A share certificate is a legal document that serves as evidence of ownership in a company. It is issued by a corporation to its shareholders to acknowledge their ownership of a specific number of shares in the company. The share certificate typically includes important information such as the shareholder's name, the company's name, the class or type of shares owned, the number of shares held, and a unique identification number for the certificate. Share certificates are often used in companies with a traditional paper-based system of recording ownership. They are typically issued when shares are first purchased or transferred to a new owner. Share certificates serve as tangible evidence of an individual's ownership in a company. They provide legal documentation that verifies the number of shares held by a shareholder and their entitlement to the associated rights and benefits. Share certificates are essential for exercising shareholder rights. They establish a shareholder's eligibility to participate in shareholder meetings, vote on company matters, and receive dividends and other shareholder benefits. Share certificates facilitate the transfer of ownership from one shareholder to another. When a shareholder sells or transfers their shares, the share certificate is typically endorsed or transferred to the new owner. Share certificates play a vital role in protecting shareholders' interests. They provide a legal framework to prevent unauthorized transfers of shares and fraudulent activities. Shareholders can rely on their share certificates to safeguard their ownership rights and prevent unauthorized changes to their shareholdings. Share certificates help companies comply with regulatory requirements. Many jurisdictions mandate the issuance of share certificates as a legal requirement for companies to document and validate share ownership. Share certificates serve as historical records of a company's ownership structure. They document the ownership history and changes in share ownership over time. These records can be valuable for auditing purposes, historical analysis, or in the case of disputes or legal proceedings. Common share certificates represent ownership in a company with voting rights and the potential for capital appreciation. They are typically held by common shareholders and provide a proportionate stake in the company's profits and assets. Preferred share certificates, on the other hand, offer shareholders preferential treatment over common shareholders in terms of dividend payments and liquidation preferences. They may have limited or no voting rights but provide investors with a fixed dividend rate. Convertible share certificates give shareholders the option to convert their shares into another class of shares, typically common shares, at a predetermined conversion ratio. This type of certificate offers flexibility and potential for enhanced returns based on market conditions. The share certificate includes crucial information about the issuing company, such as its name, registered address, incorporation details, and sometimes even a company seal. This section provides details about the shareholder, including their name, contact information, and sometimes their shareholder identification number. The share certificate outlines the specifics of the shares, such as the number of shares owned, the class of shares, and any special rights or restrictions associated with them. Each share certificate is assigned a unique certificate number and includes the date of issuance. These details are crucial for record-keeping, identification, and traceability. The issuance of share certificates involves a series of steps, including share allocation, shareholder information verification, printing or electronic generation of certificates, and their delivery to shareholders. It is essential to comply with legal and regulatory requirements during this process. Transferring ownership of share certificates requires adherence to specific procedures. Shareholders must execute a valid transfer instrument, update the company's records, and deliver the share certificate to the new owner. Adhering to corporate laws and regulatory requirements is crucial when dealing with share certificates to ensure compliance and protect the interests of shareholders and the company. Companies issuing share certificates must comply with the relevant corporate laws and regulations governing the issuance, transfer, and maintenance of share ownership records. This includes ensuring accuracy, transparency, and proper documentation throughout the process. In many jurisdictions, including the United States, the issuance and transfer of share certificates are subject to specific regulations set forth by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). These regulations aim to safeguard investors' interests, ensure fair markets, and promote transparency in securities transactions. Maintaining accurate and up-to-date records is essential for share certificates. Companies are often required to keep detailed records of share issuances, transfers, and ownership changes. These records serve as an audit trail and provide crucial information for shareholders, regulatory compliance, and legal purposes. Protecting share certificates from loss, theft, or damage is crucial. Companies and shareholders must take appropriate measures to safeguard these valuable documents. Various security measures can be implemented to protect share certificates. This may include secure storage facilities, encryption technologies for electronic certificates, and restricted access to physical certificates. In the unfortunate event of a lost or stolen share certificate, prompt reporting to the issuing company is necessary. Shareholders should notify the company, provide necessary details, and follow the prescribed procedures for mitigating any potential risks. The process for obtaining replacement share certificates typically involves filing a request with the issuing company, providing relevant documentation and proof of ownership, and complying with any administrative requirements. Companies will follow a systematic procedure to verify the request and issue a replacement certificate. As technology advances, the landscape of share certificates is evolving. The emergence of digital securities has introduced new possibilities and challenges for shareholders and companies. Digital advancements have led to the issuance of electronic share certificates. These certificates exist in digital form, often recorded on distributed ledger technologies like blockchain. Electronic certificates offer benefits such as enhanced security, efficiency in transferability, and potential cost savings. Enhanced Security: Digital share certificates leverage advanced cryptographic techniques and decentralized ledgers, providing robust security against fraud, counterfeiting, and unauthorized alterations. Efficient Transferability: Digital share certificates enable seamless and near-instantaneous transfer of ownership, eliminating the need for physical paperwork and manual processing. This enhances liquidity and reduces administrative burdens. Cost Savings: By eliminating the costs associated with printing, storing, and distributing physical share certificates, companies can achieve cost savings in the issuance and maintenance of share ownership records. Regulatory Framework: Regulators are working to establish guidelines that ensure investor protection, market integrity, and compliance with existing securities laws. Technological Infrastructure: This includes reliable platforms, smart contract protocols, and interoperability standards to ensure compatibility across different systems and networks. Cybersecurity Risks: Digital share certificates are susceptible to cybersecurity threats, such as hacking, data breaches, and unauthorized access. Companies and investors must implement stringent cybersecurity measures to safeguard digital assets and protect sensitive shareholder information. Adoption and Acceptance: Transitioning from traditional physical share certificates to digital formats may face resistance and require broad acceptance from regulators, investors, and market participants. Education and awareness campaigns can facilitate the adoption process and build trust in digital securities. Share certificates play a crucial role in corporate finance and shareholder rights. They serve as tangible proof of ownership, providing legal documentation of the number of shares held and associated rights. Share certificates are necessary for exercising shareholder rights such as voting and receiving dividends, acting as eligibility proof. They also facilitate the transparent transfer of ownership when shares are sold or transferred. Share certificates protect shareholders by preventing unauthorized transfers and fraudulent activities. They aid regulatory compliance by documenting and validating share ownership. Share certificates act as historical records of ownership, valuable for auditing and analysis. While electronic systems are more common, share certificates remain significant, particularly in smaller companies and certain jurisdictions. They provide tangible evidence, protect rights, and contribute to transparent corporate governance.What Is a Share Certificate?
Purpose and Significance of Share Certificates
Serve as Proof of Ownership
Grant Shareholder Rights
Facilitate Transfer of Ownership
Provide Shareholder Protection
Ensure Regulatory Compliance
Serve as a Historical Record
Types of Share Certificates
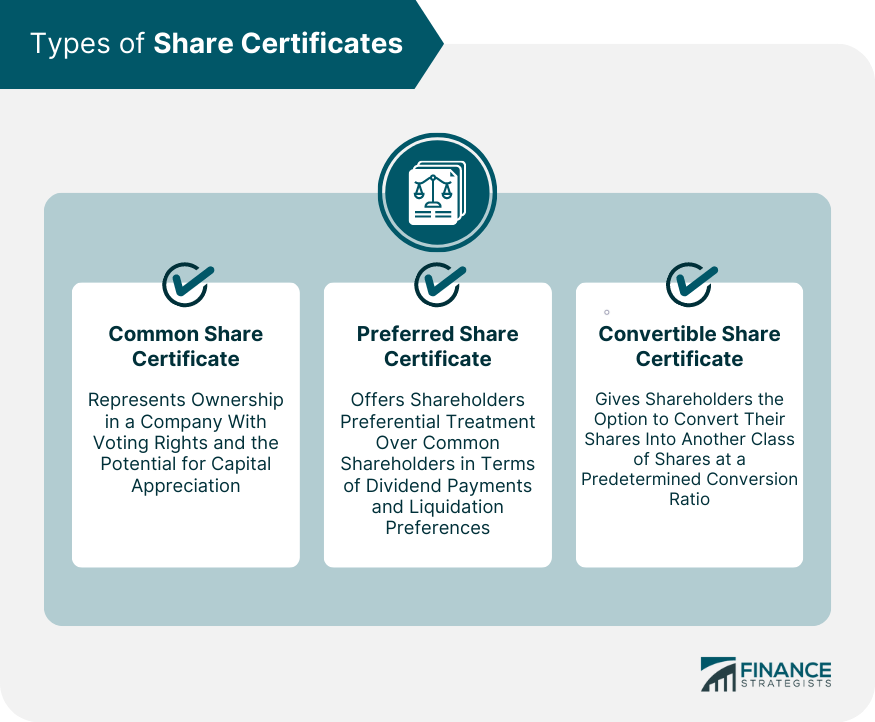
Common Share Certificates
Preferred Share Certificates
Convertible Share Certificates
Key Components of a Share Certificate
Company Information
Shareholder Information
Share Details
Certificate Number and Date
Issuance and Transfer of Share Certificates
Process of Issuing Share Certificates
Transferring Ownership of Share Certificates
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Compliance With Corporate Laws
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Regulations
Record-Keeping and Documentation Requirements
Safeguarding and Replacement of Share Certificates
Security Measures for Share Certificates
Reporting Lost or Stolen Share Certificates
Procedure for Obtaining Replacement Certificates
Share Certificates in the Digital Era
Advantages of Digital Share Certificates
Challenges of Digital Share Certificates
Conclusion
Share Certificate FAQs
A share certificate is a legal document issued by a company to its shareholders, confirming their ownership of a specific number of shares in the company.
To obtain a share certificate, you typically need to purchase shares in a company and complete the necessary paperwork, including providing your personal details and the number of shares you own. The company will then issue the share certificate to you.
A share certificate typically includes important details such as the shareholder's name, the company's name, the class of shares held, the number of shares owned, the share certificate number, and any special rights or restrictions associated with the shares.
Yes, a share certificate can be transferred from one person to another. The transfer process usually involves signing the back of the certificate and completing a share transfer form. The new owner must submit these documents to the company for the share ownership to be officially transferred.
If you lose your share certificate, you should immediately inform the company and follow their specific procedures for replacing a lost certificate. This typically involves completing a lost share certificate declaration form and paying a fee. The company will then issue a new share certificate to you. It is important to report the loss promptly to protect your ownership rights.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











