Commercial real estate (CRE) refers to properties that are primarily used for business or income-generating purposes. These properties are typically bought, sold, or leased for commercial purposes, such as office spaces, retail stores, industrial facilities, multifamily buildings, hospitality establishments, and special-purpose properties. These properties are instrumental in facilitating economic activity, promoting job creation, and generating income for investors. By offering spaces for businesses to operate and thrive, commercial real estate serves as a fundamental driver of economic growth across various sectors. Furthermore, it provides opportunities for entrepreneurs, fosters innovation, and contributes to the overall development and vibrancy of local and global economies. Office buildings are commercial properties designed for business operations, providing workspace for companies and organizations. They range from small office spaces to high-rise towers and can cater to a variety of industries and professional services. Retail properties encompass a wide range of establishments, including shopping centers, malls, standalone stores, and restaurants. These properties are used for retail sales and consumer-oriented businesses. Industrial properties include warehouses, manufacturing facilities, distribution centers, and industrial parks. These properties are specifically designed to support industrial activities, storage, and logistics. Multifamily properties are residential buildings that house multiple units, such as apartments, condominiums, and townhouses. These properties are primarily used for rental purposes. Hospitality properties consist of hotels, resorts, motels, and other lodging establishments. They provide accommodation and related services to travelers and tourists. Special purpose properties are unique properties that are designed for specific uses, such as hospitals, educational institutions, religious facilities, sports arenas, and entertainment venues. These properties cater to specialized industries or activities. One of the key characteristics of commercial real estate is its potential to generate income through rental payments. Tenants typically sign lease agreements and pay rent to the property owner, creating a steady stream of cash flow. Commercial real estate is typically governed by lease agreements, which outline the terms and conditions of the property's use. These agreements specify rental rates, lease duration, tenant responsibilities, and other relevant provisions. Valuing commercial real estate often involves different methods, such as the income approach, sales comparison approach, and cost approach. These methods consider factors like rental income, market trends, property condition, and comparable sales to determine the property's value. Factors such as economic conditions, population growth, business expansion, and industry trends can impact the demand for commercial properties and affect their value and profitability. Commercial real estate offers several benefits for investors, making it an attractive asset class for wealth accumulation and portfolio diversification. Investing in commercial real estate can provide a reliable source of long-term income. Rental income from tenants can generate regular cash flow, potentially providing stable returns over an extended period. Commercial real estate can serve as a diversification tool within an investment portfolio. It has a low correlation with other asset classes like stocks and bonds, which can help reduce overall investment risk and increase portfolio stability. Commercial properties have the potential to appreciate in value over time, leading to capital gains for investors. Market dynamics, improvements in the property or surrounding area, and demand-supply dynamics can contribute to property appreciation. Investing in commercial real estate can offer various tax advantages, including depreciation deductions, mortgage interest deductions, and the potential for tax-deferred exchanges through 1031 exchanges. Commercial real estate is often considered a hedge against inflation. Rental income and property values tend to increase with inflation, helping to preserve and grow the real value of investments. While commercial real estate offers many benefits, it also comes with risks and challenges that investors should be aware of. Commercial real estate values can be sensitive to economic and market fluctuations. Economic recessions, changes in interest rates, and shifts in market conditions can impact property values, occupancy rates, and rental income. The success of a commercial property investment is dependent on securing and retaining reliable tenants. Tenant turnover, lease defaults, and vacancies can pose risks and affect cash flow and investment returns. Managing and maintaining commercial properties can be complex and require ongoing attention. Property management responsibilities, such as tenant relations, property maintenance, and repairs, can be time-consuming and involve additional costs. Financing commercial real estate acquisitions can involve significant borrowing and interest rate exposure. Changes in interest rates can impact borrowing costs, loan affordability, and investment returns. Commercial real estate investments are subject to various regulatory and legal requirements. Zoning regulations, building codes, environmental regulations, and tenant-related laws can affect property use, operational costs, and legal obligations. The core investment strategy focuses on acquiring stable and income-generating properties in prime locations. Investors seek long-term, steady returns with low risk and prioritize properties with reliable tenants and strong lease agreements. The value-add investment strategy involves acquiring properties with potential for improvement, renovation, or repositioning to increase their value. Investors aim to enhance cash flow and property appreciation by making strategic improvements and operational changes. The opportunistic investment strategy involves taking advantage of unique market opportunities, such as distressed properties or undervalued assets. Investors seek high-risk, high-reward opportunities and employ active management and value creation strategies. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and real estate funds offer investors the opportunity to gain exposure to commercial real estate through professionally managed portfolios. REITs are publicly traded entities that own and operate income-generating properties, while real estate funds pool investor capital to invest in a diversified portfolio of properties. Commercial Real Estate (CRE) refers to properties used for business purposes, such as office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial facilities. It encompasses a wide range of property types and plays a crucial role in the economy. Commercial Real Estate exhibits key characteristics such as income generation through leases, various valuation methods, sensitivity to market trends and demand, and the potential for long-term appreciation and capital gains. Investing in CRE offers benefits like potential for stable income, portfolio diversification, tax advantages, and inflation hedging. However, it also carries risks, including economic volatility, tenant and lease-related risks, property management challenges, financing risks, and regulatory and legal complexities. When approaching CRE investment, different strategies are available. Choosing the right strategy depends on risk tolerance, investment goals, and market conditions.What Is Commercial Real Estate?
Types of Commercial Real Estate
Office Buildings
Retail Properties
Industrial Properties
Multifamily Properties
Hospitality Properties
Special Purpose Properties

Key Characteristics of Commercial Real Estate
Income Generation
Lease Agreements
Valuation Methods
Market Trends and Demand
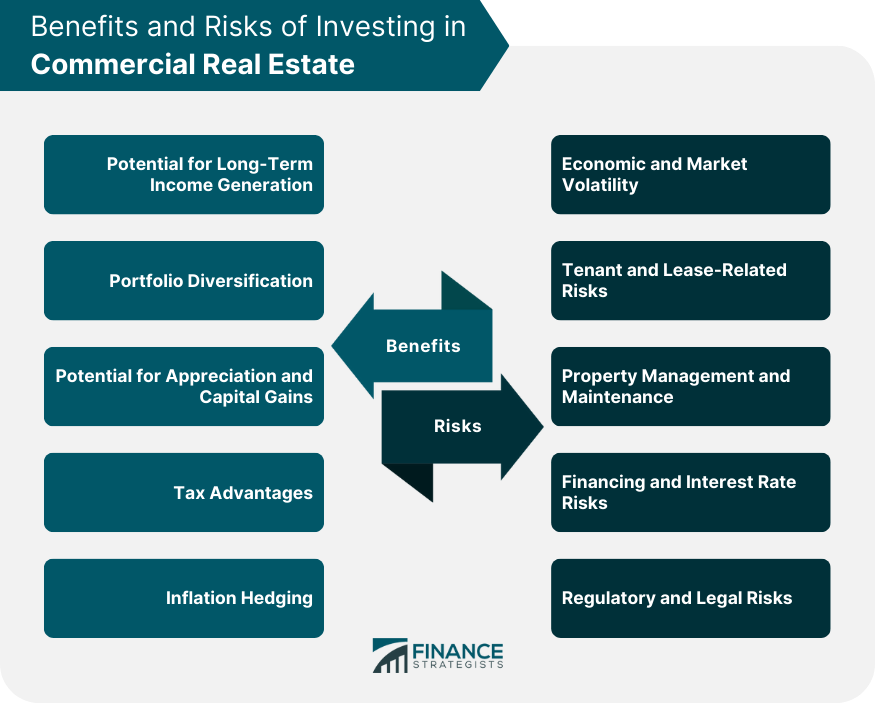
Benefits of Investing in Commercial Real Estate
Potential for Long-Term Income Generation
Portfolio Diversification
Potential for Appreciation and Capital Gains
Tax Advantages
Inflation Hedging
Risks and Challenges of Commercial Real Estate
Economic and Market Volatility
Tenant and Lease-Related Risks
Property Management and Maintenance
Financing and Interest Rate Risks
Regulatory and Legal Risks
Commercial Real Estate Investment Strategies
Core Investment Strategy
Value-Add Investment Strategy
Opportunistic Investment Strategy
REITs and Real Estate Funds
The Bottom Line
Commercial Real Estate FAQs
Commercial real estate refers to properties primarily used for business or income-generating purposes, such as office buildings, retail properties, industrial properties, multifamily properties, hospitality properties, and special purpose properties.
Commercial real estate plays a crucial role in the economy, providing spaces for businesses to operate, contributing to job creation, and generating income for investors. It supports economic growth in various sectors.
Investing in commercial real estate offers potential for long-term income generation, portfolio diversification, appreciation and capital gains, tax advantages, and inflation hedging.
Risks include economic and market volatility, tenant and lease-related risks, property management and maintenance, financing and interest rate risks, and regulatory and legal risks.
Investment strategies include core investment strategy, value-add investment strategy, opportunistic investment strategy, and investing through REITs and real estate funds. Each strategy caters to different risk-return objectives and investment preferences.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











