Requirements for stock market listing are like a checklist of rules that a company needs to follow to have its shares bought and sold on a stock exchange. These rules make sure that only solid, trustworthy companies can sell their shares to the public. Also, these requirements are important for several reasons. First, they protect people who want to invest in these companies. They do this by making sure that any company selling shares to the public is in good financial health and operates openly. Second, they help build trust in the market by promoting fairness, efficiency, and clear information for all. Finally, meeting these requirements can boost a company's reputation, making it more attractive to potential investors. Market capitalization represents the total dollar market value of a company's outstanding shares of stock. Many stock exchanges require companies to maintain a certain market cap to ensure they are of significant size. Some exchanges set a minimum share price to prevent extremely low-priced securities, often called penny stocks, from being listed. This requirement ensures a minimum level of liquidity in the stock, making it easier for investors to buy and sell shares without significantly affecting the share price. Listing requirements may include conditions related to a company's financial health, such as minimum levels of revenue, profit, net assets, or operating cash flow. Some exchanges also consider the company's trading volume, which represents the number of shares traded during a specific period, ensuring adequate market interest in the company. This includes adherence to a set of best practices in managing and controlling a company. It involves the composition of the board of directors, management's fiduciary duties, shareholders' rights, and more. Companies are often required to follow specific accounting standards such as the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to ensure consistent and transparent financial reporting. Exchanges mandate listed companies to comply with robust disclosure requirements, ensuring that investors receive essential information about the company's operations, financial status, and material business developments. The NYSE, one of the world's largest stock exchanges, enforces stringent listing requirements, including a high market capitalization threshold and strict corporate governance rules. NASDAQ, the first electronic stock market, demands both quantitative and qualitative listing requirements, with an emphasis on the company's financial condition and corporate governance. LSE, one of Europe's premier exchanges, also has rigorous standards, with particular emphasis on disclosure requirements and adherence to UK Corporate Governance Code. TSE requires Japanese firms to meet high market capitalization standards, maintain a large number of shareholders, and comply with the Japanese Corporate Governance Code. SSE, one of the fastest-growing exchanges globally, imposes strict requirements on earnings and revenue, along with robust disclosure standards and adherence to Chinese accounting standards. 1. Submission of Application: Getting listed begins with a formal application submitted to the stock exchange, accompanied by a host of supporting documents detailing the company's financials, business operations, management, and more. 2. Review by the Exchange: Upon receiving the application, the exchange reviews the materials to verify if the company satisfies all listing requirements. 3. Verification and Approval: The final stage involves a thorough verification process by the exchange. If the company complies with all requirements, the exchange grants listing approval. Issuance of Warnings: If a listed company fails to maintain the required standards, the exchange issues a warning or notice of non-compliance, giving the company a period to rectify the situation. Delisting Process: Persistent failure to meet the requirements may result in delisting, wherein the company's securities are removed from the exchange. Reduced Access to Capital: Delisting often leads to a loss of reputation, reduced access to capital, lower liquidity, and generally adverse impacts on the company's market performance. Several regulators are in charge of checking and making sure companies follow listing requirements. In the United States, this job is done by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which keeps an eye on whether companies are sticking to these standards. If a company doesn't follow these listing requirements, it can face serious legal trouble. This can include everything from fines and penalties to being taken to court by shareholders or regulators. Listing requirements are vital tools to maintain the integrity of financial markets. They are the checklist for companies wanting to sell shares on a stock exchange, ensuring only reputable and financially secure businesses have access to public markets. These guidelines are comprehensive, including both quantitative and qualitative measures from market capitalization to corporate governance standards. Top stock exchanges like NYSE and NASDAQ have stringent rules, safeguarding investors and promoting market transparency. Non-compliance can lead to delisting and legal consequences. Regulators, like the SEC in the US, vigilantly oversee these standards. The procedure for getting listed is rigorous, further emphasizing the high caliber of companies that meet these requirements. By understanding listing requirements, investors can make informed decisions, contributing to the efficiency and fairness of financial markets.Listing Requirements Overview
Types of Listing Requirements
Quantitative Listing Requirements
Market Capitalization
Share Price
Number of Publicly Traded Shares
Financial Condition and Earnings
Trading Volume
Qualitative Listing Requirements
Corporate Governance Standards
Accounting Standards
Disclosure Standards
Major Stock Exchanges and Their Listing Requirements
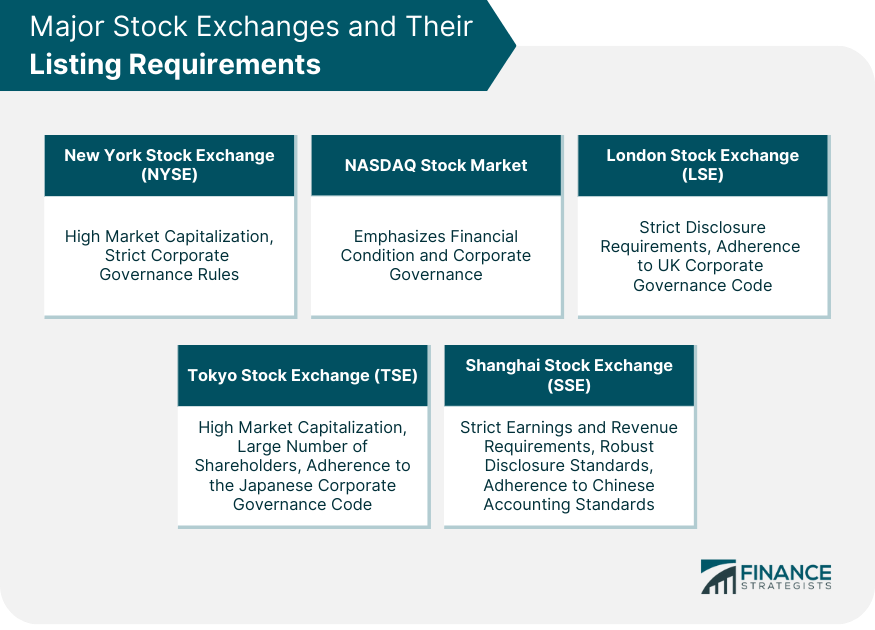
New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
NASDAQ Stock Market
London Stock Exchange (LSE)
Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE)
Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE)
Procedure for Getting Listed

Consequences of Failing to Meet Listing Requirements
Regulatory and Legal Aspects of Listing Requirements
Regulatory Oversight and Enforcement
Legal Implications for Non-compliance
Bottom Line
Listing Requirements FAQs
Quantitative listing requirements are numerical standards that companies must meet to get listed on an exchange. These often include minimum thresholds for market capitalization, share price, the number of publicly traded shares, financial condition (including revenue, profit, net assets, or operating cash flow), and trading volume.
Qualitative listing requirements focus on non-numerical aspects of a company, contributing to its integrity and stability. These standards often include adherence to corporate governance best practices, compliance with specific accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS, and fulfilling stringent disclosure requirements for transparent and consistent information dissemination.
Listing requirements vary among different stock exchanges to align with their market specifications and regulatory environment. For instance, the NYSE emphasizes high market capitalization and strict corporate governance. NASDAQ focuses on a company's financial condition and corporate governance, while LSE mandates strict disclosure requirements and adherence to the UK Corporate Governance Code. TSE and SSE also have unique listing requirements, reflecting the financial landscapes of Japan and China, respectively.
Failure to comply with the listing requirements can have serious consequences for a company. Initially, a notice of non-compliance or warning is issued by the exchange, allowing the company to rectify the situation. Persistent failure can lead to the company's securities being delisted, impacting its reputation, liquidity, market performance, and access to capital.
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing and enforcing listing requirements. These regulators, such as the SEC in the United States, monitor the compliance of listed companies with these requirements and take appropriate actions, including fines and legal proceedings, in case of non-compliance. This oversight ensures the integrity and transparency of the financial markets.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











