Large-cap stocks are shares of companies with a market capitalization of $10 billion or more. The market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the company's share price by the number of outstanding shares. A company with a market capitalization of $10 billion or more is considered a large-cap stock. These stocks are typically issued by well-established companies that have been in operation for many years and have a proven track record of success. Examples of large-cap stocks include well-known companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon. Investors often include large-cap stocks in their portfolios to help mitigate risk and provide stability. These stocks tend to be less volatile than smaller, less established companies, making them an attractive investment option for many investors. In addition, large-cap companies often have more resources and market power than smaller companies, allowing them to weather economic storms and continue to perform well over time. Large-cap stocks can be an essential component of any well-diversified investment portfolio. They can provide investors with stability, diversification, and steady returns over time. As previously mentioned, large-cap stocks are defined by their market capitalization of $10 billion or more. These companies tend to be the largest in their respective industries and may have a dominant market position. Large-cap companies tend to generate significant revenue due to their size and market position. This revenue can help support the company's operations and provide a stable source of income for investors. Large-cap companies often have strong profitability due to their market position and economies of scale. This profitability can translate into steady returns for investors. Large-cap companies are often well-established and have a long track record of success. This stability can provide investors with confidence in the company's ability to weather economic storms and continue to perform well over time. Many large-cap companies distribute dividends to their shareholders. These dividends can provide investors with a reliable source of income and help to offset potential losses during market downturns. One of the primary advantages of investing in large-cap stocks is their lower risk profile. These stocks are issued by well-established companies with a proven track record of success and market dominance. This makes them less susceptible to market volatility and other external factors that can impact the stock price of smaller companies. Large-cap stocks tend to have more stable earnings and revenue, making them a more stable investment option. Additionally, large-cap companies have a higher level of financial stability, which helps them to weather economic storms and continue to perform well over time. This defensive quality makes them a preferred choice for conservative investors who prioritize capital preservation over aggressive returns. Large-cap stocks can provide investors with steady returns over time. While these returns may not be as high as those offered by smaller, more volatile companies, they tend to be more consistent and reliable. Large-cap companies often have predictable earnings and revenue growth, making it easier for investors to estimate future returns. These companies typically have a strong competitive position in their respective industries, leading to more stable and predictable growth. Furthermore, large-cap companies tend to have a history of paying dividends to their shareholders, which can provide investors with a reliable source of income and offset potential losses during market downturns. Large-cap stocks are typically very liquid, meaning that they can be bought and sold quickly and easily. This liquidity can be particularly appealing to investors who need to access their funds quickly. Large-cap companies tend to have higher trading volumes and a larger number of investors, making it easier to buy and sell shares without significant price impact. This liquidity can also make it easier for investors to enter or exit a position without incurring significant transaction costs. Investing in large-cap stocks can help to diversify an investor's portfolio. Large-cap companies span a wide range of industries and sectors, providing investors with exposure to different areas of the market. This diversification can help investors to spread their risk and reduce the impact of market fluctuations. Investing in a mix of large-cap stocks from different sectors can help to create a well-diversified portfolio that balances risk and return. One of the main disadvantages of investing in large-cap stocks is their limited growth potential. These companies are already established in their respective industries, and their size and market position can make it challenging for them to achieve significant growth over time. In addition, larger companies may face more regulatory scrutiny and higher barriers to entry, limiting their ability to innovate or expand into new markets. While large-cap companies may have a strong competitive position in their respective industries, they may struggle to maintain their growth rates over time, leading to lower returns for investors. Large-cap companies may be slower to adapt to changes in the market or implement new strategies. This lack of flexibility can make it challenging for these companies to stay competitive over time. For example, large-cap companies may be slower to embrace new technologies or business models, making it difficult for them to keep up with smaller, more agile competitors. Additionally, large-cap companies may be more bureaucratic and less able to respond quickly to changing market conditions. This lack of flexibility can limit their ability to generate growth or outperform their peers. While large-cap stocks may be less volatile than smaller companies, they are still exposed to market fluctuations. Economic downturns or changes in interest rates can impact these stocks, potentially leading to losses for investors. In addition, large-cap companies may be more vulnerable to geopolitical events or other external factors that can impact their business operations. While large-cap companies may be more stable than smaller companies, they are not immune to market risks. One strategy for investing in large-cap stocks is the buy and hold strategy. This strategy involves purchasing shares of large-cap companies and holding them for the long term, regardless of short-term market fluctuations. This strategy can help to minimize risk and maximize returns over time. Another strategy for investing in large-cap stocks is the value investing strategy. This involves identifying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals and holding them until they reach their true value. This strategy can help investors to identify high-quality stocks that may be trading at a discount. The growth investing strategy involves identifying companies with strong growth potential and investing in them early on. This strategy can help investors to identify companies that may become large-cap stocks in the future and benefit from their growth potential. Finally, the income investing strategy involves investing in large-cap stocks that pay dividends. This strategy can provide investors with a reliable source of income and help to offset potential losses during market downturns. Large-cap stocks are an important part of any well-diversified investment portfolio. These stocks provide stability, steady returns, liquidity, and diversification. While they may have some limitations, such as limited growth potential or lack of flexibility, their defensive qualities make them a valuable addition to any investor's portfolio. By understanding the key characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and strategies for investing in large-cap stocks, investors can make informed decisions and create a well-rounded investment strategy that meets their long-term goals.Definition of Large-Cap Stocks
Characteristics of Large-Cap Stocks
Market Capitalization
Revenue
Profitability
Stability
Dividend Payouts
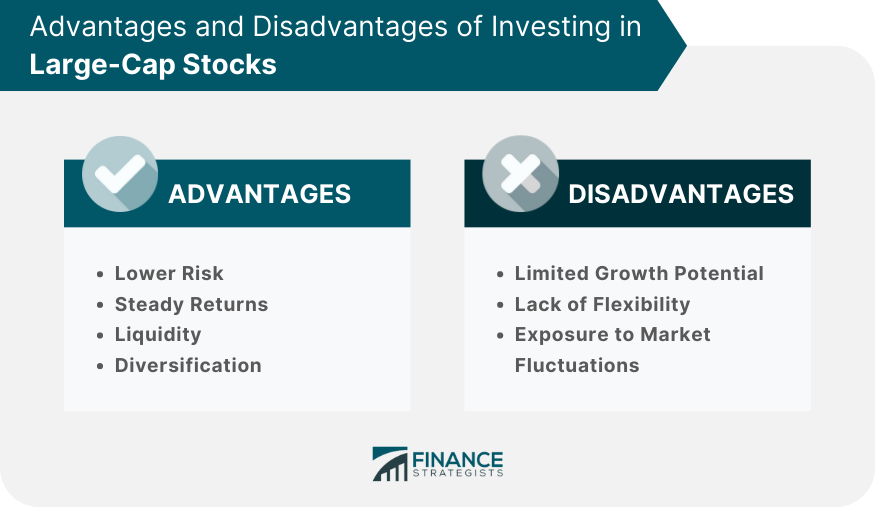
Advantages of Investing in Large-Cap Stocks
Lower Risk
Steady Returns
Liquidity
Diversification
Disadvantages of Investing in Large-Cap Stocks
Limited Growth Potential
Lack of Flexibility
Exposure to Market Fluctuations
Strategies for Investing in Large-Cap Stocks
Buy and Hold Strategy
Value Investing Strategy
Growth Investing Strategy
Income Investing Strategy
Bottom Line
Large-Cap Stocks FAQs
Large-cap stocks are shares of large companies with a market capitalization of $10 billion or more.
Large-cap stocks tend to have high market capitalization, stable revenue, profitability, and dividend payouts.
Investing in large-cap stocks can provide lower risk, steady returns, liquidity, and diversification.
Large-cap stocks may have limited growth potential, lack of flexibility, and exposure to market fluctuations.
You can invest in large-cap stocks by purchasing shares through a broker, using mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or investing in index funds.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











