Stock dilution is a term used to describe a reduction in the ownership percentage of a shareholder in a company as a result of the issuance of new shares. This reduction in ownership can have a significant impact on the value of the shareholder's investment, as well as on the financial statements of the company. Understanding stock dilution is essential for investors, executives, financial analysts, and accounting professionals. Below are the types of stock dilution: Primary stock dilution occurs when a company issues new shares to raise additional capital. The issuance of new shares can provide additional capital that can be used for growth and expansion. However, this additional capital comes at a cost: the dilution of existing shareholders. As new shares are issued, the percentage of ownership of each existing shareholder decreases. This can lead to a decrease in the value of their investment, as well as a loss of control over the company's operations. Secondary stock dilution occurs when existing shareholders sell their shares to new investors. The impact of secondary stock dilution on the value of a shareholder's investment depends on the price at which the shares are sold. If the shares are sold at a higher price than their original purchase price, the shareholder can make a profit. However, if the shares are sold at a lower price than their original purchase price, the shareholder can experience a loss. Stock dilution can have several effects on investors, depending on the extent of the dilution and the circumstances surrounding the issuance of new shares. As new shares are issued, the percentage of ownership of each existing shareholder decreases, leading to a dilution of ownership. This can impact an investor's voting rights, as well as their ability to influence the decision-making process of the company. Dilution of ownership can also impact the value of an investor's shares, as the total value of the company is now divided among a greater number of shareholders. This can reduce the Earnings Per Share (EPS) and, consequently, the return on investment for shareholders. The issuance of new shares can lead to a decrease in the stock price, which negatively affects investors. This is because the increase in the supply of shares can lead to a reduction in demand, which can lead to a lower stock price. This can negatively impact the value of an investor's shares, reducing their return on investment. In addition, a lower stock price can also affect the perception of the company in the market, leading to a decrease in investor confidence and a further decline in the stock price. The EPS can decrease as a result of stock dilution, leading to a lower return on investment. This is because the EPS calculation takes into account the number of outstanding shares, and as new shares are issued, the denominator of the calculation increases. This can lead to a decrease in the EPS, which can impact the perception of the company and its attractiveness to investors. A lower EPS can also lead to a decrease in dividend payouts, which can further reduce the return on investment for shareholders. Dividend payouts may decrease as the number of outstanding shares increases, which can impact the attractiveness of the company to income investors. This is because dividend payments are usually calculated on a per-share basis, and as the number of shares increases, the total amount of dividends paid out may decrease. This can negatively impact the return on investment for income investors, who rely on regular dividend payments to generate income. Investing in companies that use stock dilution can be risky, as it can lead to a dilution of ownership, a decrease in the stock price, a decrease in EPS, and a decrease in dividend payouts. However, there are also potential benefits to investing in such companies, such as the ability to raise additional capital for growth and expansion. Investors must weigh the risks and benefits of investing in such companies and seek the advice of a wealth management advisor before making investment decisions. Stock dilution can have several effects on a company, including dilution of ownership, impact on financial statements, and impact on shareholder value. Stock dilution can lead to a dilution of ownership, which can impact the decision-making process of the company. As new shareholders enter the picture, the ownership percentage of existing shareholders decreases, reducing their ability to influence the direction of the company. This can lead to a decrease in shareholder activism and a less engaged shareholder base. The issuance of new shares can impact the financial statements of the company in several ways. Firstly, it can increase the equity portion of the balance sheet, which can impact ratios such as Return on Equity (ROE) and price-to-earnings ratio. Secondly, it can lead to a decrease in EPS, which can negatively affect investor perception and lead to a decrease in the stock price. Finally, it can lead to a decrease in dividend payouts, which can impact the attractiveness of the company to income investors. Stock dilution can also impact shareholder value in several ways. Firstly, it can lead to a decrease in the value of existing shares, as the total value of the company is now divided among a greater number of shareholders. This can negatively affect shareholder return on investment. Secondly, it can lead to a decrease in the stock price, which can reduce the market capitalization of the company and lead to a decrease in the overall value of the company. This can negatively impact the company's ability to raise additional capital and lead to a decline in investor confidence. Stock dilution has significant effects on the financial statements of the company, including an impact on the balance sheet, income statement, and other key financial ratios. The issuance of new shares can impact the equity portion of the balance sheet. As new shares are issued, the total equity of the company increases, which can impact ratios such as return on equity and debt-to-equity ratio. This can also lead to a dilution of ownership, reducing the ownership percentage of existing shareholders. The impact of stock dilution on the balance sheet can be significant, leading to changes in the overall financial structure of the company. Stock dilution can also impact the income statement of the company. As new shares are issued, the EPS can decrease, which can impact the perception of the company in the market. This can lead to a decrease in the stock price and a reduction in the overall value of the company. A decrease in EPS can also lead to a decrease in dividend payouts, which can impact the attractiveness of the company to income investors. Stock dilution can also impact key financial ratios used to assess the financial health of the company. For example, the price-to-earnings ratio can decrease as the EPS decreases, which can lead to a decrease in investor confidence. Additionally, the ROE can also decrease as the equity portion of the balance sheet increases, which can impact the overall profitability of the company. Anti-dilution measures are used to protect existing shareholders from the negative effects of stock dilution. These measures can take several forms, including ratchet provisions, weighted average anti-dilution, and full-ratchet anti-dilution. Ratchet Provisions adjust the conversion price of convertible securities in the event of a subsequent issuance of shares at a lower price. This protects the value of the convertible securities, ensuring that existing shareholders are not unfairly diluted. Weighted Average Anti-dilution adjusts the conversion price of convertible securities based on the average price of the new shares issued. This ensures that existing shareholders are not unfairly diluted if the new shares are issued at a lower price. Full-Ratchet Anti-dilution adjusts the conversion price of convertible securities based on the price of the new shares issued. It provides maximum protection to existing shareholders, preventing their dilution even with new shares issued at lower prices. Stock dilution can have a significant impact on the value of a shareholder's investment, as well as on the financial statements of the company. The different types of stock dilution, its effects on investors and companies, and the various anti-dilution measures must be understood to make informed investment decisions and for managing a company's finances effectively. To help navigate this complex landscape and make informed decisions, it is highly recommended to hire the services of a wealth manager. Wealth managers have the expertise and experience to help investors and business owners make smart investment decisions and manage their finances effectively. What Is Stock Dilution?
Types of Stock Dilution
Primary Stock Dilution
Secondary Stock Dilution
Effects of Stock Dilution on Investors

Dilution of Ownership
Impact on Stock Price
Impact on Earnings per Share (EPS)
Impact on Dividend Payouts
Risks and Benefits of Investing in Companies that Use Stock Dilution
Effects of Stock Dilution on Companies
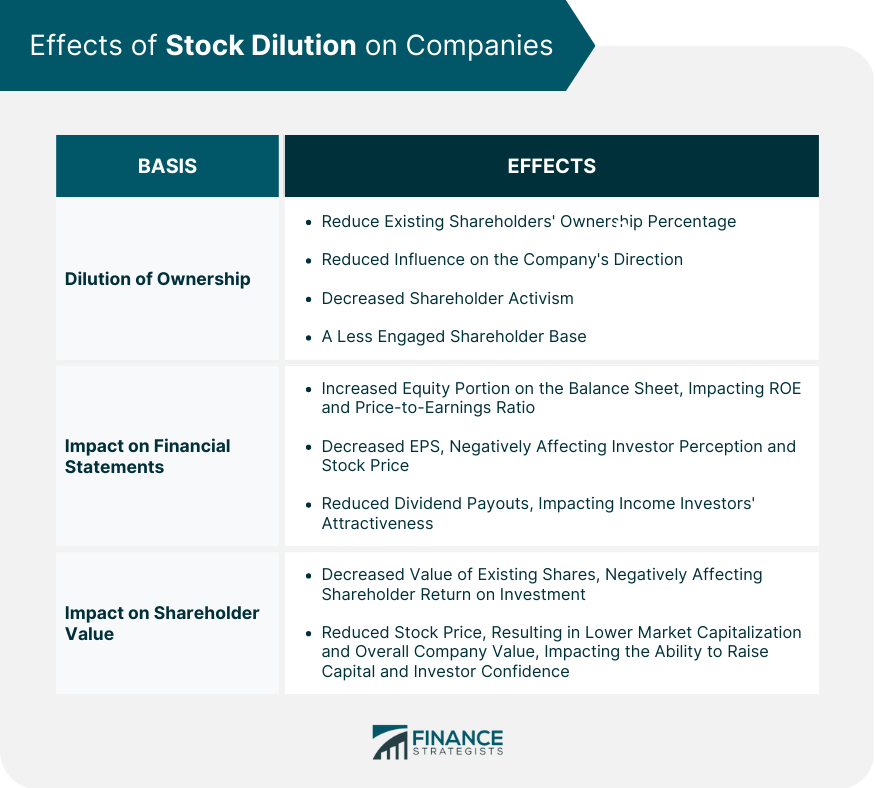
Dilution of Ownership
Impact on Financial Statements
Impact on Shareholder Value
Effects of Stock Dilution on Financial Statements

Impact on the Balance Sheet
Impact on the Income Statement
Impact on Financial Ratios
Anti-Dilution Measures
Final Thoughts
Stock Dilution FAQs
Stock dilution refers to a reduction in the ownership percentage of a shareholder in a company as a result of the issuance of new shares. It can impact investors by diluting their ownership, reducing the stock price, impacting earnings per share, and decreasing dividend payouts.
The two primary types of stock dilution are primary and secondary. Primary stock dilution occurs when a company issues new shares to raise additional capital, while secondary stock dilution occurs when existing shareholders sell their shares to new investors.
Anti-dilution measures are used to protect existing shareholders from the negative effects of stock dilution. They can take several forms, including ratchet provisions, weighted average anti-dilution, and full-ratchet anti-dilution, and work by adjusting the conversion price of convertible securities to ensure that existing shareholders are not unfairly diluted.
Stock dilution can impact a company's financial statements by increasing the equity portion of the balance sheet, decreasing the value of existing shares, reducing earnings per share, and impacting ratios such as return on equity and price-to-earnings ratio.
Understanding stock dilution is crucial for investors, business owners, financial analysts, and accounting professionals. It helps to make informed investment decisions, manage a company's finances effectively, comply with regulatory requirements, and protect existing shareholders from the negative effects of stock dilution.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











