Earnings, often referred to as net income or profit, denote the income that a company generates after deducting all the operating expenses, taxes, cost of sales, and other costs from its total revenue. Earnings provide a clear snapshot of a company's profitability over a specific period and are a crucial component of any financial analysis or company evaluation. Valuation refers to the process of determining the present worth of an asset, a company, or an investment based on its earnings, growth prospects, and the inherent risk. In essence, valuation is an estimation of how much a business would sell for on the open market. It can be used by investors to decide whether a company's shares are overvalued or undervalued, thereby informing investment decisions. High earnings can indicate a successful and potentially profitable company, often leading to a higher valuation. On the other hand, consistently poor earnings may signify problems within the company, which can lower its valuation. Earnings, as a reflection of a company's profitability, directly impact its valuation. Investors and analysts often rely on a company's earnings to estimate its intrinsic value and make predictions about its future cash flows. The more earnings a company generates relative to the number of shares it has outstanding, the more valuable each share is to investors. Therefore, when evaluating a company, analysts calculate the earnings-per-share, or EPS. EPS is a metric that divides the earnings available to common shareholders by the number of outstanding shares a company has. For example, if a company has $100,000 in earnings and 50,000 outstanding shares, then its EPS is $2 per share. When a company has strong earnings, it is often interpreted as a sign of financial health and strong future prospects, leading to a higher valuation. Conversely, weak or declining earnings could suggest underlying issues and can lead to a lower valuation. These models, such as the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) or the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio, use earnings to compute the intrinsic value of a company. Earnings are seen as a reflection of a company's ability to generate profit, which is the primary driver of its value. Earnings not only reflect a company's current financial condition but also serve as a key measure of its performance and profitability. Higher earnings often indicate a well-performing company with strong financial management and competitive advantage, leading to a higher valuation. Conversely, lower earnings might suggest operational or financial inefficiencies, which could result in a lower valuation. Earnings are integral to cash flow projections, which are a critical component of valuation models. Analysts use earnings data to forecast future cash flows, and these projections are then discounted to their present value to determine the company's valuation. Furthermore, earnings stability or volatility can influence risk assessments, with inconsistent earnings potentially indicating higher risk and leading to a lower valuation. The Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method is a valuation technique that estimates the value of an investment based on its future cash flows. By forecasting a company's cash flows and discounting them to their present value, the DCF method can provide an estimate of the intrinsic value of the company. The accuracy of this valuation heavily relies on the accuracy of the earnings forecasts and the selected discount rate. The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio is a valuation ratio that compares a company's current share price to its earnings per share. A high P/E ratio could mean that a company's stock is overpriced, or it could indicate that investors are expecting high growth rates in the future. Conversely, a low P/E ratio might mean that the company's stock is underpriced, or it could signal that the company is performing poorly. The Comparable Company Analysis method, also known as "comps," involves comparing the valuation ratios of the company being valued to similar companies within the same industry. These ratios often include the P/E ratio, the Price-to-Sales (P/S) ratio, and the Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio. This method relies on the assumption that companies in the same industry will have similar valuation multiples. Analysts take this number and compare it to other P/E ratios of similar companies, and with the broader market. In equity valuation, using ratios such as P/E is called a multiples-based approach. Growth prospects are a crucial component of a company's valuation. Companies with high growth potential are often valued higher than companies with lower growth prospects. Investors and analysts look at a company's earnings, among other factors, to gauge its growth prospects. Companies with higher risk profiles usually command lower valuations because the potential for future earnings is less certain. The stability and predictability of a company's earnings can be an indicator of its risk level. Industry benchmarks or standards are also used in valuation. By comparing a company's earnings and other financial metrics with industry averages, investors and analysts can assess whether a company is overvalued or undervalued. Companies that consistently generate high earnings are likely to command high valuations because these earnings signal the company's ability to generate profits and potentially provide a return on investment. Companies that exhibit strong growth in earnings over time can see their valuations increase because earnings growth often signifies expanding business operations, increasing market share, or improving profitability. High-quality earnings—those that are sustainable and backed by actual cash flows—are likely to lead to higher valuations. In contrast, low-quality earnings—those that may be based on one-time events or accounting changes—can result in lower valuations. Companies with stable, predictable earnings are generally seen as less risky and can attract higher valuations. On the other hand, companies with volatile earnings may be viewed as riskier, which can negatively affect their valuations. Analysts also use the price-to-earnings ratio, or P/E ratio, which is the market price of a share divided by the EPS. For example, if the same company sold each share for $10, then the P/E ratio is 5.0. Analysts calculate the P/E ratio by dividing the market price of a share by the earnings per share (EPS). Higher earnings can lead to a higher P/E ratio, indicating a higher valuation in the eyes of investors. High earnings indicate financial strength and potential profitability, leading to a higher valuation, while weak or declining earnings can result in a lower valuation. Earnings are utilized in various valuation methods, such as the discounted cash flow (DCF) method and the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio method, as they provide a fundamental input and measure of company performance and profitability. Additionally, earnings influence cash flow projections and risk assessments, further impacting a company's valuation. Understanding a company's earnings allows investors to assess a company's financial health, profitability, and growth prospects. Additionally, it can help investors identify promising investment opportunities and generate potential returns.Overview of Earnings and Valuation
Earnings Affect Valuation of a Company
Role of Earnings in Valuation Methods
Fundamental Input in Valuation Models
Measure of Company Performance and Profitability
Cash Flow Projections and Risk Assessments
Valuation Methods Used
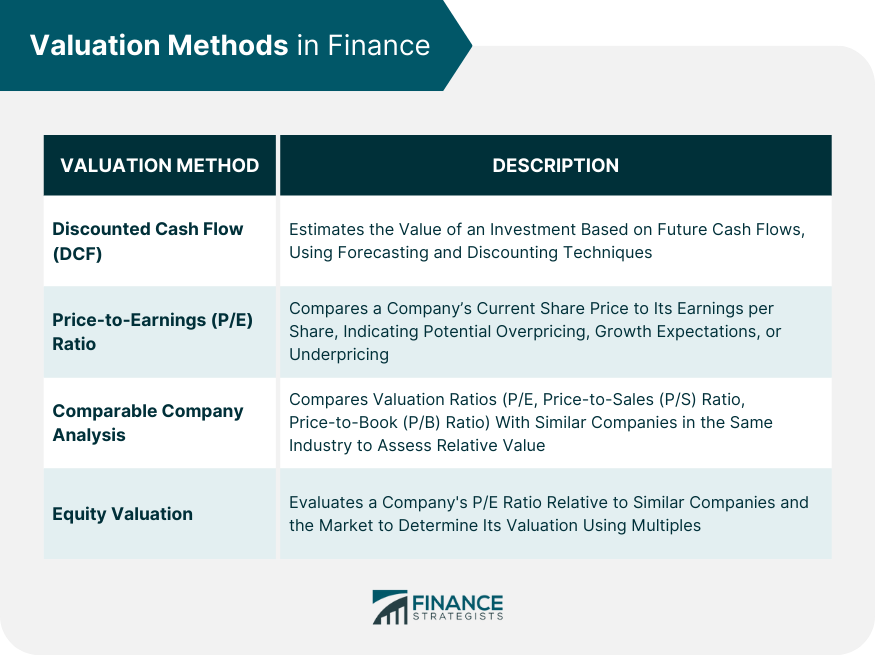
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio Method
Comparable Company Analysis Method
Equity Valuation
Factors Considered in Valuation
Growth Prospects
Risk
Industry Benchmarks

Earnings' Impact on Valuation
Positive Relationship
Earnings Growth
Earnings Quality
Earnings Stability

Example of How Earnings Affect Valuation
Conclusion
How Earnings Affect Valuation FAQs
Earnings are an important factor influencing valuation, as they provide insight into the financial performance and profitability of a business. A company’s ability to generate profits will directly affect its value in both the short-term and long-term, as it indicates whether or not it has staying power and potential for growth.
Earnings growth is one of the most important factors considered when evaluating a company’s worth, as it reflects whether or not the business is growing over time. Companies with higher rates of earnings growth tend to be more valuable than those with stagnant or declining earnings.
In addition to analyzing a company’s earnings, other financial metrics such as revenue, cash flow, debt-to-equity ratio, and return on equity are also taken into account when assessing valuation. These metrics provide further insight into a business’s overall financial performance and can be used to make more accurate calculations of value.
Economic conditions can have a significant impact on a company’s valuation, as these changes may result in decreased revenues or higher costs which can ultimately lower its value. It is important to monitor macroeconomic developments and adjust valuations accordingly to ensure accuracy.
Book value is an accounting metric that reflects a company’s assets minus its liabilities, while market value is determined by supply and demand in the stock market, and as such can fluctuate significantly over time. Market value may be greater or lesser than book value depending on investor sentiment.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











