A sale-leaseback agreement is a financial arrangement in which an owner sells an asset, typically real estate, to another party and subsequently leases it back for continued use. This transaction enables the original owner to access capital tied up in the asset while maintaining its operational benefits. The primary goal of a sale-leaseback transaction is to provide companies with access to capital without having to rely on traditional financing methods. Some benefits of these transactions include: Improved liquidity Increased financial flexibility Reduced debt levels Potential tax benefits Better management of assets The main parties involved in a sale-leaseback agreement are the seller-lessee, who is the original owner of the asset, and the buyer-lessor, who acquires the asset and leases it back to the seller. Sale-leaseback agreements are a popular financing option for companies that own valuable assets such as real estate or equipment. This arrangement provides the company with immediate cash while allowing it to continue using the assets. The industries that commonly utilize sale-leaseback agreements include manufacturing, retail, hospitality, and healthcare. Manufacturing companies often own large, expensive pieces of equipment that they use to produce their products. By entering into a sale-leaseback agreement, these companies can unlock the value of their equipment and use the cash to invest in other areas of their business. Retailers may also use sale-leaseback agreements to finance their operations, particularly if they own prime real estate locations. In the hospitality industry, sale-leaseback agreements are often used to finance hotels and resorts. These properties are typically expensive to build or acquire, and a sale-leaseback transaction can provide the necessary capital to purchase or improve them. Healthcare companies may also use sale-leaseback agreements to finance the construction or renovation of medical facilities. Sale-leaseback agreements provide companies with a flexible financing option that can help them unlock the value of their assets while continuing to use them in their operations. Sale-leaseback transactions typically has two main components: the sale of the asset and the leaseback of the asset. The asset's value is determined through an appraisal process that considers factors such as the asset's location, condition, market value, and potential income generation. The sale price is negotiated between the seller and the buyer, taking into account the asset's valuation and other relevant factors. Once the sale price is agreed upon, the ownership of the asset is transferred from the seller to the buyer. The lease agreement is negotiated and executed, outlining terms such as lease duration, rent payments, and responsibilities of the lessee and lessor. Rent payments are usually made monthly or quarterly, and the lease duration can vary from short-term to long-term, depending on the parties' preferences and business objectives. The lease agreement outlines the specific responsibilities of both parties, such as maintenance, insurance, and taxes. Sale-leaseback transactions have various financial and tax implications for both the seller-lessee and the buyer-lessor. By engaging in a sale-leaseback transaction, a company can improve its balance sheet by converting a fixed asset into cash and reducing debt levels. This can lead to improved financial ratios, such as debt-to-equity and return on assets. Seller-lessees may benefit from tax advantages such as the ability to deduct rent payments as a business expense and defer capital gains taxes on the sale of the asset. Buyer-lessors can benefit from depreciation deductions on the acquired asset and tax deductions on interest expenses related to the acquisition. There are some risks and disadvantages to consider, such as potential tax liabilities, loss of control over the asset, and the potential impact on credit ratings. Sale-leaseback agreements involve various legal and regulatory aspects that need to be addressed to ensure a smooth transaction. A well-drafted sale-leaseback agreement should clearly outline the rights and obligations of both parties, including provisions related to the sale, lease terms, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Both parties must comply with all applicable laws and regulations, such as zoning laws, environmental regulations, and tax laws, to avoid potential legal issues. It is essential for both parties to conduct thorough due diligence to identify and mitigate potential risks associated with the transaction, including assessing the asset's condition, legal status, and potential liabilities. Disputes may arise in sale-leaseback transactions related to issues such as rent payments, lease terms, or asset maintenance. It is crucial to have a clear dispute resolution mechanism in place to address any conflicts efficiently and fairly. Sale-leaseback agreements are a flexible financing option for companies that own valuable assets, such as real estate or equipment. By engaging in a sale-leaseback transaction, companies can unlock the value of their assets while continuing to use them in their operations. The primary benefits of these transactions include improved liquidity, increased financial flexibility, reduced debt levels, and potential tax advantages. The key participants in a sale-leaseback agreement are the seller-lessee and the buyer-lessor, who negotiate the sale price, transfer ownership, and establish lease terms. While there are risks and disadvantages to consider, such as potential tax liabilities and loss of control over the asset, a well-drafted sale-leaseback agreement can help companies mitigate these risks. Finally, compliance with relevant laws and regulations, thorough due diligence, and clear dispute resolution mechanisms are essential for a successful sale-leaseback transaction. Overall, sale-leaseback agreements can provide companies with a valuable financing tool to boost their financial flexibility and growth.Definition of Sale-Leaseback Agreements
Purpose and Benefits of Sale-Leaseback Transactions
Key Participants in Sale-Leaseback Agreements
Common Industries Utilizing Sale-Leaseback Agreements
Manufacturing
Retailers
Hospitality Industry
Healthcare
Structure of Sale-Leaseback Agreements
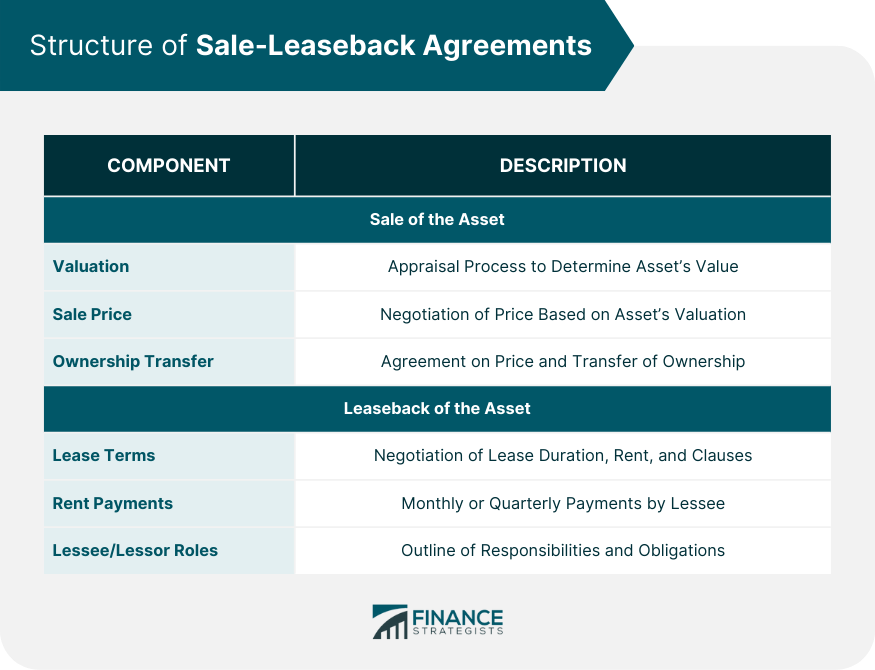
Sale of the Asset
Valuation of the Asset
Negotiation of Sale Price
Transfer of Ownership
Leaseback of the Asset
Lease Terms and Conditions
Rent Payments and Lease Duration
Responsibilities of the Lessee and Lessor
Financial and Tax Implications of Sale-Leaseback Agreements
Impact on Balance Sheet and Financial Ratios
Tax Advantages for Seller-Lessees
Tax Implications for Buyer-Lessors
Potential Risks and Disadvantages
Legal and Regulatory Considerations of Sale-Leaseback Agreements
Contractual Terms and Provisions
Compliance with Relevant Laws and Regulations
Due Diligence Requirements
Potential Legal Disputes and Resolutions
Bottom Line
Sale-Leaseback Agreements FAQs
Sale-leaseback agreements offer businesses several benefits, including improved liquidity, increased financial flexibility, reduced debt levels, potential tax advantages, and better management of assets.
Sale-leaseback agreements can improve a company's balance sheet by converting a fixed asset into cash and reducing debt levels. This can result in improved financial ratios, such as debt-to-equity and return on assets.
Seller-lessees can benefit from tax advantages in sale-leaseback agreements, such as the ability to deduct rent payments as a business expense and defer capital gains taxes on the sale of the asset.
Legal and regulatory considerations in sale-leaseback agreements include drafting clear contractual terms and provisions, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations, conducting thorough due diligence, and establishing a dispute resolution mechanism.
Growth of sale-leaseback agreements in emerging industries, innovations in structuring transactions, the role of technology in facilitating agreements, and the potential impact of economic, political, and regulatory changes, may influence the popularity and structure of sale-leaseback transactions in the business landscape.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











