or contraction and provides policymakers, analysts, and investors with valuable information on which to base their economic decisions.
Real GDP has limitations as a measure of economic well-being and as a sole indicator of economic performance. It does not consider other factors that affect the well-being of citizens, such as income distribution, quality of life, and environmental sustainability.
Real GDP plays an important role in the formulation of economic policies such as monetary policy and fiscal policy. Policymakers use Real GDP to assess the state of the economy and decide on policies to improve it.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











