Shareholder Engagement and Proxy Voting: Overview
Shareholder engagement and proxy voting are two essential components of corporate governance.
Shareholder engagement involves companies' interactions with their shareholders to foster a positive relationship and obtain input on important matters such as executive compensation, social responsibility, and strategic direction.
On the other hand, proxy voting is the mechanism through which shareholders can exercise their voting rights on matters brought up for a vote at annual meetings, including the election of directors, approval of executive pay, and other significant corporate decisions.
Effective shareholder engagement and proxy voting can increase transparency, accountability, and long-term value creation for all stakeholders.
What Is Shareholder Engagement?
Shareholder engagement is the process through which shareholders communicate with a company's management and board of directors to discuss various issues and concerns related to the company's performance, governance, and long-term value creation.
Shareholder engagement can take various forms, such as meetings, conference calls, written correspondence, or electronic communications.
Benefits of Shareholder Engagement
Engaging with shareholders can provide several benefits to companies, including:
1. Improved Corporate Performance: Effective shareholder engagement can lead to better decision-making, as management and boards can gain valuable insights from shareholders regarding company performance and strategic direction.
2. Enhanced Long-Term Value Creation: Companies can better align their strategies with shareholder interests by engaging with shareholders, leading to greater long-term value creation for all stakeholders.
3. Strengthened Accountability and Transparency: Shareholder engagement can promote greater transparency and accountability within a company as management, and boards become more responsive to shareholder concerns and expectations.
Key Stakeholders Involved in Shareholder Engagement
Several stakeholders play essential roles in shareholder engagement:
1. Individual Shareholders: Retail investors who own shares of a company and seek to protect their investments by engaging with management and boards on various issues.
2. Institutional Investors: Large organizations, such as pension funds, mutual funds, and insurance companies, that invest in companies on behalf of their clients and have a significant influence on corporate decision-making through their engagement efforts.
3. Corporate Boards and Management: A company's leadership is responsible for addressing shareholder concerns and making decisions that promote long-term value creation for all stakeholders.
What Is Proxy Voting?
Proxy voting is the process through which shareholders delegate their voting rights to another party, often a professional proxy voting agent, to vote on their behalf at company meetings.
This process enables shareholders to participate in corporate decision-making without attending the meetings in person.
Role of Proxy Voting in Shareholder Engagement

Proxy voting is an essential aspect of shareholder engagement, as it enables shareholders to:
1. Facilitate Participation: Proxy voting allows shareholders to participate in company meetings and vote on critical issues, even if they cannot attend the meetings in person.
2. Express Shareholder Interests: Through proxy voting, shareholders can express their views and preferences on various matters, such as executive compensation, board composition, and corporate governance policies.
3. Influence Corporate Decisions: Shareholders can exert pressure on management and boards by voting against proposals that they deem unfavorable, promoting better decision-making and accountability.
Proxy Advisory Firms
Proxy advisory firms play a crucial role in the proxy voting process by providing research, analysis, and recommendations to institutional investors on how to vote on various issues presented at company meetings.
These firms significantly influence proxy voting outcomes due to the vast number of institutional investors relying on their advice.
However, the regulatory environment surrounding proxy advisory firms is evolving, with regulators increasingly scrutinizing their practices and potential conflicts of interest.
Best Practices for Shareholder Engagement and Proxy Voting
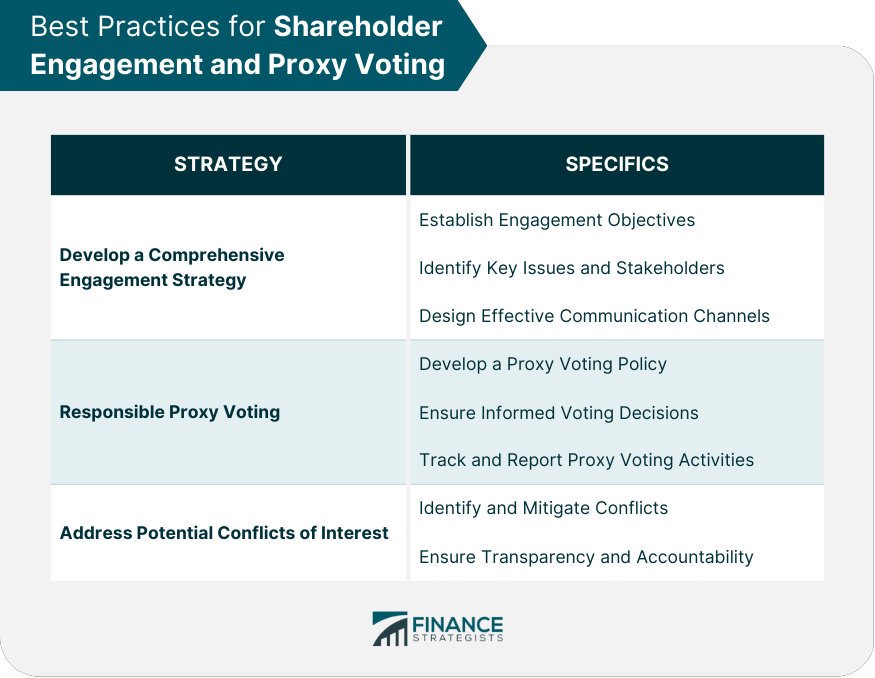
Developing a Comprehensive Engagement Strategy
Companies should adopt a well-rounded engagement strategy to facilitate productive communication with shareholders, incorporating the following elements:
Establishing Engagement Objectives
Companies should clearly define their goals for shareholder engagement, such as improving transparency, soliciting feedback on corporate strategy, or addressing specific shareholder concerns.
Identifying Key Issues and Stakeholders
Companies should prioritize the most critical issues and stakeholders for engagement, focusing their efforts on addressing concerns that are likely to have the most significant impact on the company's performance and shareholder value.
Designing Effective Communication Channels
Companies should develop appropriate communication channels, such as email, webcasts, and social media platforms, ensuring that shareholders have ample opportunities to voice their concerns and receive timely responses from the company.
Responsible Proxy Voting
Shareholders, particularly institutional investors, should adopt responsible proxy voting practices to protect their interests and promote long-term value creation, including:
Developing a Proxy Voting Policy
Investors should establish a comprehensive proxy voting policy that outlines their approach to voting on various issues, taking into consideration factors such as company performance, corporate governance practices, and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria.
Ensuring Informed Voting Decisions
Shareholders should make well-informed voting decisions based on thorough research and analysis rather than blindly following the recommendations of proxy advisory firms.
Tracking and Reporting Proxy Voting Activities
Investors should maintain accurate records of their proxy voting activities and report them to their clients or beneficiaries, promoting transparency and accountability.
Addressing Potential Conflicts of Interest
Both companies and shareholders should proactively identify and address potential conflicts of interest in the engagement and proxy voting process, ensuring that decision-making remains unbiased and aligned with shareholder interests.
Identifying and Mitigating Conflicts
Companies and investors should regularly assess their engagement and proxy voting activities for potential conflicts of interest, implementing measures to mitigate or eliminate such conflicts when they arise.
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Companies and investors should disclose relevant information about their engagement and proxy voting activities, including any potential conflicts of interest, to promote transparency and maintain the trust of all stakeholders.
Final Thoughts
Social engagement and proxy voting are essential elements of corporate governance, allowing shareholders to participate actively in decision-making processes and hold management accountable for their actions.
As companies and investors navigate the evolving landscape of shareholder engagement and proxy voting, they should adopt best practices, address potential conflicts of interest, and remain aware of emerging trends to promote long-term value creation for all stakeholders.
The future of shareholder engagement and proxy voting will likely be characterized by an increased focus on ESG factors, continued technological advancements, and a dynamic regulatory environment.
In light of these complexities and the increasing importance of effective shareholder engagement and proxy voting, it is crucial for investors to seek professional guidance.
Wealth management services can help you navigate the complexities of shareholder engagement, proxy voting, and the broader investment landscape.
By leveraging expert advice, you can make well-informed decisions that align with your values and investment objectives, ultimately maximizing your portfolio's potential for long-term growth and value creation.
Shareholder Engagement and Proxy Voting FAQs
Shareholder engagement is the process through which shareholders communicate with a company's management and board of directors to discuss various issues and concerns related to the company's performance, governance, and long-term value creation. Engaging with shareholders can provide several benefits to companies, including improved corporate performance, enhanced long-term value creation, and strengthened accountability and transparency.
Several stakeholders play essential roles in shareholder engagement, including individual shareholders, institutional investors, and corporate boards and management.
Proxy voting is the process through which shareholders delegate their voting rights to another party, often a professional proxy voting agent, to vote on their behalf at company meetings. This process enables shareholders to participate in corporate decision-making without attending the meetings in person. Proxy voting is an essential aspect of shareholder engagement as it enables shareholders to facilitate participation, express shareholder interests, and influence corporate decisions.
Proxy advisory firms provide research, analysis, and recommendations to institutional investors on how to vote on various issues presented at company meetings. These firms significantly influence proxy voting outcomes due to the vast number of institutional investors relying on their advice.
Companies should adopt a well-rounded engagement strategy, including establishing engagement objectives, identifying key issues and stakeholders, and designing effective communication channels. Shareholders, particularly institutional investors, should adopt responsible proxy voting practices, including developing a proxy voting policy, ensuring informed voting decisions, and tracking and reporting proxy voting activities.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











