The MSCI Emerging Markets Index is a widely followed benchmark that tracks the performance of emerging market equities. It is designed to provide investors with a comprehensive understanding of the risk and return characteristics of these markets. The purpose of the index is to offer a reliable and transparent measure of the emerging market equities performance, helping investors make informed decisions about allocating their assets in these economies. The MSCI Emerging Markets Index was launched in 1988, as investors began to recognize the potential growth opportunities in emerging economies. Over the years, the index has evolved to include a diverse range of countries and sectors, reflecting the growing importance of emerging markets in the global economy. Since its inception, the MSCI Emerging Markets Index has become an essential tool for investors seeking exposure to developing economies, serving as a benchmark for numerous investment products such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, and other index-linked investment vehicles. The MSCI Emerging Markets Index is composed of equities from 26 emerging market countries. The largest constituents by weight are China, South Korea, Taiwan, India, and Brazil, which collectively account for a significant portion of the index's overall market capitalization. This diverse geographical representation offers investors exposure to a wide array of economies, each with its unique growth drivers and risk factors, providing a well-rounded investment opportunity in emerging markets. The MSCI Emerging Markets Index covers all the major sectors of the economy, such as information technology, financials, consumer discretionary, and more. The sector allocation within the index shifts over time as emerging market economies evolve and new industries gain prominence. By investing in a broad range of sectors, investors can benefit from the growth potential across different industries, while also mitigating the risks associated with any single sector's underperformance. The MSCI Emerging Markets Index includes large- and mid-cap stocks from its constituent countries, using a market capitalization-weighted methodology. Stocks are selected based on their liquidity, size, and free-float-adjusted market capitalization. This approach ensures that the index represents the most significant and liquid equities in each emerging market, providing a comprehensive and investable benchmark for these economies. The MSCI Emerging Markets Index is weighted by free-float-adjusted market capitalization, meaning that each constituent's weight is determined by its market cap adjusted for the proportion of shares available to investors. This weighting and rebalancing methodology provides investors with a transparent and easy-to-understand benchmark, which accurately reflects the performance of the emerging markets' investable equity universe. The MSCI Emerging Markets Index has experienced significant growth since its inception, outperforming many developed market indices over the long term. Despite the higher volatility, many investors have been attracted to the index due to its potential for higher returns, driven by the rapid economic growth and development in its constituent countries. The MSCI Emerging Markets Index exhibits a unique risk-return profile, characterized by higher potential returns but also increased volatility compared to developed market indices. This is due to several factors, including political and economic instability, less mature financial markets, and currency fluctuations. However, the higher risk associated with emerging markets can be partially mitigated by the index's diversification across different countries and sectors. By investing in a broad range of equities within the index, investors can benefit from the growth opportunities while also managing the associated risks. Exchange-traded funds are investment vehicles that allow investors to gain exposure to a specific index, sector, or asset class by purchasing shares of the ETF. ETFs that track the MSCI Emerging Markets Index offer an efficient and cost-effective way to access the performance of emerging market equities without the need to buy individual stocks. Investing in ETFs that follow the MSCI Emerging Markets Index can provide a passive strategy for participating in the growth of emerging economies, offering diversification benefits and ease of trading due to their liquidity and ability to be bought and sold like individual stocks. Mutual funds are actively managed investment vehicles that pool investors' money to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. Many mutual funds focus on emerging market equities and use the MSCI Emerging Markets Index as their benchmark, aiming to outperform the index by carefully selecting securities with higher return potential or lower risk. By investing in mutual funds that target emerging market equities, investors can benefit from the expertise of professional fund managers who have extensive knowledge of the unique opportunities and challenges present in these markets. Index futures and options are financial derivatives that allow investors to gain exposure to the MSCI Emerging Markets Index without directly owning the underlying stocks. Index futures are contracts that enable investors to buy or sell the index at a specified price on a future date, while options give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price before the option's expiration date. Investing in index futures and options can provide a means to hedge against potential losses, speculate on the future direction of the index, or implement various trading strategies, such as arbitrage, that aim to exploit pricing inefficiencies between the index and its constituents. Active management refers to an investment strategy in which a fund manager actively selects securities with the goal of outperforming a specific benchmark, such as the MSCI Emerging Markets Index. In contrast, passive management involves investing in a portfolio that replicates a specific index, seeking to match its performance rather than attempting to outperform it. The choice between active and passive management depends on an investor's individual risk tolerance, investment goals, and preferences. Active management may offer the potential for higher returns if the fund manager can successfully identify undervalued stocks or sectors, while passive management typically involves lower costs and provides a more transparent and consistent exposure to the performance of the index. Emerging markets can be subject to a higher degree of economic and political risks compared to developed markets. Issues such as political instability, corruption, and economic policy uncertainty can impact the performance of the MSCI Emerging Markets Index. However, these risks can also present opportunities for investors who are willing to take on additional risk in exchange for potentially higher returns, as these challenges may create mispriced investment opportunities within the index's constituents. Market liquidity and infrastructure can be less developed in emerging markets compared to their developed counterparts. This can lead to increased transaction costs and difficulties in executing trades, which may impact the performance of the MSCI Emerging Markets Index. Despite these challenges, the continued development and growth of emerging market economies can lead to improvements in market liquidity and infrastructure, potentially benefiting investors in the long term. Emerging markets have the potential to experience rapid growth in the coming years, driven by factors such as demographic shifts, urbanization, and technological advancements. This growth can translate into strong performance for the MSCI Emerging Markets Index and its constituents. Investing in the MSCI Emerging Markets Index can provide investors with exposure to the long-term growth potential of these economies, offering an opportunity to benefit from their continued development and expansion. Emerging markets are increasingly becoming centers of innovation and technological development, with industries such as information technology, renewable energy, and e-commerce experiencing rapid growth. These trends can contribute to the strong performance of the MSCI Emerging Markets Index. By investing in the index, investors can gain exposure to the innovative companies driving growth and change within the emerging market economies, capitalizing on the potential for strong returns from these industries.Definition of MSCI Emerging Markets Index
Constituent Countries & Sectors of MSCI Emerging Markets Index
Geographical Distribution
Sector Breakdown
Methodology and Calculation of MSCI Emerging Markets Index
Selection Criteria
Weighting and Rebalancing
The index is rebalanced quarterly to account for changes in market capitalization, ensuring that the index remains an accurate reflection of the emerging markets' equity landscape.Performance and Risk-Return Profile of MSCI Emerging Markets Index
Historical Performance
However, it has also exhibited higher volatility compared to its developed market counterparts, reflecting the inherent risks associated with investing in emerging markets.Risk-Return Characteristics
Investment Vehicles and Strategies for MSCI Emerging Markets Index
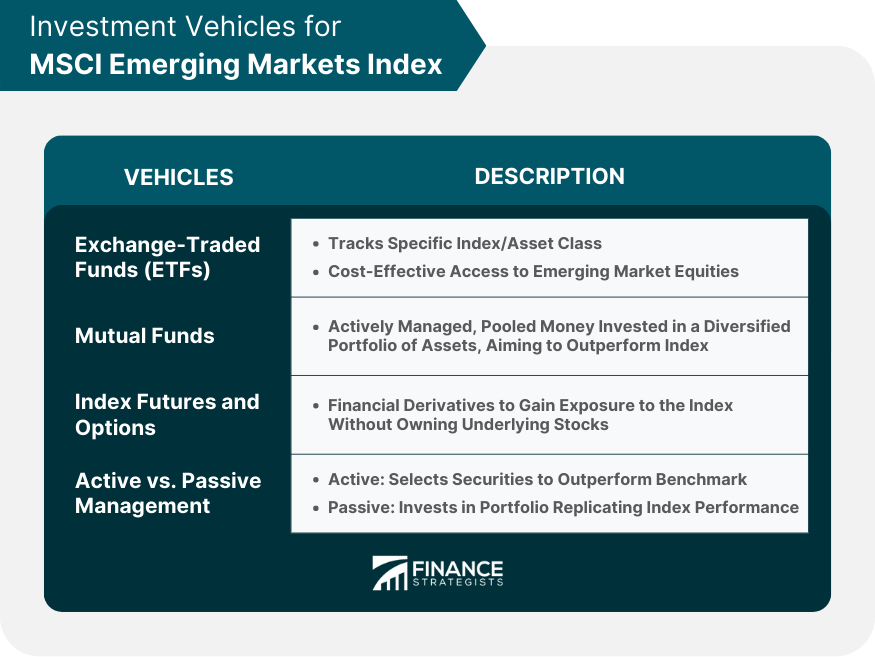
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Mutual Funds
Index Futures and Options
Active vs. Passive Management
Challenges and Opportunities in Emerging Markets
Economic and Political Risks
Market Liquidity and Infrastructure
Final Thoughts
MSCI Emerging Markets Index FAQs
MSCI Emerging Markets Index is a stock market index that tracks the performance of emerging market countries' stock markets.
The MSCI Emerging Markets Index includes countries such as China, Brazil, South Korea, Taiwan, India, and many others.
The MSCI Emerging Markets Index is calculated using a market capitalization-weighted method, where the index's components are weighted according to their market value.
Yes, you can invest in the MSCI Emerging Markets Index through exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds that track the index.
Investing in emerging markets comes with risks such as political instability, currency fluctuations, and liquidity risks. It is important to assess these risks before investing.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











