OTCQX, standing for Over the Counter Quotation Exchange, is a marketplace for securities that are not listed on traditional exchanges such as the NYSE or NASDAQ. Operated by the OTC Markets Group, the OTCQX forms the top tier of three marketplaces, with the OTCQB and Pink markets comprising the other tiers. The OTCQX provides an important avenue for companies to raise capital and enhance their visibility among investors without the need for a traditional exchange listing. It serves a vital purpose in the financial ecosystem by offering a diverse range of securities and increasing the accessibility of the financial market to a broader range of participants. In addition to this, it can serve as an effective platform for foreign companies to gain access to U.S. investors. Thus, OTCQX plays a significant role in the global financial landscape. The OTCQX market structure is unique, given that it operates outside traditional exchanges. It uses a dealer market model involving broker-dealers who negotiate directly with each other rather than through a centralized exchange. This decentralized structure allows for flexibility in trading and enables direct communication between market participants. Trading on the OTCQX market is primarily conducted through electronic quotation systems. These systems provide a platform for market participants to access real-time quotes, execute trades, and disseminate relevant market information. By utilizing electronic quotation systems, the OTCQX market enhances the efficiency, speed, and transparency of trading, enabling investors to access and respond to market data in a timely manner. Market makers on the OTCQX are responsible for ensuring liquidity and providing fair, orderly markets for the securities they cover. They do this by standing ready to buy and sell securities at publicly quoted prices. Issuers are the companies whose securities are traded on the OTCQX. These can range from small, lesser-known firms to large, internationally recognized companies that choose to list on the OTCQX for various reasons. Investors on the OTCQX include both institutional and retail participants. These investors are attracted to the diversity of offerings and the opportunities for potentially high returns, despite the increased risk compared to traditional exchanges. The OTCQX is the top tier of three platforms provided by the OTC Markets Group. The other two are the OTCQB and the Pink markets. The OTCQX has the highest financial standards and regulatory compliance, providing more transparency and better information for investors than the other tiers. Companies that are listed on the OTCQX gain enhanced visibility among investors, which can lead to increased liquidity for their securities. The cost of listing on the OTCQX is typically less than on a traditional exchange. This lower cost barrier makes it accessible for smaller companies to get their securities listed and traded. For foreign companies, listing on the OTCQX can provide them with greater access to the vast pool of US investors, thereby broadening their potential investor base. Given that OTCQX operates over-the-counter, there is generally less regulatory oversight compared to traditional exchanges. This could potentially expose investors to greater risk. Some securities on the OTCQX might experience lower trading volumes, which could affect the liquidity and price stability of these securities. Securities on the OTCQX may also be subject to higher price volatility due to lower liquidity and less comprehensive information available. FINRA oversees the OTCQX along with all other OTC markets. It ensures compliance with fair-trading practices and the integrity of the market, protecting investors from fraudulent activities. The SEC also has jurisdiction over the OTCQX, primarily in terms of enforcing federal securities laws and regulating broker-dealers. The OTCQX has its own set of rules and regulations, which include minimum bid price requirements, annual financial disclosures, and corporate governance standards. These regulations are more stringent than those for the lower-tier OTC markets but less so compared to major exchanges. Companies listed on the OTCQX must comply with various requirements, such as submitting annual financial statements, maintaining a minimum bid price, and meeting specified corporate governance standards. Failure to comply with these standards could lead to delisting from the OTCQX. To be eligible for listing on the OTCQX, a company must meet certain financial and corporate governance standards. These include audited financial statements, a minimum bid price, and a specific number of public shareholders. The process for listing on the OTCQX begins with an application submitted to the OTC Markets Group. This application includes a range of materials, such as financial statements, details of the company's business, and a listing fee. Upon review and approval, the company's securities can be traded on the OTCQX. Listing fees for the OTCQX vary based on the company's size and other factors. These fees are typically less than those for listing on a traditional exchange, making the OTCQX a more affordable option for many companies. The OTCQX plays a crucial role in the global financial scene by providing an accessible platform for securities trading. As the top tier of OTC marketplaces, it offers high standards of transparency and information quality, drawing in a diverse range of issuers and investors. Companies listing on the OTCQX can achieve greater visibility and liquidity alongside lower costs than traditional exchanges. Meanwhile, investors have access to a wider variety of securities, although they must consider higher risks. Regulatory bodies like FINRA and the SEC work to uphold market integrity. OTCQX forms a critical component in the broader financial ecosystem, offering unique opportunities and challenges for its market players.What Is an OTCQX?
Structure of the OTCQX Market
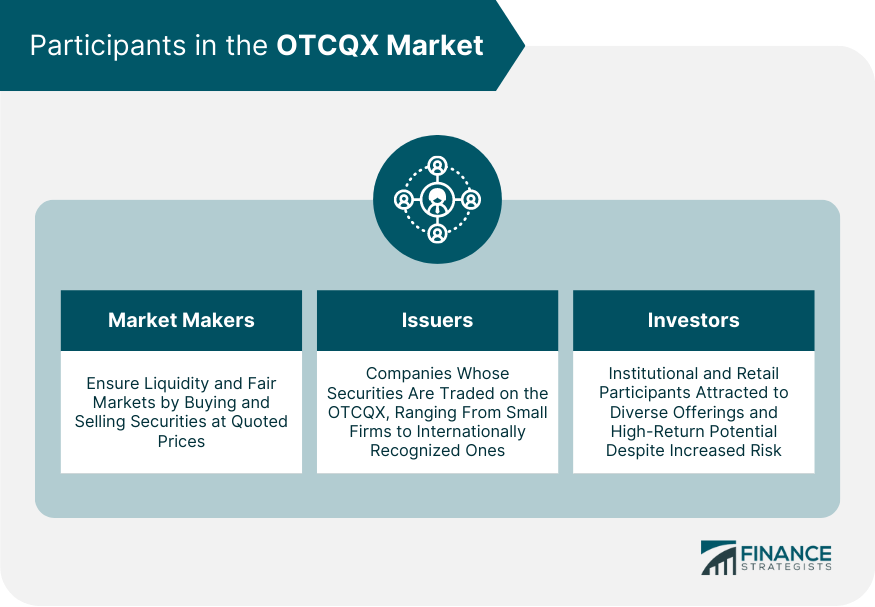
Key Participants in the OTCQX Market
Market Makers
Issuers
Investors
Comparison to Other OTC Tiers
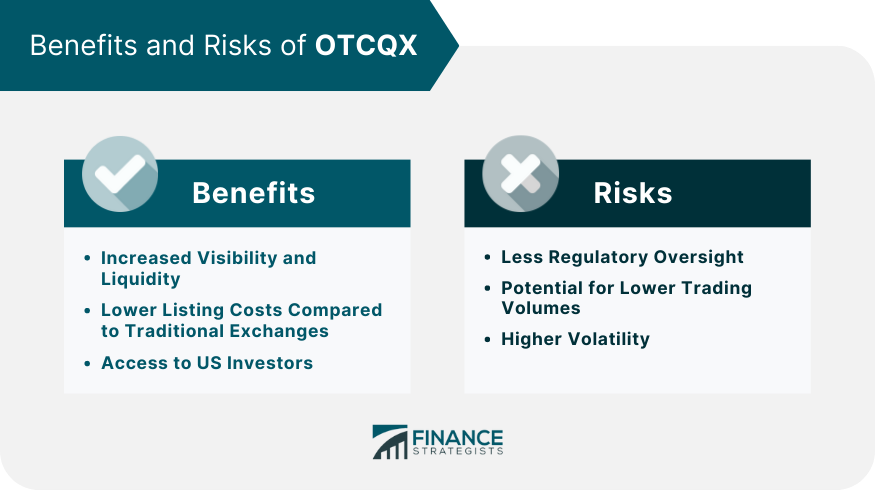
Benefits and Risks of OTCQX
Increased Visibility and Liquidity
Lower Listing Costs Compared to Traditional Exchanges
Access to US Investors
Risks of OTCQX
Less Regulatory Oversight
Potential for Lower Trading Volumes
Higher Volatility
Regulatory Environment of OTCQX
Role of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA)
Role of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
Rules and Regulations Specific to OTCQX
Compliance Requirements for Companies Listed on OTCQX
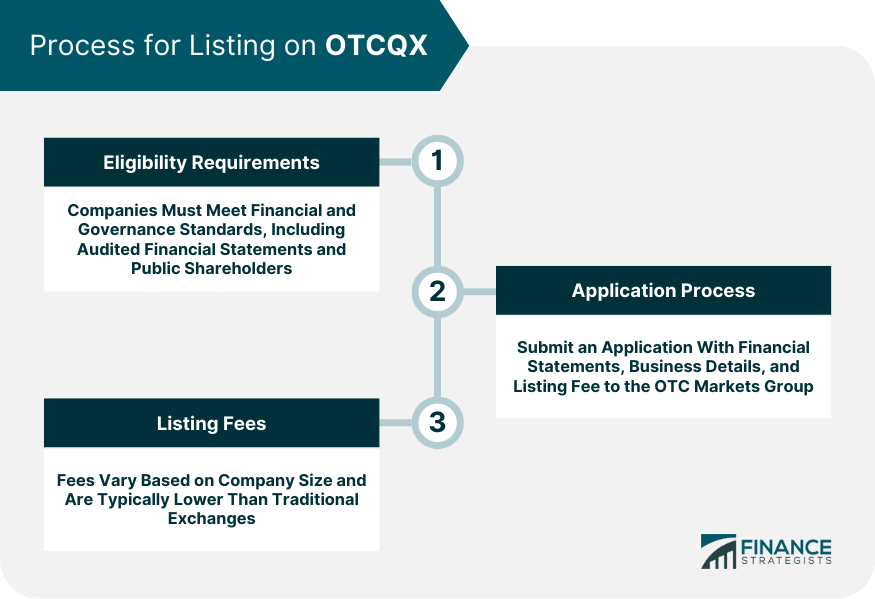
Process for Listing on OTCQX
Eligibility Requirements
Application Process
Listing Fees
Conclusion
OTCQX FAQs
The Over the Counter Quotation Exchange (OTCQX) is a marketplace for securities that are not listed on traditional stock exchanges. It provides a platform for companies to trade their securities and gain visibility among investors. Its significance lies in promoting a diverse, robust market and granting investors access to a wide variety of securities.
The OTCQX is the highest tier offered by the OTC Markets Group, the others being the OTCQB and Pink markets. The OTCQX has stricter financial and regulatory standards, providing more transparency and better information for investors.
Benefits of the OTCQX include increased visibility and liquidity, lower listing costs compared to traditional exchanges, and access to US investors for foreign companies. However, risks involve less regulatory oversight, the potential for lower trading volumes, and higher price volatility.
To get listed on the OTCQX, a company must first meet certain financial and governance standards. Then, the company submits an application to the OTC Markets Group, including financial statements, business details, and a listing fee. After approval, the company's securities can be traded on the OTCQX.
The OTCQX market may be significantly influenced by technological advancements such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, which could transform trading and information sharing processes. The regulatory environment is also likely to evolve, impacting the OTCQX operations and listing requirements. Lastly, an increase in the number and diversity of companies choosing the OTCQX for their securities is also anticipated.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











