Small-cap funds invest in small-cap stocks with a market capitalization between $250 million and $2 billion. Investing in small-cap funds can expose investors to the potential for growth and innovation of these companies, which may not be available in larger-cap stocks. Small-cap funds invest in a diversified portfolio of small-cap stocks to reduce the risk of individual stock fluctuations and overall portfolio volatility. This diversification provides investors with the potential for higher returns while minimizing risk. Small-cap funds can offer investors several advantages, including the potential for higher returns, diversification opportunities, accessibility, durability during economic cycles, and the opportunity to use a value investing strategy. Small-cap stocks can provide investors with higher returns than larger-cap stocks due to their potential for growth and innovation. Companies offering small-cap funds have room to grow and can generate substantial returns for investors who identify and invest in companies with growth potential. Small-cap funds can provide investors with a diversified portfolio of these companies, increasing their chances of achieving higher returns. Having a diversified portfolio is crucial for two reasons. Firstly, it helps to minimize risk as your investment funds are distributed across various asset classes. Secondly, it is a strategy to enhance the performance of the portfolio. If your investment approach primarily focuses on mid-cap or large-cap stocks and funds, including some small-cap funds in your portfolio could increase your overall returns while reducing risk. Small-cap funds are accessible to investors of all sizes and experience levels. These funds are available through mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and index funds. Investors can choose from a wide range of small-cap funds that offer varying levels of diversification, risk, and return. While not all small-cap funds do so, most invest in stocks crucial to maintaining the stability of the economy, regardless of its current cycle. These may include stocks representing essential consumer goods, discretionary spending, healthcare, infrastructure, and financial sectors. Some small-cap funds can be seen as defensive positions as they can withstand economic pressures better than mid- or large-caps during recessions or stock market turbulence. Small-cap value funds may be a viable option for those relying on value investing strategies. Such funds primarily invest in undervalued small-cap companies. By investing in these funds, investors stand to gain significant benefits from potential price appreciation in their shares in case the companies take off. Small-cap funds can also pose risks to investors, including their tendency to be a more volatile and short track record. Small-cap funds are known to be more volatile due to the fact that many small-cap companies are still trying to establish themselves in the market. Such companies may be more prone to business direction or mission changes, which could affect share prices. Additionally, small-cap companies may take more risks in attempting to be innovative, which could backfire if a new product line fails to generate revenue or if an updated marketing strategy does not succeed as anticipated. Small-cap funds can be considered riskier investments because many of the companies in these funds are new and do not have a long track record like mid- or large-caps do. While an up-and-coming small-cap company may seem like a promising investment, it could just as easily be surpassed by a competitor with a similar product or service. This is similar to how Facebook became dominant while MySpace declined, demonstrating the potential fragility of small-cap investments. Deciding whether to invest in a small-cap fund depends on various factors, including investment style, risk tolerance, time horizon, and goals. If the objective is generating dividend income, small-cap funds may not be the best option since many of these companies tend to reinvest their profits instead of making periodic payments to investors. Moreover, small-cap funds may not be suitable for investors uncomfortable with potentially volatile investments. Small-cap stocks and their funds can experience significant price fluctuations, which can be unsettling for those focused on short-term capital appreciation. However, these price swings may not be an issue for long-term investors committed to investing in small caps. Small-cap and large-cap funds are two different types of mutual funds that invest in companies with varying market capitalizations. Small-cap funds tend to invest in companies with market capitalizations ranging from a few hundred million dollars to a few billion dollars. On the other hand, large-cap funds invest in companies with market capitalizations greater than $10 billion, with some mega-cap stocks exceeding $200 billion. Small-cap funds are generally riskier than large-cap funds, as smaller companies tend to have fewer financial resources, less overall business strength, and more volatile stock prices. However, small-cap stocks have historically outperformed large-cap stocks over time and have more growth potential due to their smaller size. Small-cap stocks also tend to reinvest profits for growth rather than pay dividends to investors. On the other hand, large-cap stocks are considered safer and less volatile than small-cap stocks. They tend to have deep financial resources, higher overall business strength, and less growth potential because they operate in mature industries. Large-cap stocks usually pay dividends to investors and are less likely to reinvest profits for growth. In summary, small-cap funds are generally riskier but have greater potential for growth, while large-cap funds are considered safer but have less growth potential. Understanding the differences between these two types of funds can help investors make informed decisions about their investments. Small-cap funds invest in small-cap stocks, offering the potential for higher returns and diversification opportunities. Small-cap funds are accessible to investors of all sizes and experience levels and can provide durability during economic cycles. They can also be a good option for value investing strategies. However, small-cap funds are riskier than large-cap funds, as smaller companies tend to have fewer financial resources, less overall business strength, and more volatile stock prices. Investors should consider their investment style, risk tolerance, time horizon, and goals before investing in small-cap funds. If you are interested in investing in small-cap funds and need assistance, consider seeking the services of a wealth management professional who can provide expert guidance on investing in small-cap funds.What Are Small-Cap Funds?
Benefits of Investing in Small-Cap Funds
Potential for Higher Returns
Diversification Opportunities
Accessible to Investors
Durability During Economic Cycles
Good Option for Value Investing Strategy
Risks of Small-Cap Funds
Tendency to Be More Volatile
Short Track Record
Should You Invest in Small-Cap Funds?
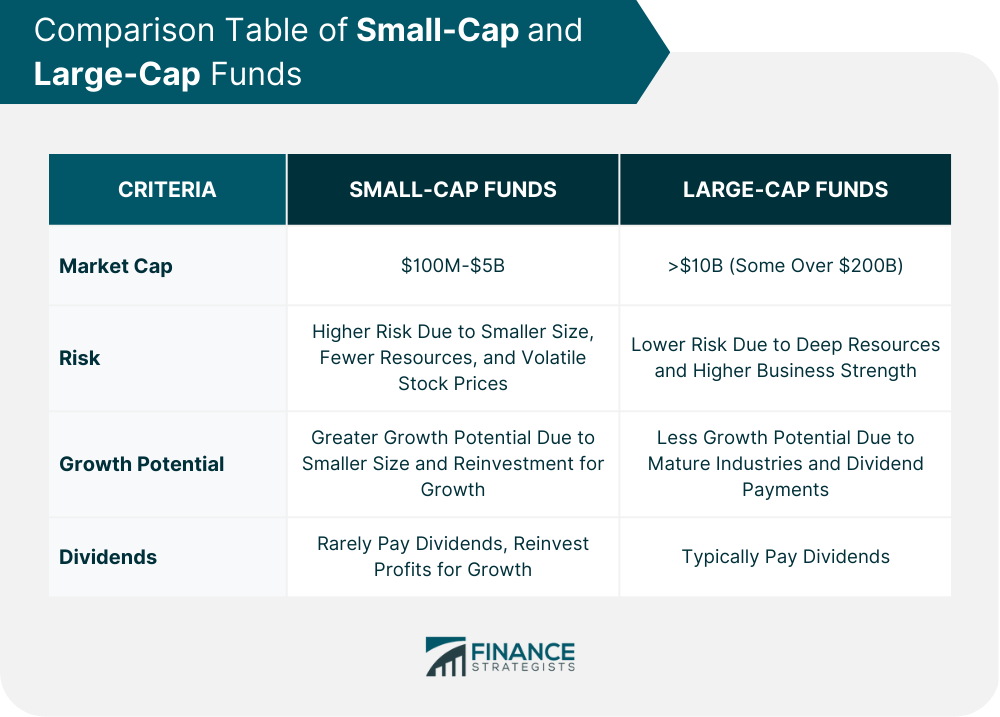
Small-Cap vs Large-Cap Funds
Final Thoughts
Small-Cap Funds FAQs
Small-cap funds are mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that invest in small-cap stocks, which are companies with a market capitalization typically between $250 million to $2 billion. These funds aim to provide capital appreciation to investors by investing in companies with high growth potential.
Investing in small-cap funds may provide higher potential returns than large-cap funds, as small-cap companies have more room for growth. Small-cap companies tend to be less researched by Wall Street analysts, which may lead to pricing inefficiencies and opportunities for active fund managers to find undervalued stocks.
Small-cap funds are mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that invest in small-cap stocks, which are companies with a market capitalization typically between $250 million to $2 billion. These funds may invest in a diversified portfolio of small-cap stocks across various industries or sectors.
Whether to invest in small-cap funds depends on your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and portfolio diversification strategy. Small-cap funds can provide higher potential returns but also carry higher risks and volatility than large-cap funds. It is essential to consult a financial advisor to determine if small-cap funds are suitable for your investment portfolio.
When choosing a small-cap fund to invest in, investors should consider various factors, such as fund performance, expense ratios, management team, investment strategy, and historical volatility. It is crucial to perform thorough research and due diligence before investing in any fund.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











