The Wilshire 5000 Total Market Index (also known as the Wilshire 5000 Index) is a stock market index that tracks the performance of all publicly traded companies in the United States. It was created in 1974 by Wilshire Associates and is widely considered to be the broadest measure of the U.S. stock market. The index includes all U.S. equities with readily available price data, including small, mid, and large-cap stocks. The Wilshire 5000 is a market-capitalization-weighted index, meaning that companies with higher market capitalizations have a greater impact on the index's performance. The index is often used as a benchmark for the overall performance of the U.S. stock market and as a tool for portfolio managers to measure the performance of their investments. The Wilshire 5000 was launched in 1974 by Wilshire Associates, a global investment management firm. The index was designed to provide a comprehensive representation of the U.S. equity market, including large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks. It was named "Wilshire 5000" due to the approximate number of stocks it included at the time of its inception. Since its creation, the Wilshire 5000 has experienced numerous changes in its constituent companies, reflecting the ever-evolving landscape of the U.S. stock market. The number of companies included in the index has fluctuated over time, expanding during economic booms and contracting during downturns. Market sectors represented in the index have also shifted, with technology and healthcare stocks becoming increasingly prominent in recent years. To be included in the Wilshire 5000, a company must be headquartered in the United States and be publicly traded on a major stock exchange. The index does not impose any minimum market capitalization or liquidity requirements, which allows it to provide a comprehensive representation of the U.S. equity market. The Wilshire 5000 covers a diverse range of market sectors, including technology, healthcare, financial services, consumer goods, and energy, among others. This broad sector representation enables investors to gain a well-rounded understanding of the U.S. stock market's performance. The index uses a float-adjusted market capitalization weighting methodology, which means that each company's weight in the index is determined by its market capitalization adjusted for the number of shares available to the public. This approach ensures that larger companies have a more significant impact on the index's performance. Investors can gain exposure to the Wilshire 5000 through index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the index. While investing in these funds offers a convenient way to diversify one's portfolio, investors should be aware of potential drawbacks, such as management fees and tracking errors. The Wilshire 5000 is often used as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of investment portfolios and individual stocks. By comparing their investments' returns to the index's performance, investors can gauge how well their portfolios are performing relative to the overall U.S. equity market. The index is also used as an economic indicator, as its performance reflects the overall health of the U.S. stock market. Market analysts often study the Wilshire 5000 to identify trends and assess market volatility. While the Wilshire 5000's comprehensive representation of the U.S. equity market is one of its strengths, some critics argue that the inclusion of a large number of companies dilutes the focus on market leaders. As a result, the index may not accurately reflect the performance of the most influential companies in the market. In contrast, narrower indexes, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average, focus on larger, more established companies that often drive market trends. Another limitation of the Wilshire 5000 is its exclusive focus on U.S.-based companies, which means that investors tracking the index may miss out on opportunities in global markets. As international companies play an increasingly significant role in the global economy, investors may need to diversify their portfolios by including assets from other countries and regions to mitigate risks and capture potential growth opportunities. The Wilshire 5000 Total Market Index is a widely recognized benchmark for the U.S. stock market, tracking the performance of all publicly traded companies in the United States. The index includes companies from a diverse range of sectors and utilizes a float-adjusted market capitalization weighting methodology. While the index's comprehensive representation of the U.S. equity market is a strength, some criticize its large number of constituent companies, which may dilute the focus on market leaders. Additionally, the index's exclusive focus on U.S.-based companies means that investors may miss out on opportunities in global markets. Nonetheless, the Wilshire 5000 remains a useful tool for portfolio managers and investors to measure the performance of their investments and evaluate market trends.What Is Wilshire 5000?
History of Wilshire 5000
Origins and Creation
Evolution and Changes Over Time
Composition of Wilshire 5000
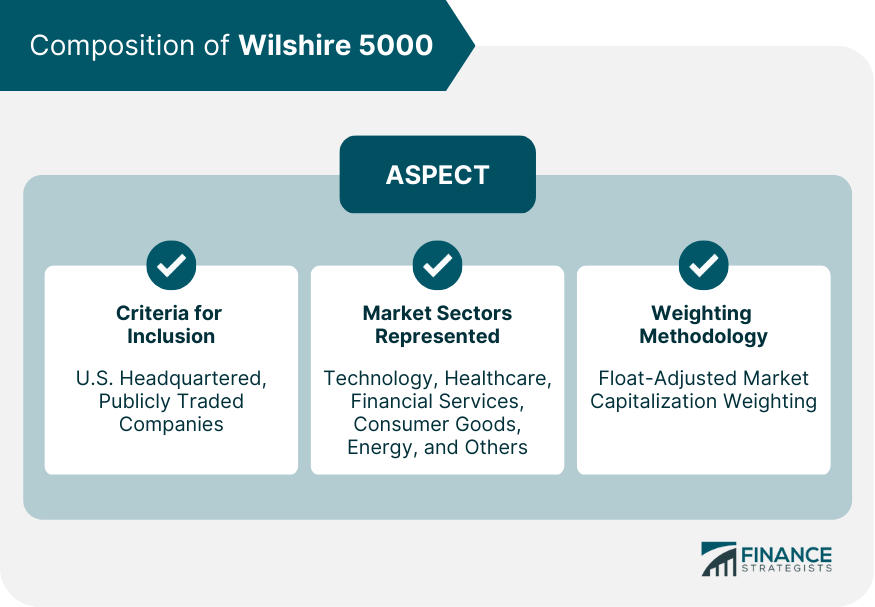
Criteria for Inclusion
Market Sectors Represented
Market Capitalization Weighting
Tracking the Wilshire 5000
Index Funds and ETFs
Performance Measurement
Market Sentiment and Analysis
Criticisms and Limitations of Wilshire 5000
Inclusion of a Large Number of Companies
Exclusion of International Companies
Final Thoughts
Wilshire 5000 FAQs
The Wilshire 5000 is a market index representing the performance of virtually all publicly traded U.S. stocks. It offers investors a comprehensive view of the U.S. equity market, covering various market sectors and company sizes, making it an essential benchmark for evaluating investment performance and market health.
While both the Wilshire 5000 and the S&P 500 are market capitalization-weighted indexes, the Wilshire 5000 is more comprehensive, including nearly all publicly traded U.S. stocks. In contrast, the S&P 500 focuses on 500 of the largest and most established U.S. companies, often considered market leaders.
While you cannot invest directly in the Wilshire 5000, you can invest in index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the index, such as the Schwab Total Stock Market Index Fund (SWTSX) and the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI). These funds provide a convenient way to gain exposure to the performance of the U.S. equity market.
The Wilshire 5000 is a valuable tool for understanding market sentiment and trends, as its performance reflects the overall health of the U.S. stock market. By tracking the index, investors and market analysts can identify trends, assess market volatility, and gain insights into the state of the U.S. economy.
The primary criticisms and limitations of the Wilshire 5000 include the inclusion of a large number of companies, which may dilute the focus on market leaders, and the exclusion of international stocks, limiting exposure to global market trends. Despite these limitations, the index remains an essential benchmark for investors seeking a comprehensive view of the U.S. equity market.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











