Lease rates are recurring payments made for the use of an asset, like a car, office space, or machinery, typically calculated on a monthly or yearly basis. The rate depends on factors such as the asset's value, lease term, and market conditions. They're pivotal in financial planning and budgeting as they impact the lessee's cost structure. For businesses, a high lease rate might inflate operational costs, potentially denting profitability. For individuals, lease rates affect personal finance management, influencing lifestyle and saving capacity. These rates reflect broader economic trends, thus providing context about market health. Negotiating favorable lease rates can significantly enhance financial efficiency, underscoring their importance in financial decision-making. The average cost of a commercial lease is $680.00. However, this figure is subject to fluctuation based on various elements. The kind of lease, the intricacy of the contract, and the geographical location of the property are all critical determinants that can influence the overall cost associated with a commercial leasing arrangement. Car lease rates are typically calculated using a money factor, which can be roughly equated to an annual interest rate divided by 2400, ranging from 0 to around 0.003 (0%-7.2% APR). Equipment lease rates also greatly depend on the type of equipment, its value, and the lease duration. Equipment with a value under $100,000 often carries a steeper finance rate, which can range between 8% and 20%. More costly, larger-scale equipment is typically leased at a comparatively lower financing rate, usually between 6% and 8%. Lease rates can be categorized into different types based on how they are structured. These include fixed lease rates, variable lease rates, graduated lease rates, percentage lease rates, and net lease rates. A fixed lease rate is a set amount that a tenant pays throughout the term of the lease. It is simple, straightforward, and does not change over time, providing stability for both the tenant and the landlord. Unlike fixed lease rates, variable lease rates can change over the lease term. Changes are usually pegged to a predetermined index, like the Consumer Price Index or an interest rate, providing a hedge against inflation for the landlord. A graduated lease rate is a type of lease rate that incrementally increases over the lease term. The increments and intervals are predetermined and written into the lease agreement, providing long-term visibility for the tenant. A percentage lease rate is commonly used in retail leasing. In this setup, the tenant pays a base rent and a percentage of their monthly or annual gross sales. In a net lease rate, the tenant not only pays a fixed rental amount but is also responsible for certain property expenses. These could include taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs. Net lease rates can further be categorized into single-net, double-net, and triple-net lease rates, depending on the responsibilities assigned to the tenant. Several factors influence lease rates. These include market conditions, location and property type, lease term, tenant creditworthiness, and the amenities and services included in the lease. Lease rates are highly susceptible to prevailing market conditions. When demand for properties outstrips supply, lease rates tend to increase, and vice versa. The location and type of a property are pivotal in determining its lease rate. Properties in prime locations and high-demand property types command higher lease rates. Long-term leases often have lower lease rates due to the stability they provide to landlords. Short-term leases may command higher rates due to the increased turnover risk for the landlord. A tenant's financial stability and creditworthiness can impact the lease rate. Landlords may charge a higher rate to riskier tenants to offset potential losses. Properties with more amenities and services tend to have higher lease rates. These can include things like cleaning services, security, and utilities. Calculating lease rates can be complex as it involves several variables. The method of calculation can vary depending on the type of lease rate. The basic formula for calculating the lease rate is to divide the total cost of the lease by the lease term. However, different types of leases require different considerations. Understanding how to calculate different types of lease rates is essential to accurately compare leasing options. Fixed lease rates are relatively simple to calculate, as they involve dividing the total cost by the length of the lease. For variable lease rates, the calculation needs to account for changes in the reference index over time. In graduated lease rates, each period's lease payment must be calculated individually based on the agreed increases. Percentage lease rates require the calculation of a percentage of the tenant's gross sales on top of the base rent. Net lease rates involve adding the tenant's proportionate share of the property's running costs to the base rent. Lease rates have significant implications for both tenants and landlords and also play a critical role in real estate investing. For tenants, the lease rate directly affects their cost of living or operating a business. Higher lease rates may result in reduced profitability for businesses or financial strain for residential tenants. For landlords, the lease rate affects their return on investment. Higher lease rates translate into higher profits, provided the property remains leased. Lease rates are a critical consideration for real estate investors. They directly affect a property's potential income and, therefore, its overall value. Lease rates, integral to personal finance and business budgeting, are influenced by various factors, including asset value, lease term, and market conditions. Average rates can vary, with commercial leases and equipment leases being subject to differing influencing elements. Lease rates take diverse forms, from fixed to variable, graduated, percentage, and net, each with distinct characteristics. Factors like market conditions, property location, lease term, tenant's creditworthiness, and included amenities can significantly sway lease rates. Understanding lease rate calculations is pivotal to making informed leasing decisions. These rates have far-reaching implications for tenants, landlords, and real estate investors, influencing profitability and overall value. Mastering the nuances of lease rates is a strategic step toward effective financial management and smart investment decisions.What Are Lease Rates?
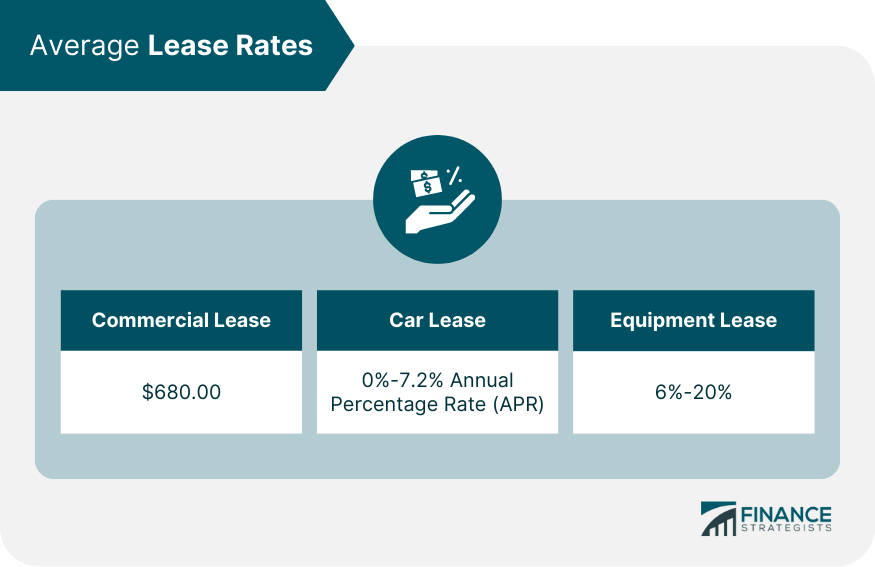
Average Lease Rates
Commercial Lease
Car Lease Rates
Equipment Lease Rates
Types of Lease Rates
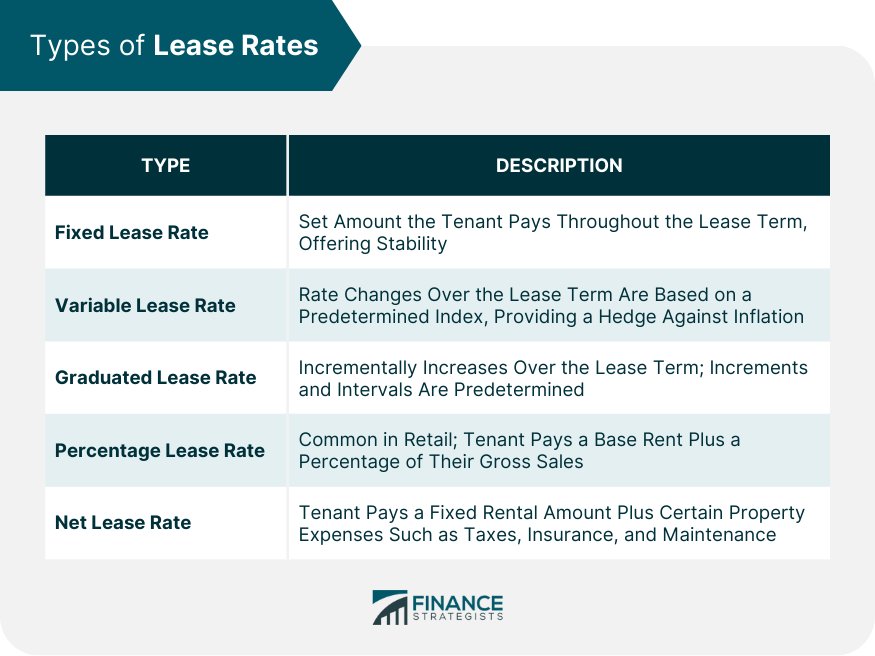
Fixed Lease Rate
Variable Lease Rate
Graduated Lease Rate
Percentage Lease Rate
Net Lease Rate
Factors Influencing Lease Rates
Market Conditions
Location and Property Type
Lease Term
Tenant Creditworthiness
Amenities and Services Included

Calculating Lease Rates
Overview of the Calculation Process
Specifics of Calculating Different Types of Lease Rates
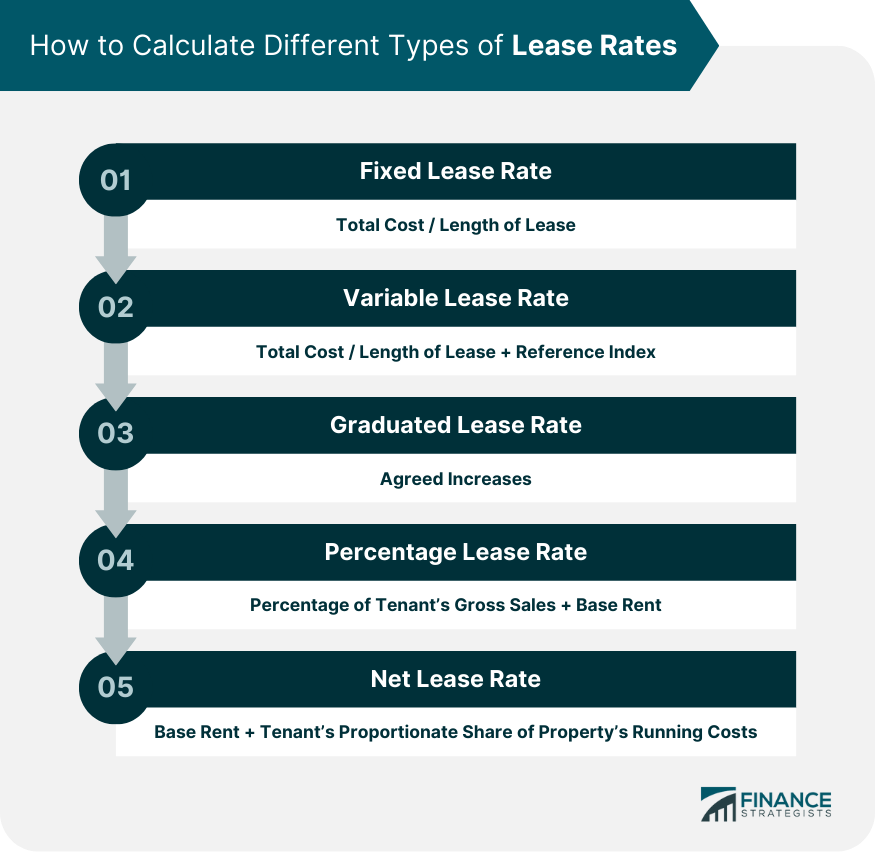
Fixed Lease Rate Calculation
Variable Lease Rate Calculation
Graduated Lease Rate Calculation
Percentage Lease Rate Calculation
Net Lease Rate Calculation
Implications of Lease Rates
Impact on Tenants
Impact on Landlords
Role in Real Estate Investing
Final Thoughts
Lease Rates FAQs
A lease rate is the amount a tenant is obligated to pay in rent over the duration of the lease. This rate is typically agreed upon before the lease starts and is clearly stated in the lease agreement.
There are several types of lease rates, including fixed lease rates, variable lease rates, graduated lease rates, percentage lease rates, and net lease rates. Each type is calculated and structured differently and is suitable for different leasing scenarios.
The basic formula for calculating a lease rate is to divide the total cost of the lease by the lease term. However, the method of calculation may vary depending on the type of lease rate. For instance, variable lease rates take into account changes in a reference index over time, while graduated lease rates require each period's lease payment to be calculated individually based on the agreed increases.
The lease rate directly affects the tenant's cost of living or operating a business and the landlord's return on investment. For tenants, a higher lease rate may lead to reduced profitability or financial strain. For landlords, higher lease rates increase profits, provided the property stays leased.
Future trends in lease rates can be influenced by several factors, including economic predictions, technological changes, and shifts in work and lifestyle trends. For example, anticipated economic growth can result in increased demand for properties and potential upward pressure on lease rates. Similarly, the rise of remote work could impact commercial property lease rates.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











