Definition of Real Estate Syndication
Real Estate Syndication is a collaborative investment strategy wherein multiple investors pool their financial resources and expertise to acquire, develop, or manage a property or portfolio of properties.
This collective approach enables participants to access more significant and potentially more profitable real estate opportunities than they could individually.
Key Players in Real Estate Syndication

Sponsors
Sponsors are responsible for identifying, acquiring, and managing the real estate investments within a syndicate. They bring industry knowledge and expertise to the table, ensuring the success of the venture.
Roles and Responsibilities
Sponsors are responsible for several tasks, including:
Identifying and acquiring investment properties
Securing financing and equity partners
Overseeing property management and operations
Coordinating with real estate professionals, such as brokers, attorneys, and accountants
Types of Sponsors
There are two main types of sponsors:
1. General Partners (GPs) are responsible for the day-to-day management of the syndicate and typically contribute a portion of the equity.
2. Limited Partners (LPs) are passive investors who contribute capital but do not participate in the day-to-day management of the syndicate.
Investors
Investors in real estate syndicates can be classified into two categories:
Active Investors
Active investors are those who actively participate in the management and decision-making process of the syndicate. They are typically general partners or sponsors.
Passive Investors
Passive investors contribute capital to the syndicate but do not participate in its management. They rely on the expertise of the sponsors to manage the investment and generate returns.
Real Estate Professionals
Real estate syndicates work with various professionals to ensure the success of their investments. Some of these professionals include:
Property managers
Real estate brokers
Attorneys
Accountants
Types of Real Estate Syndications
There are three primary types of real estate syndications:
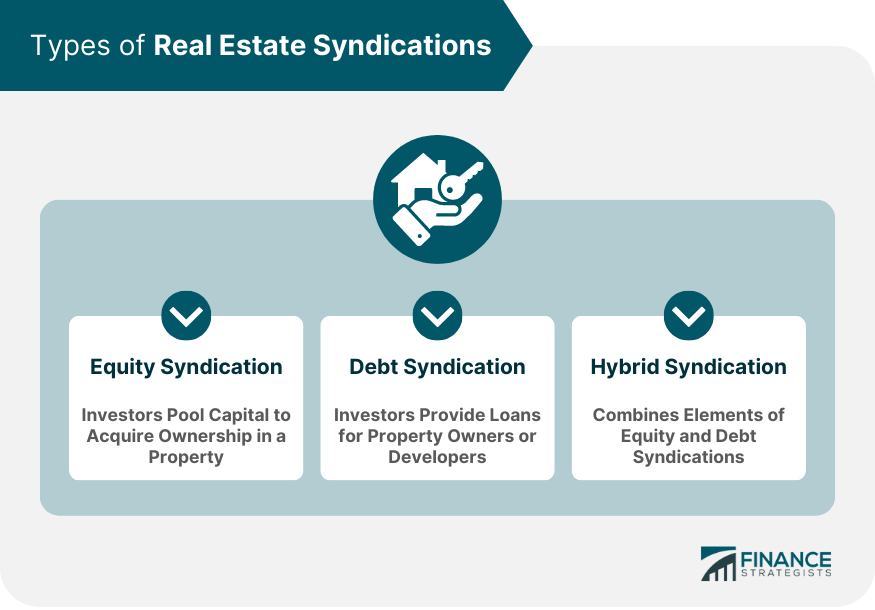
Equity Syndications
In equity syndications, investors pool their capital to acquire ownership of a property. They share in the property's cash flow, appreciation, and profits from the eventual sale of the property.
Debt Syndications
Debt syndications involve investors pooling their capital to provide loans for property owners or developers. The investors earn returns from the interest and principal repayments made by the borrower.
Hybrid Syndications
Hybrid syndications combine elements of both equity and debt syndications. Investors may provide both debt financing and equity investments in a single property or project.
Structure of Real Estate Syndication
Legal Structures
Real estate syndications can take on various legal structures, such as:
Limited Partnerships
Limited partnerships consist of one or more general partners who manage the syndicate and limited partners who contribute capital but do not participate in management. Limited partners have limited liability for the partnership's debts and obligations.
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
LLCs are popular legal structures for real estate syndications, offering limited liability protection for investors and flexible management options. They can be structured as single-member or multi-member LLCs.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
REITs are publicly traded or non-traded investment vehicles that pool investor capital to invest in income-producing real estate properties. REITs offer investors the benefits of real estate ownership without the direct responsibility of property management.
Investment Structures
Real estate syndications can be structured in various ways, including:
Direct Investment
Investors directly invest in the syndicate, either as equity partners or debt providers.
Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding platforms enable investors to pool their capital and invest in real estate syndications online. This method provides broader access to investment opportunities and simplifies the investment process for smaller investors.
Private Placements
Private placements involve raising capital from accredited investors through private offerings. These offerings are exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, provided they meet specific criteria.
Real Estate Syndication Process
The real estate syndication process involves several steps:

Identifying Investment Opportunities
Sponsors research and analyze potential investment properties, considering factors such as location, market conditions, property type, and potential returns.
Due Diligence and Property Analysis
Sponsors perform thorough due diligence on the selected properties, evaluating their physical condition, financial performance, and potential risks and rewards.
Assembling the Syndication Team
Sponsors assemble a team of real estate professionals, including property managers, brokers, attorneys, and accountants, to support the syndication process.
Securing Financing
Sponsors secure financing from banks, private lenders, or investors to fund the acquisition and management of the property.
Legal Documentation and Formation
Sponsors create the legal structure and draft the necessary documentation, such as operating agreements, private placement memorandums, and subscription agreements.
Property Acquisition and Management
Once the syndication is established, the sponsors acquire the property and oversee its management, including property improvements, leasing, and maintenance.
Exit Strategies and Distribution of Profits
Sponsors identify exit strategies, such as selling the property or refinancing, to generate returns for investors. Profits are distributed according to the agreed-upon terms in the syndication documents.
Regulatory and Compliance Aspects
Real estate syndications must adhere to several regulatory and compliance aspects, including:
Securities Laws and Exemptions
Securities laws govern the offering and sale of investments in real estate syndications. Syndicators must comply with these laws or qualify for exemptions, such as Regulation D private placements.
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Regulations
Real estate syndications must comply with SEC regulations, including filing appropriate forms and disclosures. Non-compliance can result in fines, penalties, or legal action.
State Securities Regulations
In addition to federal regulations, real estate syndications must also comply with state securities laws, which may vary from state to state.
Benefits of Real Estate Syndication
Real estate syndication offers several benefits for investors, including:
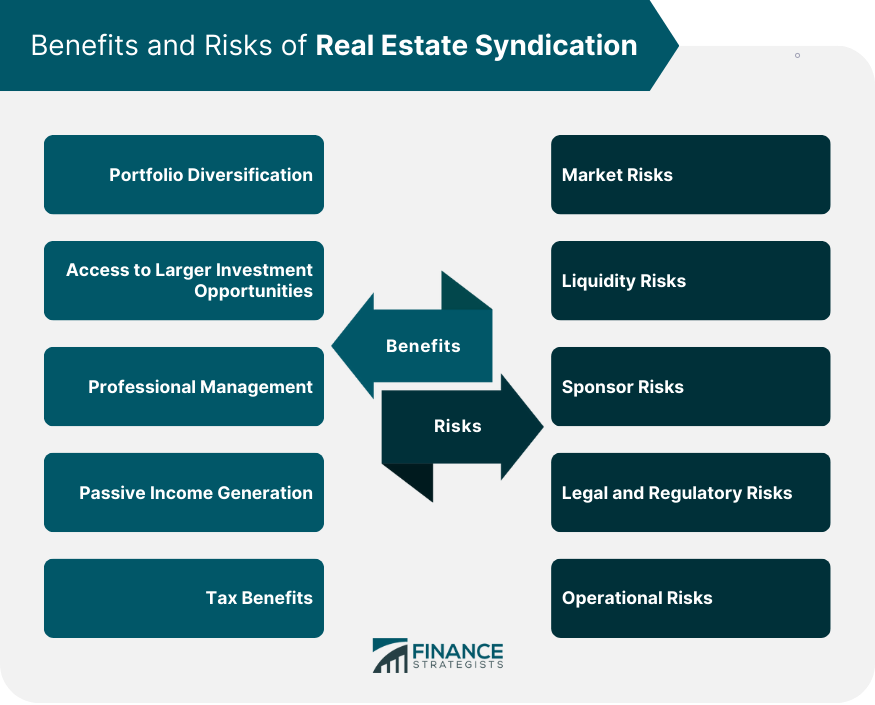
Portfolio Diversification
Investing in real estate syndications allows investors to diversify their portfolios by adding real estate assets, reducing the overall risk of their investments.
Access to Larger Investment Opportunities
By pooling resources, syndication investors can access larger, more profitable investment opportunities than they could individually.
Professional Management
Syndication investors benefit from the expertise of professional sponsors and real estate managers who oversee the acquisition and management of properties.
Passive Income Generation
Passive investors in real estate syndications can earn income from cash flow and property appreciation without actively managing the investment.
Tax Benefits
Real estate syndications offer various tax benefits, including depreciation deductions and pass-through taxation.
Risks and Challenges of Real Estate Syndication
Investing in real estate syndications comes with certain risks and challenges, such as:
Market Risks
Changes in market conditions, such as economic downturns or fluctuations in property values, can negatively impact the performance of real estate syndications.
Liquidity Risks
Real estate syndications are relatively illiquid investments, which means that investors may not be able to easily sell their interests or access their capital when needed.
Sponsor Risks
The success of syndication depends on the expertise and performance of the sponsor. Poor management or decision-making can result in losses for investors.
Legal and Regulatory Risks
Real estate syndications are subject to various legal and regulatory requirements, and non-compliance can result in financial penalties or legal disputes.
Operational Risks
Operational risks, such as property damage, tenant vacancies, or mismanagement, can adversely affect the performance of real estate syndications.
Best Practices for Real Estate Syndication Success
To maximize the potential for success in real estate syndications, investors and sponsors should consider the following best practices:
Sponsor Selection and Due Diligence
Investors should thoroughly research potential sponsors, evaluating their track record, experience, and reputation in the industry.
Communication and Transparency
Sponsors should maintain open lines of communication with investors, providing regular updates on property performance, financial results, and any significant events or changes.
Risk Management and Diversification
Investors should diversify their real estate syndication investments to reduce exposure to specific property types, markets, or sponsors.
Financial Planning and Analysis
Sponsors should conduct regular financial analyses of their syndication investments, evaluating performance against projections and adjusting strategies as needed.
Ongoing Education and Networking
Investors and sponsors should stay informed about industry trends and best practices by participating in educational events, networking with other professionals, and reading industry publications.
Conclusion
Real estate syndication is a powerful investment strategy that allows multiple investors to pool their resources and expertise to access more significant and profitable real estate opportunities.
Key players in syndications include sponsors, investors, and real estate professionals, while legal structures can range from limited partnerships to LLCs and REITs.
There are various types of syndications, such as equity, debt, and hybrid, each with its own benefits and risks.
To ensure success, it is crucial for investors and sponsors to follow best practices, including thorough due diligence, effective communication, risk management, and ongoing education.
By understanding the intricacies of real estate syndication, investors can unlock its potential and diversify their investment portfolios while generating passive income and enjoying the benefits of professional management.
Real Estate Syndication FAQs
Real estate syndication is a method of pooling financial resources and expertise from multiple investors to invest in larger, more lucrative properties than they could individually. The process involves key players such as sponsors, investors, and real estate professionals working together to acquire, manage, and eventually sell the property or generate income from its operations.
There are three primary types of real estate syndications: equity syndications, debt syndications, and hybrid syndications. Equity syndications involve investors pooling their capital to acquire ownership of a property, while debt syndications involve investors providing loans for property owners or developers. Hybrid syndications combine elements of both equity and debt syndications.
Investing in real estate syndications offers several benefits, including portfolio diversification, access to larger investment opportunities, professional management, passive income generation, and tax benefits. These advantages can make real estate syndications an attractive option for investors seeking to expand their investment portfolios.
Some risks associated with real estate syndications include market risks, liquidity risks, sponsor risks, legal and regulatory risks, and operational risks. Investors should carefully consider these risks before participating in syndication and conduct thorough due diligence to minimize potential losses.
To get started with real estate syndication investments, you can research potential sponsors, investment opportunities, and legal structures. Consider networking with other investors, joining real estate investment groups, or participating in industry events to learn more about syndication opportunities. Additionally, you can explore online crowdfunding platforms that offer access to syndicated investments. It's essential to conduct thorough due diligence before investing in any real estate syndication to ensure a successful outcome.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











