Blue-chip stocks refer to shares of well-established, financially stable, and leading companies in their respective industries. These companies have a long track record of consistent performance, strong financials, and often pay regular dividends to shareholders. The term "blue-chip" is derived from poker, where the blue chips hold the highest value. Similarly, blue-chip stocks represent high-value investments due to the stability and reliability of the underlying companies. Blue-chip stocks typically have the following characteristics: Market leadership and dominance in their respective industries A long history of financial stability and consistent performance A strong balance sheet and credit rating Regular dividend payments to shareholders Global presence and brand recognition Blue-chip stocks are a crucial component of many investment portfolios due to their stability, long-term growth potential, and income generation through dividends. They can help investors achieve diversification, reduce portfolio volatility, and preserve capital during economic downturns. Some well-known blue-chip technology stocks include Apple Inc., Microsoft Corporation, and Alphabet Inc. (the parent company of Google). Examples of blue-chip healthcare stocks are Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer Inc., and Merck & Co., Inc. Prominent blue-chip consumer goods stocks include The Procter & Gamble Company, The Coca-Cola Company, and Walmart Inc. Leading blue-chip financial services stocks consist of JPMorgan Chase & Co., Visa Inc., and Goldman Sachs Group Inc. Examples of blue-chip industrial stocks are The Boeing Company, Caterpillar Inc., and 3M Company. Blue-chip stocks are known for their stable growth and consistent dividend payments, which can provide investors with a steady stream of income and capital appreciation over the long term. Blue-chip companies have strong financials, including robust balance sheets and high credit ratings. This financial strength provides a solid foundation for these companies to weather economic downturns and maintain their competitive edge. Blue-chip stocks are generally more resilient during economic downturns, as these companies have the resources and market presence to navigate challenging conditions. This resilience can help protect investors' capital during periods of market volatility. Investing in blue-chip stocks across various sectors can help investors achieve diversification in their portfolios, reducing risk and enhancing long-term returns. Blue-chip companies often have a significant global presence, allowing them to benefit from growth opportunities in emerging markets and maintain their market dominance. Blue-chip stocks can sometimes become overvalued due to their perceived safety and strong performance history. Investors should carefully consider valuation metrics before investing in blue-chip stocks to avoid overpaying for shares. While blue-chip stocks offer stability and consistent returns, their growth potential may be more limited compared to smaller, high-growth companies. Investors seeking higher returns may need to consider other investment options. Blue-chip companies, due to their size and market dominance, can be subject to regulatory scrutiny and legal challenges, which may impact their stock prices and overall performance Blue-chip companies may face competition from smaller, more agile competitors or disruptive technologies that could potentially erode their market share and impact their growth prospects. When evaluating blue-chip stocks for investment, investors should consider various financial metrics, including: Earnings Growth: A consistent track record of earnings growth is indicative of a company's ability to increase profitability over time. Dividend Yield and Payout Ratio: A healthy dividend yield and sustainable payout ratio can signal a company's commitment to returning value to shareholders. Price-to-Earnings Ratio: A reasonable price-to-earnings ratio can help investors avoid overvalued stocks and identify potential investment opportunities. Debt-to-Equity Ratio: A low debt-to-equity ratio indicates a company's financial stability and ability to manage debt effectively. In addition to financial metrics, investors should consider various qualitative factors when evaluating blue-chip stocks: Competitive Advantage: A strong competitive advantage, such as a unique product or service offering, can help a company maintain its market position and fend off competitors. Management Quality: Effective and experienced management teams can drive a company's long-term growth and success. Industry Outlook: A positive industry outlook can create a supportive environment for blue-chip companies to thrive and grow. Brand Strength: A well-known and respected brand can contribute to a company's market dominance and pricing power. Blue-chip stocks are well-suited for long-term investing due to their stability, growth potential, and income generation capabilities. Investors can take advantage of dividend reinvestment plans (DRIPs) offered by many blue-chip companies, which automatically reinvest dividends into additional shares, potentially accelerating portfolio growth over time. Dollar-cost averaging, the practice of investing a fixed amount in a particular stock at regular intervals, can help investors mitigate the impact of market volatility and reduce the risk of poor market timing when investing in blue-chip stocks. Incorporating blue-chip stocks across various sectors can help investors achieve a diversified portfolio, reducing risk and enhancing long-term returns. The DJIA is a widely-followed index that tracks 30 large, blue-chip U.S. stocks across various industries, serving as a barometer for the overall health of the stock market and the U.S. economy. The S&P 500 Index is a broader market index that includes 500 large-cap U.S. companies, many of which are considered blue-chip stocks. This index is often used as a benchmark for U.S. equity market performance. The NASDAQ-100 Index comprises the 100 largest non-financial companies listed on the NASDAQ Stock Market, including many prominent blue-chip technology and biotechnology stocks. Investors can gain exposure to blue-chip stocks through exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track blue-chip indexes, such as the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA), the iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV), or the Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ). Blue-chip stocks represent shares of well-established, financially stable, and industry-leading companies. They offer investors stable growth, consistent dividends, and resilience during economic downturns. Although blue-chip stocks have their advantages, investors must also be aware of potential risks, such as overvaluation concerns, limited growth potential, and competition. Blue-chip stocks can be an essential component of a long-term investment strategy due to their stability and income generation capabilities. By incorporating blue-chip stocks into their portfolios, investors can achieve diversification, reduce risk, and enhance long-term returns. The future outlook for blue-chip stocks remains promising, as these companies continue to maintain their market dominance and capitalize on global growth opportunities. As the financial market evolves, blue-chip stocks will continue to play a significant role in the investment landscape, providing stability and income for investors seeking long-term growth and capital preservation.What Are Blue-Chip Stocks?
Definition of Blue-Chip Stocks
Origin of the Term "Blue-Chip"
Characteristics of Blue-Chip Stocks
Importance of Blue-Chip Stocks in the Investment Portfolio
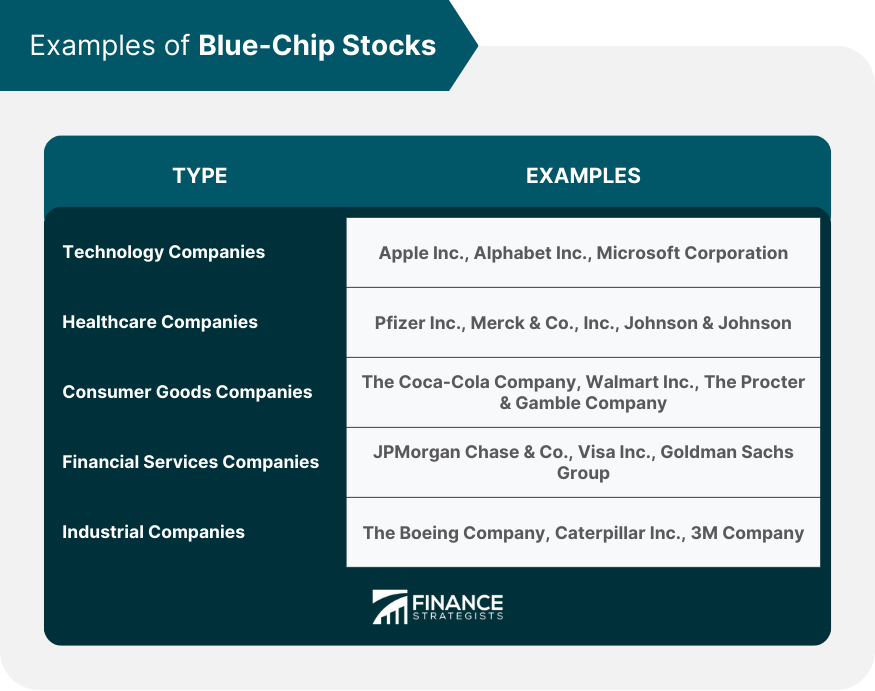
Examples of Blue-Chip Stocks
Technology Companies
Healthcare Companies
Consumer Goods Companies
Financial Services Companies
Industrial Companies
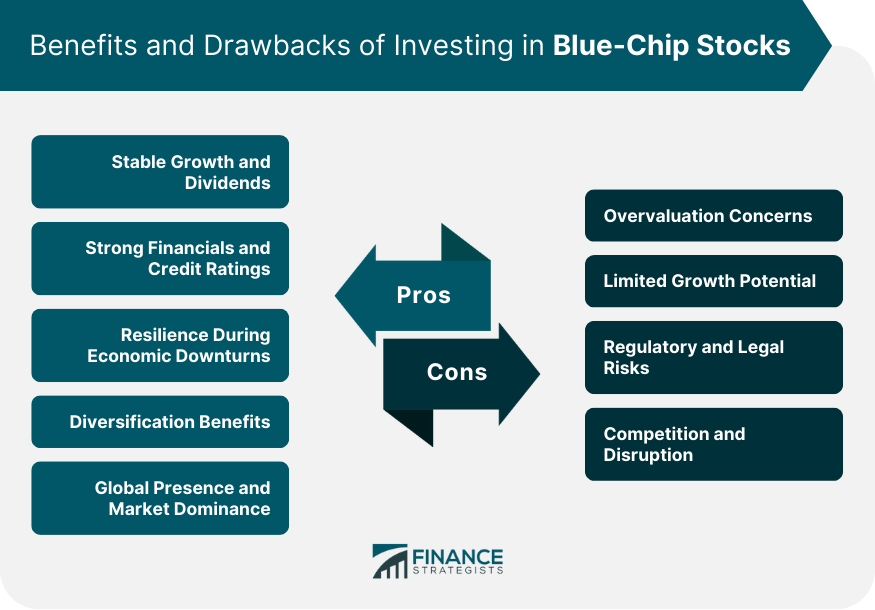
Advantages of Investing in Blue-Chip Stocks
Stable Growth and Dividends
Strong Financials and Credit Ratings
Resilience During Economic Downturns
Diversification Benefits
Global Presence and Market Dominance
Potential Risks and Drawbacks of Blue-Chip Stocks
Overvaluation Concerns
Limited Growth Potential
Regulatory and Legal Risks
Competition and Disruption
Evaluating Blue-Chip Stocks for Investment
Financial Metrics
Qualitative Factors
Incorporating Blue-Chip Stocks Into an Investment Strategy
Long-Term Investing
Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs)
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Portfolio Diversification
Blue-Chip Stock Indexes and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA)
S&P 500 Index
NASDAQ-100 Index
Select Blue-Chip ETFs
Conclusion
Blue-Chip Stocks FAQs
Blue-chip stocks are stocks of well-established companies with a long history of stable earnings and strong financials. They are typically market leaders in their industry and have a reputation for reliability and stability. Examples of blue-chip stocks include companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Johnson & Johnson.
Blue-chip stocks are considered a good investment because they tend to be less volatile than other stocks and have a track record of consistent growth. They also tend to pay steady dividends, which can provide investors with a reliable source of income. Additionally, blue-chip stocks are often seen as a safe haven during economic downturns, as investors tend to flock to stable, reliable companies during uncertain times.
You can buy blue-chip stocks through a brokerage account. Many online brokerage firms offer access to blue-chip stocks, and you can buy and sell shares using their trading platforms. You can also invest in blue-chip stocks through mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that focus on blue-chip companies.
Although blue-chip stocks are generally considered a safe investment, there are still risks involved. The value of the stock can still fluctuate based on market conditions, and there is always the risk of a company experiencing financial difficulties or unexpected events that can negatively impact its stock price. Additionally, blue-chip stocks may not offer the same level of growth potential as smaller, more volatile stocks.
When choosing which blue-chip stocks to invest in, it's important to consider factors such as the company's financial health, market position, growth potential, and dividend history. You should also consider the stock's valuation and whether it is trading at a reasonable price relative to its earnings or other financial metrics. Conducting thorough research and analysis of the company and its industry can help you make an informed investment decision.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











